|
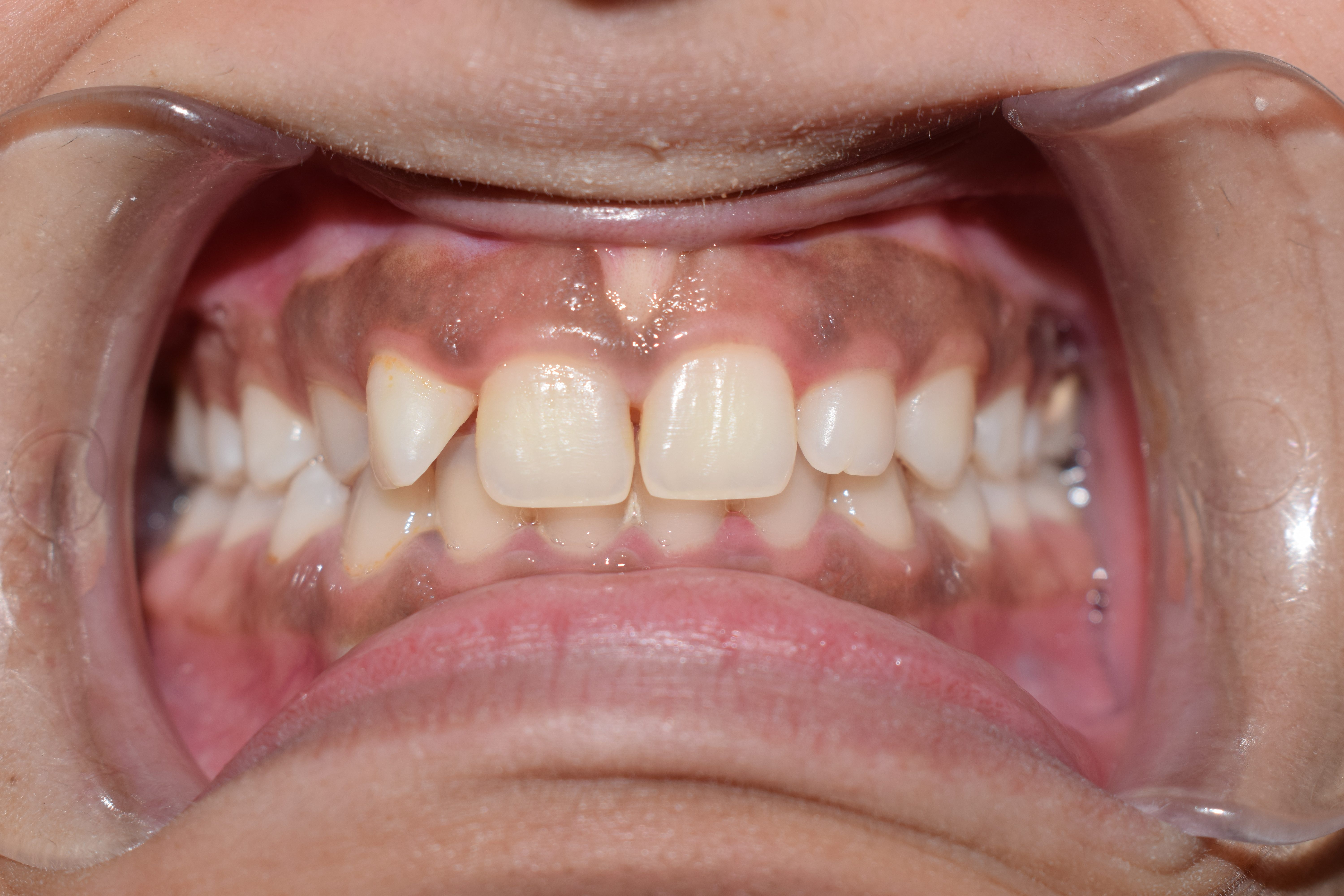
Socket Preservation
Socket preservation or alveolar ridge preservation is a procedure to reduce Dental alveolus, bone loss after tooth extraction. After tooth extraction, the jaw bone has a natural tendency to become bone remodeling, narrow, and lose its original shape because the bone quickly Bone resorption, resorbs, resulting in 30–60% loss in bone volume in the first six months. Bone loss, can compromise the ability to place a dental implant (to replace the tooth), or its aesthetics and functional ability. Socket preservation attempts to prevent bone loss by bone grafting the socket immediately after extraction. With the procedure, the gingiva, gum is retracted, the tooth extraction, tooth is removed, material (usually a Bone grafting#Allografts, bone substitute) is placed in the tooth socket, it is covered with a barrier membrane, and suturing, sutured closed. Roughly 30 days after socket preservation, the barrier membrane is either removed, or it resorption, resorbs, and the callus, callou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
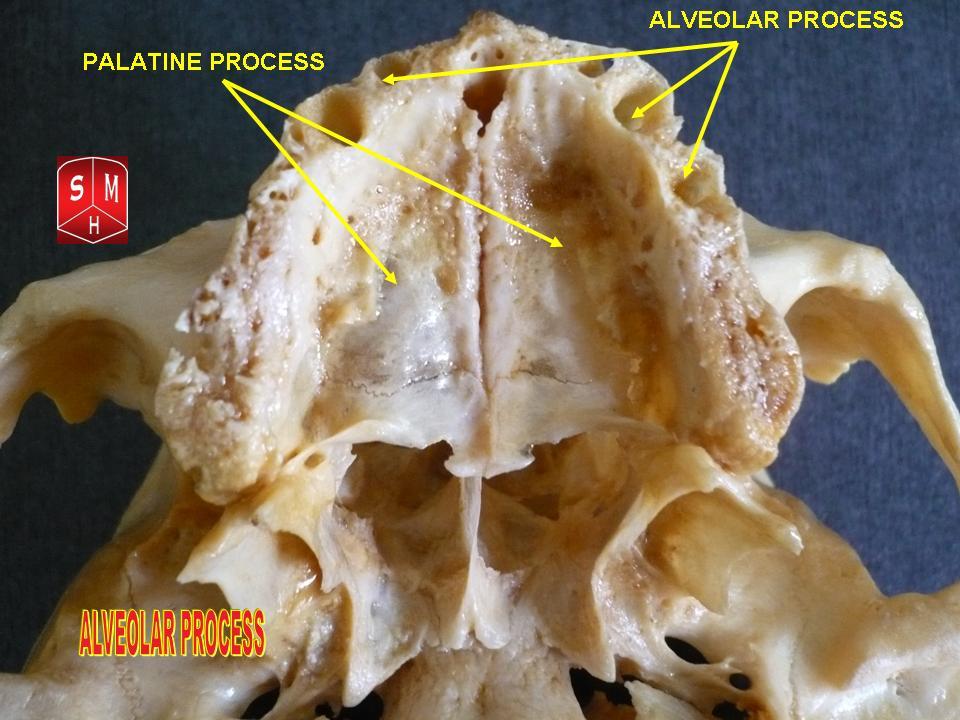
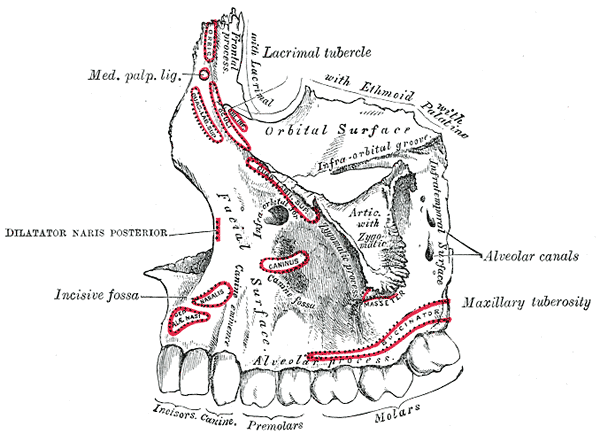
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults. The cause is usually a bacterial infection, but rarely can be a fungal infection. It may occur by spread from the blood or from surrounding tissue. Risks for developing osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, prior removal of the spleen, and trauma to the area. Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and basic laboratory tests as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).This is because plain radiographs are unremarkable in the first few days following acute infection. Diagnosis is further confirmed by blood tests, medical imaging, or bone biopsy. Treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis often involves both antimicrobials and sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship between the members of the group is still debated, and their classification into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups reflects this uncertainty. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenograft
Xenotransplantation (''xenos-'' from the Greek meaning "foreign" or strange), or heterologous transplant, is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another. Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of same species), syngeneic transplantation or isotransplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and autotransplantation (from one part of the body to another in the same person). Xenotransplantation of human tumor cells into immunocompromised mice is a research technique frequently used in pre-clinical oncology research. Human xenotransplantation offers a potential treatment for end-stage organ failure, a significant health problem in parts of the industrialized world. It also raises many novel medical, legal and ethical issues. A continuing concern is that many animals, such as pigs, have a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves. Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when Sir Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the world's leading financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autograft
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek). The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogeneic, or autogenic tissue) transplanted by such a procedure is called an autograft or autotransplant. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of the same species), syngeneic transplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and xenotransplantation (from other species). A common example is the removal of a piece of bone (usually from the hip) and its being ground into a paste for the reconstruction of another portion of bone. Autotransplantation, although most common with blood, bone, or skin, can be used for a wide variety of organs. One of the rare examples is autotransplantation of a kidney from one side of the body to the other. Kidney autotransplantation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Space
The buccal space (also termed the buccinator space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial tissue spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of each buccal space are: * the angle of the mouth anteriorly, * the masseter muscle posteriorly, * the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly, * the depressor anguli oris muscle and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly, * the buccinator muscle medially (the buccal space is superficial to the buccinator), * the platysma muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin laterally (the space is deep to platysma). Communications * to the pterygomandibular space, infratemporal space, submassete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peri-implantitis
Peri-implantitis is a destructive inflammatory process affecting the soft and hard tissues surrounding dental implants. The soft tissues become inflamed whereas the alveolar bone (hard tissue), which surrounds the implant for the purposes of retention, is lost over time. The bone loss involved in peri-implantitis differentiates this condition from peri-mucositis, a reversible inflammatory reaction involving only the soft tissues around the implant. Signs and symptoms Peri-implantitis does not present in the same way for all patients. Patients are recommended to regularly attend dental appointments and to seek advice from their dentist if they have any concerns for their oral health. Before the signs and symptoms are explained, it is worth noting that healthy peri-implant tissue should not be swollen, bleeding, producing pus, or have a reddened appearance. From a patient's perspective, he/she may notice loosening or wobbling of the implant. This symptom does not usually pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompromise
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |