|
Sokolov–Ternov Effect
The Sokolov–Ternov effect is the effect of self-polarization of relativistic electrons or positrons moving at high energy in a magnetic field. The self-polarization occurs through the emission of spin-flip synchrotron radiation. The effect was predicted by Igor Ternov and the prediction rigorously justified by Arseny Sokolov using exact solutions to the Dirac equation. Theory An electron in a magnetic field can have its spin oriented in the same ("spin up") or in the opposite ("spin down") direction with respect to the direction of the magnetic field (which is assumed to be oriented "up"). The "spin down" state has a higher energy than "spin up" state. The polarization arises due to the fact that the rate of transition through emission of synchrotron radiation to the "spin down" state is slightly greater than the probability of transition to the "spin up" state. As a result, an initially unpolarized beam of high-energy electrons circulating in a storage ring after sufficientl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is an academic publisher of scientific, technical, and medical books and journals headquartered in Singapore. The company was founded in 1981. It publishes about 600 books annually, along with 135 journals in various fields. In 1995, World Scientific co-founded the London-based Imperial College Press together with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Company structure The company head office is in Singapore. The Chairman and Editor-in-Chief is Dr Phua Kok Khoo, while the Managing Director is Doreen Liu. The company was co-founded by them in 1981. Imperial College Press In 1995 the company co-founded Imperial College Press, specializing in engineering, medicine and information technology, with Imperial College London. In 2006, World Scientific assumed full ownership of Imperial College Press, under a license granted by the university. Finally, in August 2016, ICP was fully incorporated into World Scientific under the new imprint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
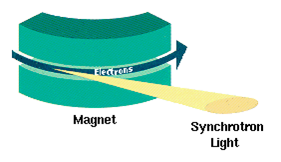
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates: # The laws of physics are invariant (that is, identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no acceleration). # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source or the observer. Origins and significance Special relativity was originally proposed by Albert Einstein in a paper published on 26 September 1905 titled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".Albert Einstein (1905)''Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper'', ''Annalen der Physik'' 17: 891; English translatioOn the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodiesby George Barker Jeffery and Wilfrid Perrett (1923); Another English translation On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies by Megh Nad Saha (1920). The incompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Froissart–Stora Equation
The Froissart–Stora equation describes the change in polarization which a high energy charged particle beam in a storage ring will undergo as it passes through a resonance in the spin tune. It is named after the French physicists Marcel Froissart and Raymond Stora. The polarization following passage through the resonance is given by : P_y = P_\left \exp\left(\right)-1\right/math> where \epsilon is the resonance strength and \alpha_0 is the speed at which the resonance is crossed. P_ is the initial polarization before resonance crossing. The resonance may be crossed by raising the energy so that the spin tune passes through a resonance, or driven with a transverse magnetic field at a frequency that is in resonance with the spin oscillations. The Froissart–Stora equation has a direct analogy in condensed matter physics in the Landau–Zener effect. Other spin-dynamics effects The original Froissart–Stora equation was derived for polarized protons. It may also be applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawking Radiation
Hawking radiation is theoretical black body radiation that is theorized to be released outside a black hole's event horizon because of relativistic quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who developed a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974. Hawking radiation is a purely kinematic effect that is generic to Lorentzian geometries containing event horizons or local apparent horizons. Hawking radiation reduces the mass and rotational energy of black holes and is therefore also theorized to cause black hole evaporation. Because of this, black holes that do not gain mass through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish. For all except the smallest black holes, this would happen extremely slowly. The radiation temperature is inversely proportional to the black hole's mass, so micro black holes are predicted to be larger emitters of radiation than larger black holes and should dissipate faster. Overview Black holes are astrophysica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unruh Effect
The Unruh effect (also known as the Fulling–Davies–Unruh effect) is a kinematic prediction of quantum field theory that an accelerating observer will observe a thermal bath, like blackbody radiation, whereas an inertial observer would observe none. In other words, the background appears to be warm from an accelerating reference frame; in layman's terms, an accelerating thermometer (like one being waved around) in empty space, removing any other contribution to its temperature, will record a non-zero temperature, just from its acceleration. Heuristically, for a uniformly accelerating observer, the ground state of an inertial observer is seen as a mixed state in thermodynamic equilibrium with a non-zero temperature bath. The Unruh effect was first described by Stephen Fulling in 1973, Paul Davies in 1975 and W. G. Unruh in 1976. It is currently not clear whether the Unruh effect has actually been observed, since the claimed observations are disputed. There is also some doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PETRA
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to the mountain of Jebel al-Madhbah, Jabal Al-Madbah, in a Depression (geology), basin surrounded by mountains forming the eastern flank of the Arabah valley running from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and the Nabataeans might have settled in what would become the capital city of Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom as early as the 4th century BC. Archaeological work has only discovered evidence of Nabataean presence dating back to the second century BC, by which time Petra had become their capital. The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub. The trading business gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (English ''German Electron Synchrotron''), commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany. It operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter, and conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science, and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen. Functions DESY's function is to conduct fundamental research. It specializes in particle accelerator development, construction and operation, particle physics research to explore the fundamental characteristics of matter and forces, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budker Institute Of Nuclear Physics
The Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (BINP) is one of the major centres of advanced study of nuclear physics in Russia. It is located in the Siberian town Akademgorodok, on Academician Lavrentiev Avenue. The institute was founded by Gersh Budker in 1959. Following his death in 1977, the institute was renamed in honour of Academician Budker. Despite its name, the centre was not involved either with military atomic science or nuclear reactors instead, its concentration was on high-energy physics (particularly plasma physics) and particle physics. In 1961 the institute began building VEP-1,A. N. Skrinsly"Accelerator field development at Novosibirsk (history, status, prospects)" Particle Accelerator Conference, Proceedings of the 1995.V. N. Baier, "Forty years of acting electron-positron colliders"arXiv:hep-ph/0611201 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev ( Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |