|
Soft Biometrics
Soft Biometrics traits are physical, behavioural or adhered human characteristics, classifiable in pre–defined human compliant categories. These categories are, unlike in the classical biometric case, established and time–proven by humans with the aim of differentiating individuals. In other words the soft biometric traits instances are created in a natural way, used by humans to distinguish their peers. Introduction The beginnings of Soft Biometrics can be identified as laid by Alphonse Bertillon in the 19th century. He first proposed a personal identification system based on biometric, morphological and anthropometric determinations. The most common traits he introduced were colour of eye, hair, beard and skin; shape and size of the head; body characteristics like height or weight as well as indelible marks such as birth marks, scars or tattoos. A majority of these descriptors presently fall into the category of Soft Biometrics. Jain lately redefined Soft Biometrics as a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance. Biometric identifiers are the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological characteristics which are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina, odor/scent, voice, shape of ears and gait. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to mouse movement, typing rhythm, gait, signature, behavioral profiling, and credentials. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics to describe the latter class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphonse Bertillon
Alphonse Bertillon (; 22 April 1853 – 13 February 1914) was a French police officer and biometrics researcher who applied the anthropological technique of anthropometry to law enforcement creating an identification system based on physical measurements. Anthropometry was the first scientific system used by police to identify criminals. Before that time, criminals could only be identified by name or photograph. The method was eventually supplanted by fingerprinting. He is also the inventor of the mug shot. Photographing of criminals began in the 1840s only a few years after the invention of photography, but it was not until 1888 that Bertillon standardized the process. His flawed evidence was used to wrongly convict Alfred Dreyfus in the infamous Dreyfus affair. Biography Bertillon was born in Paris. He was a son of statistician Louis-Adolphe Bertillon and younger brother of the statistician and demographer Jacques Bertillon. After being expelled from the Imperial Lycée o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
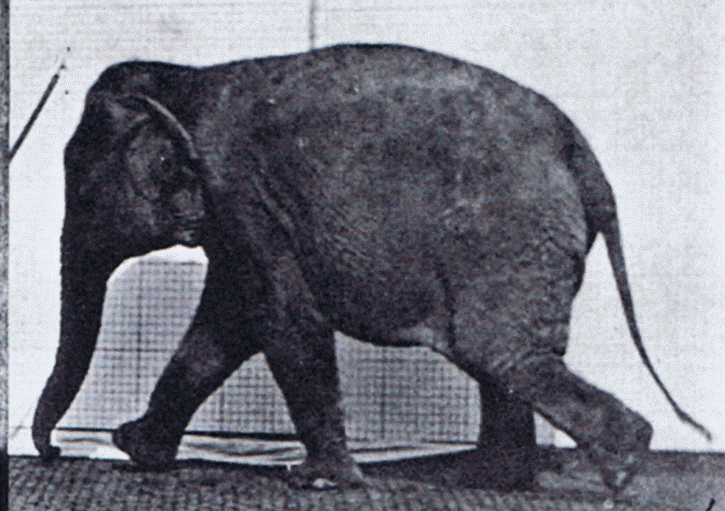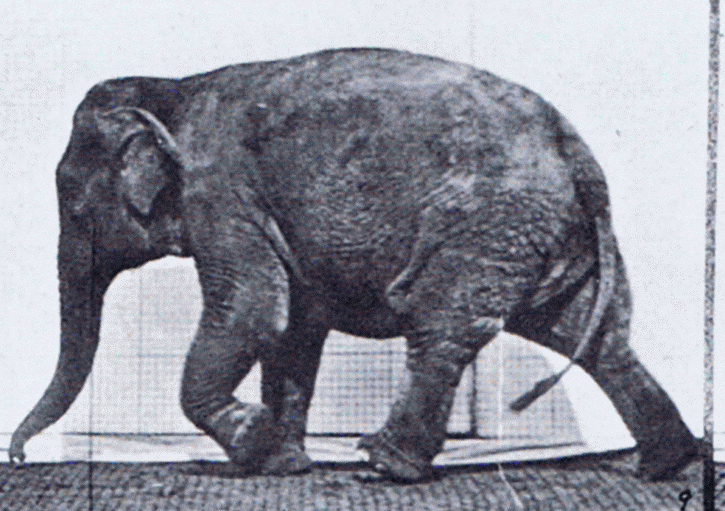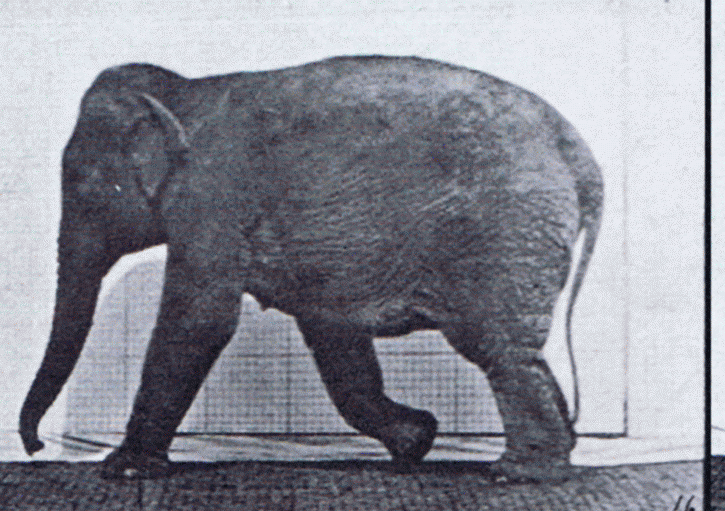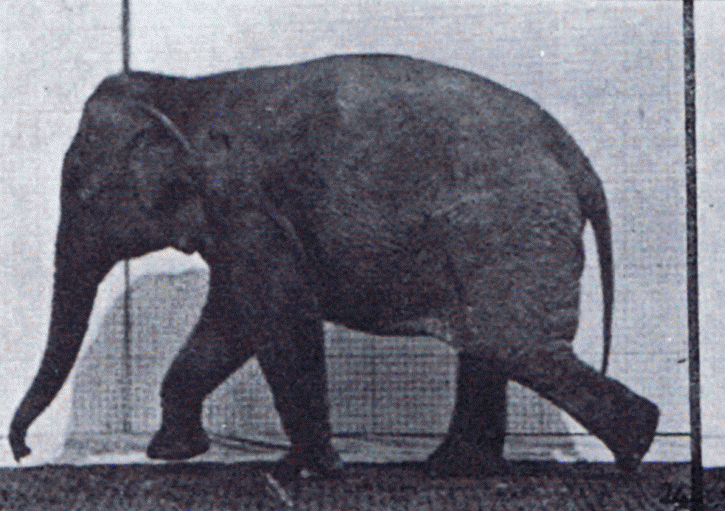
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against it (which can apply to walking while underwater as well as on land). Due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keystroke Dynamics
Keystroke dynamics, keystroke biometrics, typing dynamics and typing biometrics refer to the detailed timing information that describes when each key was pressed and released as a person is typing on a computer keyboard. Science The behavioural biometric of Keystroke Dynamics uses the manner and rhythm in which an individual types characters on a keyboard or keypad. The keystroke rhythms of a user are measured to develop a unique biometric template of the user's typing pattern for future authentication. Keystrokes are separated into static and dynamic typing, which are used to help distinguish between authorized and unauthorized users. Vibration information may be used to create a pattern for future use in both identification and authentication tasks. Data needed to analyse keystroke dynamics is obtained by keystroke logging. Normally, all that is retained when logging a typing session is the sequence of characters corresponding to the order in which keys were pressed. Timing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
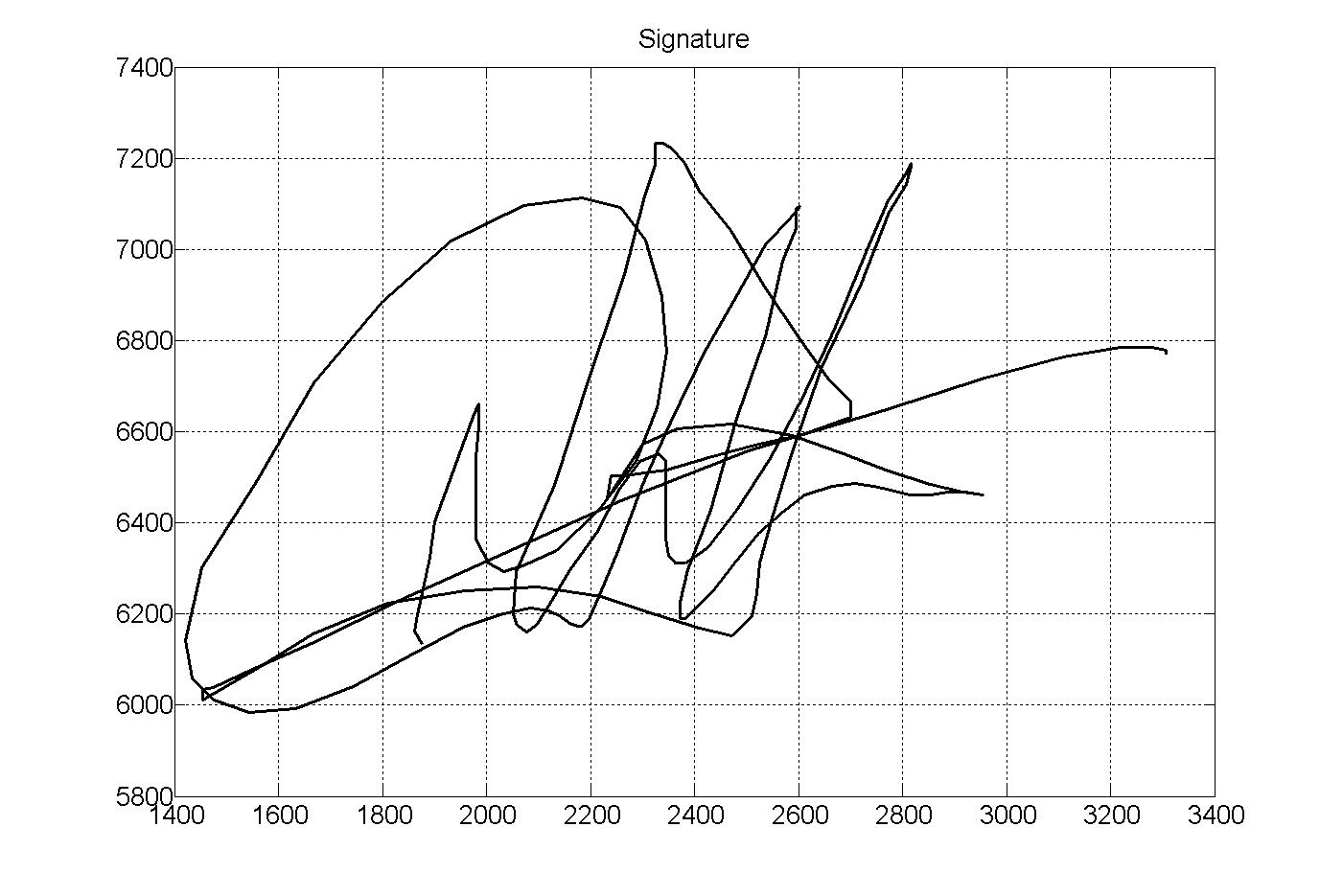
Signature Recognition
Signature recognition is an example of behavioral biometrics that identifies a person based on their handwriting. It can be operated in two different ways: Static: In this mode, users write their signature on paper, and after the writing is complete, it is digitized through an optical scanner or a camera to turn the signature image into bits. The biometric system then recognizes the signature analyzing its shape. This group is also known as "off-line". Dynamic: In this mode, users write their signature in a digitizing tablet, which acquires the signature in real time. Another possibility is the acquisition by means of stylus-operated PDAs. Some systems also operate on smart-phones or tablets with a capacitive screen, where users can sign using a finger or an appropriate pen. Dynamic recognition is also known as "on-line". Dynamic information usually consists of the following information: * spatial coordinate x(t) * spatial coordinate y(t) * pressure p(t) * azimuth az(t) * inclinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance. Biometric identifiers are the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological characteristics which are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina, odor/scent, voice, shape of ears and gait. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to mouse movement, typing rhythm, gait, signature, behavioral profiling, and credentials. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics to describe the latter class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Biometrics
Private biometrics is a form of encrypted biometrics, also called privacy-preserving biometric authentication methods, in which the biometric payload is a one-way, homomorphically encrypted feature vector that is 0.05% the size of the original biometric template and can be searched with full accuracy, speed and privacy. The feature vector's homomorphic encryption allows search and match to be conducted in polynomial time on an encrypted dataset and the search result is returned as an encrypted match. One or more computing devices may use an encrypted feature vector to verify an individual person (1:1 verify) or identify an individual in a datastore (1:many identify) without storing, sending or receiving plaintext biometric data within or between computing devices or any other entity. The purpose of private biometrics is to allow a person to be identified or authenticated while guaranteeing individual privacy and fundamental human rights by only operating on biometric data in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as closed-circuit television (CCTV), or interception of electronically transmitted information like Internet traffic. It can also include simple technical methods, such as Human intelligence (intelligence gathering), human intelligence gathering and postal interception. Surveillance is used by citizens for protecting their neighborhoods. And by governments for intelligence gathering - including espionage, prevention of crime, the protection of a process, person, group or object, or the investigation of crime. It is also used by criminal organizations to plan and commit crimes, and by businesses to Industrial espionage, gather intelligence on criminals, their competitors, suppliers or customers. Religious organisations charged with detecting he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various attempts to correlate physical with racial and psychological traits. Anthropometry involves the systematic measurement of the physical properties of the human body, primarily dimensional descriptors of body size and shape. Since commonly used methods and approaches in analysing living standards were not helpful enough, the anthropometric history became very useful for historians in answering questions that interested them. Today, anthropometry plays an important role in industrial design, clothing design, ergonomics and architecture where statistical data about the distribution of body dimensions in the population are used to optimize products. Changes in lifestyles, nutrition, and ethnic composition of populations lead to changes in the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometric Passport
A biometric passport (also known as an e-passport or a digital passport) is a traditional passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip which contains biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip (computer chip) and antenna (for both power to the chip and communication) embedded in the front or back cover, or centre page, of the passport. The passport's critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the machine readable lines and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented. Many countries are moving towards issuing biometric passports to their citizens. Malaysia was the first country to issue biometric passports in 1998. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics In Schools
Biometrics in schools refers to the use of biometric data such as fingerprints and facial recognition to identify students. This may be for daily transactions in the library or canteen or for monitoring absenteeism and behavior control. In 2002, Privacy International raised concerns that tens of thousands of UK school children were being fingerprinted by schools, often without the knowledge or consent of their parents. The supplier, Micro Librarian Systems, which uses technology similar to that used in prisons and the military, estimated that 350 schools throughout Britain were using such systems. In 2007, it was estimated that 3,500 schools are using such systems. Some schools in Belgium and the US have followed suit. Concerns have been raised by a number of groups, who suggest the harms far outweigh any putative benefits. Definition Biometrics are unique physical or behavioral characteristics which can be used to automatically identify individuals. Biometric technologies capture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |