|
Solar Storm Of 2012
The solar storm of 2012 was an unusually large and strong coronal mass ejection (CME) event that occurred on July 23 that year. It missed Earth with a margin of approximately nine days, as the equator of the Sun rotates around its own axis with a period of about 25 days. The region that produced the outburst was thus not pointed directly towards Earth at that time. The strength of the eruption was comparable to the 1859 Carrington Event that caused damage to electrical equipment worldwide, which at that time consisted mostly of telegraph systems. Overview The eruption tore through Earth's orbit, hitting the STEREO-A spacecraft. The spacecraft is a solar observatory equipped to measure such activity, and because it was far away from the Earth and thus not exposed to the strong electrical currents that can be induced when a CME hits the Earth's magnetosphere, it survived the encounter and provided researchers with valuable data. Based on the collected data, the eruption consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STEREO
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration of two loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Because the multi-dimensional perspective is the crucial aspect, the term ''stereophonic'' also applies to systems with more than two channels or speakers such as quadraphonic and surround sound. Binaural sound systems are also ''stereophonic''. Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment media such as broadcast radio, recorded music, television, video cameras, cinema, computer audio, and internet. Etymology The word ''stereophonic'' derives from the Greek (''stereós'', "firm, solid") + (''phōnḗ'', "sound, tone, voice") and it was coined in 1927 by Western E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System, and through which all the larger Solar System bodies, such as planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets, move. The IPM stops at the heliopause, outside of which the interstellar medium begins. Before 1950, interplanetary space was widely considered to either be an empty vacuum, or consisting of "aether". Composition and physical characteristics The interplanetary medium includes interplanetary dust, cosmic rays, and hot plasma from the solar wind. The temperature of the interplanetary medium varies. For dust particles within the asteroid belt, typical temperatures range from 200 K (−73 °C) at 2.2 AU down to 165 K (−108 °C) at 3.2 AU. The density of the interplanetary medium is very low, decreasing in inverse proportion to the square of the distance from the Sun. It is variable, and may be affected by magnetic fields and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 In Science
The year 2012 involved many significant scientific events and discoveries, including the first orbital rendezvous by a commercial spacecraft, the discovery of a particle highly similar to the long-sought Higgs boson, and the near-eradication of guinea worm disease. A total of 72 successful orbital spaceflights occurred in 2012, and the year also saw numerous developments in fields such as robotics, 3D printing, stem cell research and genetics. Over 540,000 technological patent applications were made in the United States alone in 2012. 2012 was declared the International Year of Sustainable Energy for All by the United Nations. 2012 also marked Alan Turing Year, a celebration of the life and work of the English mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst and computer scientist Alan Turing. Events, discoveries and inventions January * 1 January – NASA's GRAIL-B satellite successfully enters lunar orbit, joining its twin spacecraft GRAIL-A. The two satellites will study the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomagnetic Storms
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The disturbance that drives the magnetic storm may be a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or (much less severely) a co-rotating interaction region (CIR), a high-speed stream of solar wind originating from a coronal hole. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. During solar maximum, geomagnetic storms occur more often, with the majority driven by CMEs. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth's magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Solar Storms
Solar storms of different types are caused by disturbances on the Sun, most often from coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and solar flares from active regions, or, less often, from coronal holes. Minor to active solar storms (i.e. storming restricted to higher latitudes) may occur under elevated background solar wind conditions when the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) orientation is southward, toward the Earth (which also leads to much stronger storming conditions from CME-related sources). Background Active stars produce disturbances in space weather and, if strong enough, in their own space climate. Science studies such phenomena with the field of heliophysics, which is an interdisciplinary combination of solar physics and planetary science. In the Solar System, the Sun can produce intense geomagnetic and energetic particle storms capable of causing severe damage to technology. It can result in large scale power outages, disruption or blackouts of radio communications (includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August 1972 Solar Storm
The solar storms of August 1972 were a historically powerful series of solar storms with intense to extreme solar flare, solar particle event, and geomagnetic storm components in early August 1972, during solar cycle 20. The storm caused widespread electric‐ and communication‐grid disturbances through large portions of North America as well as satellite disruptions. On 4 August 1972 the storm caused the accidental detonation of numerous U.S. naval mines near Haiphong, North Vietnam. The coronal mass ejection (CME)'s transit time from the Sun to the Earth is the fastest ever recorded. Solar-terrestrial characteristics Sunspot region The most significant detected solar flare activity occurred from 2 to 11 August. Most of the significant solar activity emanated from Active region, active sunspot region McMath 11976 (MR 11976; active regions being clusters of sunspot pairs). McMath 11976 was extraordinarily magnetically complex. Its size was large although not exceptionally so. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
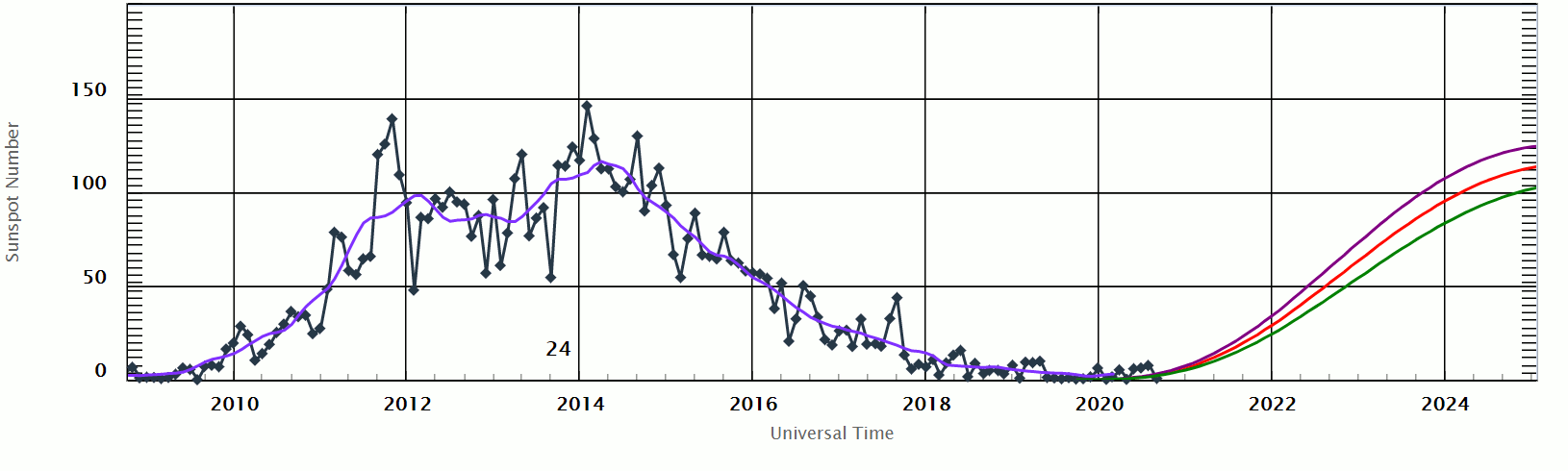
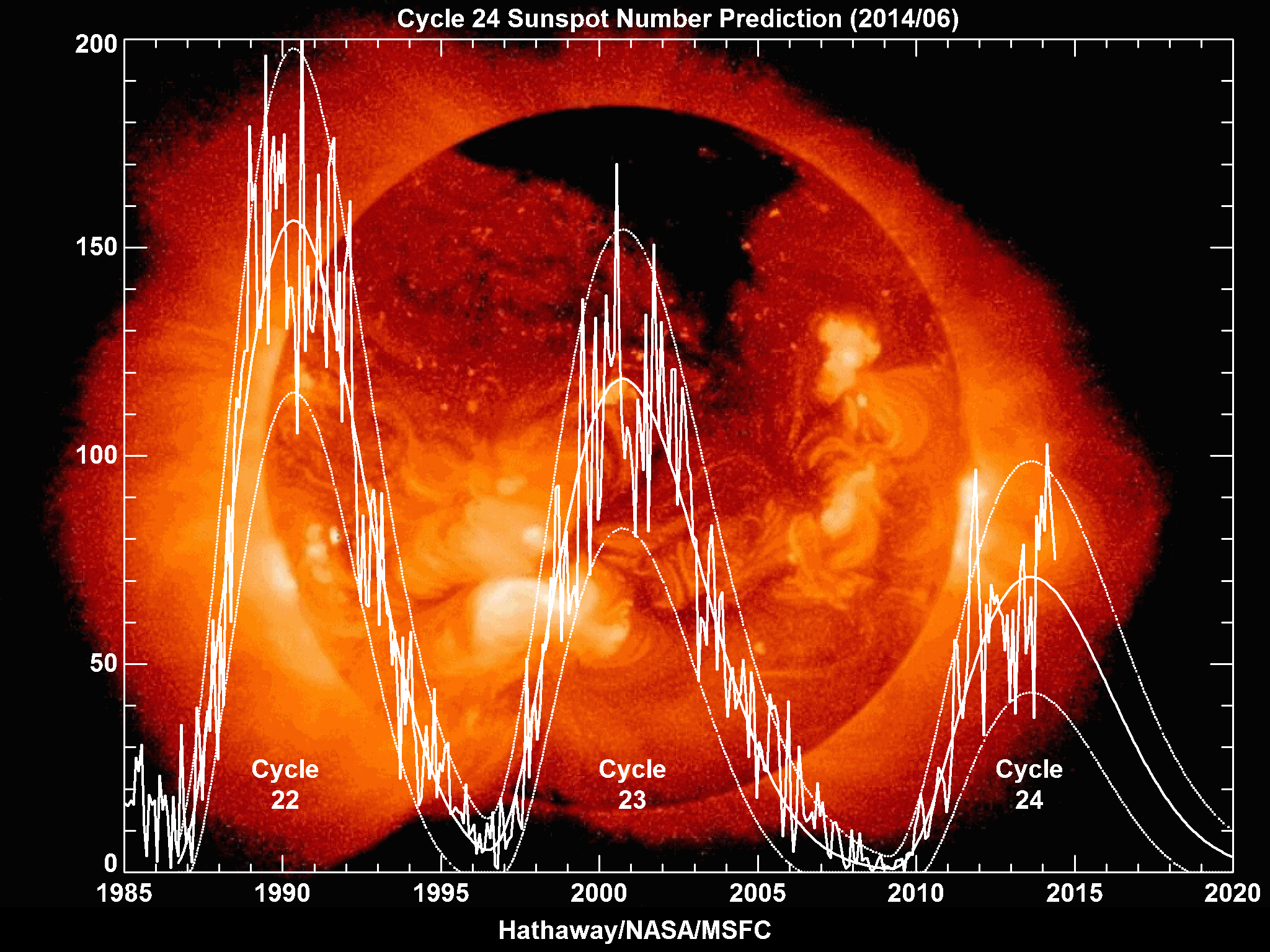
Solar Cycle 24
Solar cycle 24 is the most recently completed solar cycle, the 24th since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot activity began.Kane, R.P. (2002).Some Implications Using the Group Sunspot Number Reconstruction. ''Solar Physics'' 205(2), 383-401. It began in December 2008 with a minimum smoothed sunspot number of 2.2, and ended in December 2019. Activity was minimal until early 2010. It reached its maximum in April 2014 with a 23 months smoothed sunspot number of 81.8. This maximum value was substantially lower than other recent solar cycles, down to a level which had not been seen since cycles 12 to 15 (1878-1923). Predictions Prior to the minimum between the end of Solar Cycle 23 and the beginning of Solar Cycle 24, two theories predicted how strong Solar Cycle 24 would be. One camp postulated that the Sun retained a long memory (Solar Cycle 24 would be active) while the other asserted that it had a short memory (quiet). Prior to 2006, the difference was substantial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body, the magnetic field resembles a magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation, that also protects all living organisms from potentially detrimental and dangerous consequences. This is studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Mass Ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established. If a CME enters interplanetary space, it is referred to as an interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME). ICMEs are capable of reaching and colliding with Earth's magnetosphere, where they can cause geomagnetic storms, aurorae, and in rare cases damage to electrical power grids. The largest recorded geomagnetic perturbation, resulting presumably from a CME, was the solar storm of 1859. Also known as the Carrington Event, it disabled parts of the at the time newly created United States telegraph network, starting fires and shocking some telegraph operators. Near solar maxima, the Sun produces about three CMEs every day, whereas near solar minima, there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cycle 24 Sunspot Number Progression And Prediction
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Solar, Erode, India * Solar, Iran, Iran Companies * Solar Entertainment Corporation, a Philippines television and radio media company * Solar TV, a former TV channel * Solar Television Network, Inc., a former name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined and such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the optical telegraph of Claude Chappe, invented in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railway signallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_2007-04-30_T001456.gif)

