|
Soil Thermal Properties
The thermal properties of soil are a component of soil physics that has found important uses in engineering, climatology and agriculture. These properties influence how energy is partitioned in the soil profile. While related to soil temperature, it is more accurately associated with the transfer of energy (mostly in the form of heat) throughout the soil, by radiation, conduction and convection. The main soil thermal properties are: *Volumetric heat capacity, SI Units: J∙m−3∙K−1 *Thermal conductivity, SI Units: W∙m−1∙K−1 *Thermal diffusivity, SI Units: m2∙s−1 Measurement It is hard to say something general about the soil thermal properties at a certain location because these are in a constant state of flux from diurnal and seasonal variations. Apart from the basic soil composition, which is constant at one location, soil thermal properties are strongly influenced by the soil volumetric water content, volume fraction of solids and volume fraction of air. Air is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Physics
Soil physics is the study of soil's physical properties and processes. It is applied to management and prediction under natural and managed ecosystems. Soil physics deals with the dynamics of physical soil components and their phases as solids, liquids, and gases. It draws on the principles of physics, physical chemistry, engineering, and meteorology. Soil physics applies these principles to address practical problems of agriculture, ecology, and engineering. Prominent soil physicists *Edgar Buckingham (1867–1940) :The theory of gas diffusion in soil and vadose zone water flow in soil. *Willard Gardner (1883-1964) :First to use porous cups and manometers for capillary potential measurements and accurately predicted the moisture distribution above a water table.Sterling A. Taylor: Willard Gardner, 1883-1964. Soil Science 100(2), 1965. *Lorenzo A. Richards (1904–1993) :General transport of water in unsaturated soil, measurement of soil water potential using tensiometer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
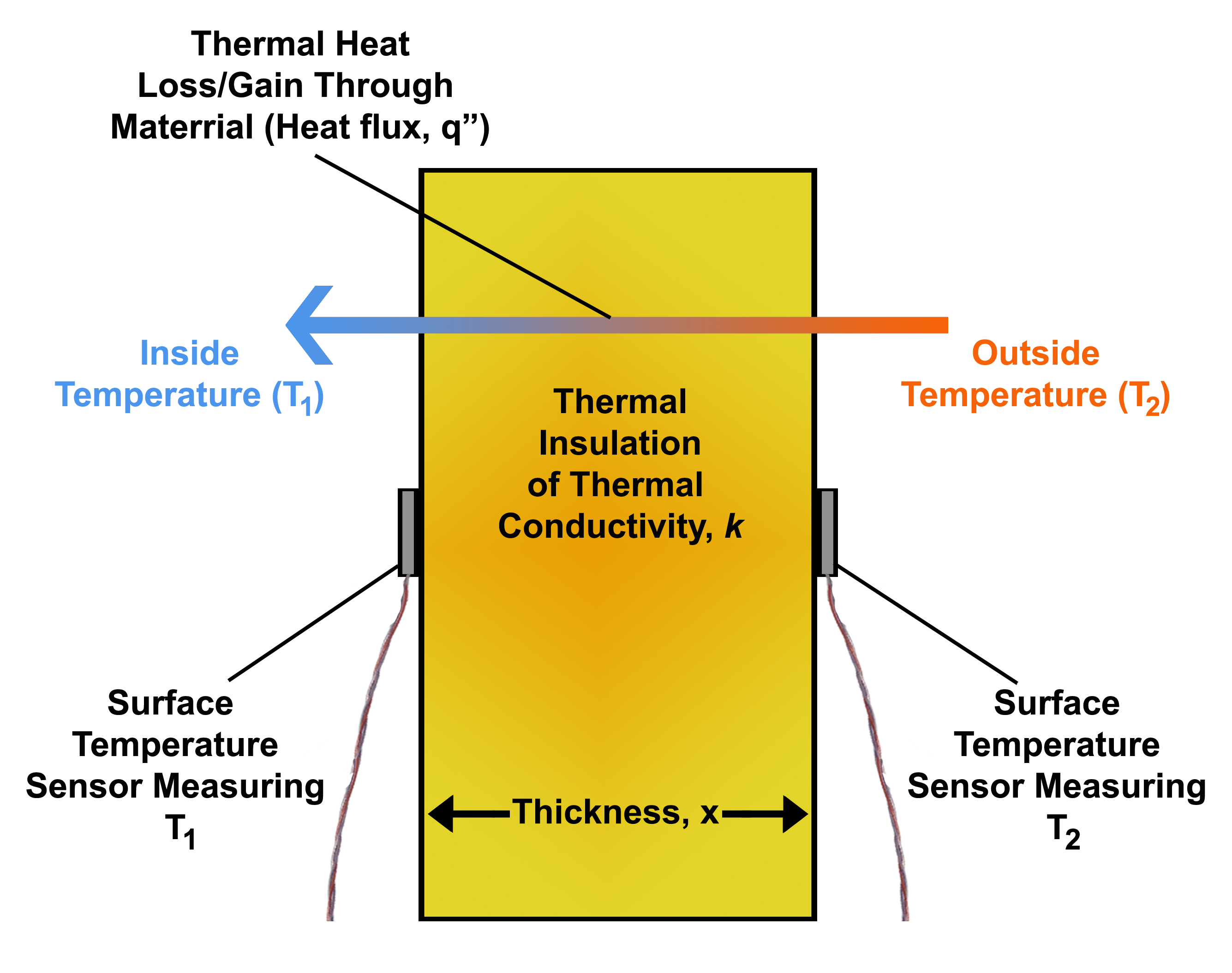
Heat Flux
Heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as ''heat flux density'', heat-flow density or ''heat flow rate intensity'' is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time. In SI its units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''mass'' or ''momentum'' flux. Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi_\text = -k \frac where k is the thermal conductivity. The negative sign shows that heat flux moves from higher temperature regions to lower temperature regions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Source Heat Pumps
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that uses a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through the seasons. Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) – or geothermal heat pumps (GHP) as they are commonly termed in North America – are among the most energy-efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating, using far less energy than can be achieved by burning a fuel in a boiler/furnace or by use of resistive electric heaters. Efficiency is given as a coefficient of performance (CoP) which is typically in the range 3 – 6, meaning that the devices provide 3 – 6 units of heat for each unit of electricity used. Setup costs are higher than for other heating systems due to the requirement to install ground loops over large areas or drill bore holes, and for this reason air source heat pumps are often used instead. Thermal prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Mine
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automatically by way of pressure when a target steps on it or drives over it, although other detonation mechanisms are also sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both. Landmines are typically laid throughout an area, creating a ''minefield'' which is dangerous to cross. The use of land mines is controversial because of their potential as indiscriminate weapons. They can remain dangerous many years after a conflict has ended, harming civilians and the economy. Seventy-eight countries are contaminated with land mines and 15,000–20,000 people are killed every year while many more are injured. Approximately 80% of land mine casualties are civilians, with children as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment. Radioactive waste is broadly classified into low-level waste (LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity, intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding, and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, so requires cooling and shielding. In nuclear reprocessing plants about 96% of spent nuclear fuel is recycled back into uranium-based and mixed-oxide (MOX) fuels. The residual 4% is minor actinides and fission products the latter of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many state-owned by OPEC and Russia. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but it was consistent among all greenhouse gases (GHG). Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than ever before. Electricity generation and transport are major emitters; the largest single source, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, is transportation, accounting for 27% of all USA greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation and other changes in land use also emit carbon dioxide and methane. The largest source of anthropogenic methane emissions is agriculture, closely followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF (millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection detected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Thermal Conductivity Measurement System
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Most so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non Steady State Probe Tp08 Hukseflux
Non, non or NON can refer to: * ''Non'', a negatory word in French, Italian and Latin People *Non (given name) *Non Boonjumnong (born 1982), Thai amateur boxer * Rena Nōnen (born 1993), Japanese actress who uses the stage name "Non" since July 2016 * NON, a name used by musician Boyd Rice Other uses * ''Non'' (album), The Amenta * ''Non!'' (EP), Big Country * ''Non'' (book), a 2009 book by Japanese model Nozomi Sasaki * Non (comics), a villain of Superman in the DC Comics universe * non, language code for Old Norse * NON Records, an independent record label based in Amsterdam, Netherlands * Abbreviation of NATO's Allied Forces North Norway Command * "Non", a song by Phinehas from the album '' Till the End'' See also * nan (other) Nan or NAN may refer to: Places China * Nan County, Yiyang, Hunan, China * Nan Commandery, historical commandery in Hubei, China Thailand * Nan Province ** Nan, Thailand, the administrative capital of Nan Province * Nan River People G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier's Law
Conduction is the process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object. The ability of the object to conduct heat is known as its ''thermal conductivity'', and is denoted . Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becoming more uniform. In conduction, the heat flow is within and through the body itself. In contrast, in heat transfer by thermal radiation, the transfer is often between bodies, which may be separated spatially. Heat can also be transferred by a combination of conduction and radiation. In solids, conduction is mediated by the combination of vibrations and collisions of molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |