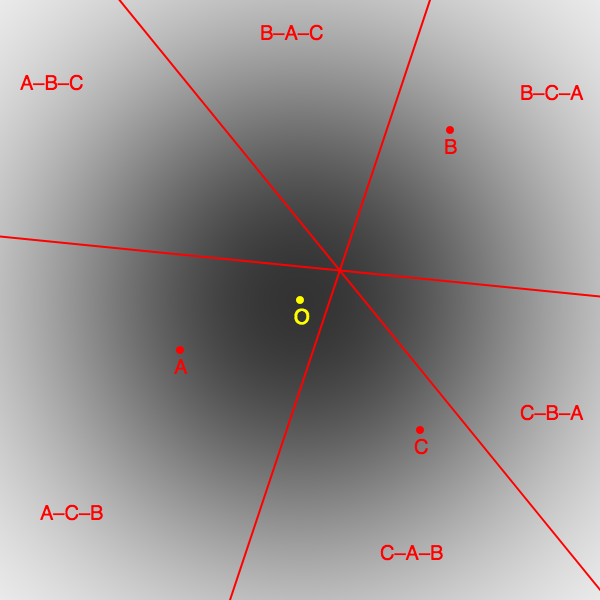
|
Social Utility Efficiency
Social utility efficiency (SUE) is a measurement of the utilitarian performance of voting methods—how likely they are to elect the candidate who best represents the voters' preferences. It is also known as utilitarian efficiency, voter satisfaction index (VSI) or voter satisfaction efficiency (VSE). Definition Social utility efficiency is defined as the ratio between the social utility of the candidate who is actually elected by a given voting method and that of the candidate who would maximize social utility, where E[]is the expected value over many iterations of the sum of all voter utilities for a given candidate: \operatorname= \frac A voting method with 100% efficiency would always pick the candidate that maximizes voter utility. A method that chooses a winner randomly would have efficiency of 0%, and a (pathological) method that did worse than a random pick would have less than 0% efficiency. SUE is not only affected by the voting method, but is a function of the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrill 1984 Figure 3 Social-Utility Efficiency For A Random Society
Merrill may refer to: Places in the United States *Merrill Field, Anchorage, Alaska *Merrill, Iowa *Merrill, Maine * Merrill, Michigan *Merrill, Mississippi, an unincorporated community near Lucedale in George County *Merrill, Oregon *Merrill, Wisconsin *Merrill (town), Wisconsin * Merrill Township, Michigan *Merrill Township, North Dakota * Merrill College at the University of California, Santa Cruz People * Merrill Moses (born 1977), Olympic water polo player *Merrill (surname) *Merrill Cook, Utah politician *Merrill Garbus, musician behind the experimental indie project Tune-yards *Merrill Ashley (born 1950), American ballet dancer and ''répétiteur'' Other uses *Merrill (company), a division of Bank of America * Skidmore, Owings and Merrill, architectural firm * USS ''Merrill'' (DD-976) * Nine men's morris, a strategy board game also called ''Merrills'' * Merrill (crater) Merrill is a lunar impact crater. It is located in the high northern latitudes, on the far side. Less t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant-runoff Voting
Instant-runoff voting (IRV) is a type of ranked preferential voting method. It uses a majority voting rule in single-winner elections where there are more than two candidates. It is commonly referred to as ranked-choice voting (RCV) in the United States (although there are other forms of ranked voting), preferential voting in Australia, where it has seen the widest adoption; in the United Kingdom, it is generally called alternative vote (AV), whereas in some other countries it is referred to as the single transferable vote, which usually means only its multi-winner variant. All these names are often used inconsistently. Voters in IRV elections rank the candidates in order of preference. Ballots are initially counted for each voter's top choice. If a candidate has more than half of the first-choice votes, that candidate wins. If not, then the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated, and the voters who selected the defeated candidate as a first choice then have their vot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Electoral Systems
Electoral systems are the rules for conducting elections, a main component of which is the algorithm for determining the winner (or several winners) from the ballots cast. This article discusses methods and results of comparing different electoral systems, both those which elect a unique candidate in a 'single-winner' election and those which elect a group of representatives in a multiwinner election. There are 4 main types of reasoning which have been used to try to determine the best voting method: # Argument by example # Adherence to logical criteria # Results of simulated elections # Results of real elections Expert opinions on single-winner voting methods In 2010, a panel of 22 experts on voting procedures were asked: "What is the best voting rule for your town to use to elect the mayor?". One member abstained. Approval voting was used to decide between 18 single-winner voting methods. The ranking (with number ''N'' of approvers from a maximum of 21) of the various syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condorcet Efficiency
Condorcet efficiency is a measurement of the performance of voting methods. It is defined as the percentage of elections for which the Condorcet winner (the candidate who is preferred over all others in head-to-head races) is elected, provided there is one. A voting method with 100% efficiency would always pick the Condorcet winner, when one exists, and a method that never chose the Condorcet winner would have 0% efficiency. The outcome of a referendum on policy can be efficient if the conditions of the efficient voter rule are met. Efficiency is not only affected by the voting method, but is a function of the number of voters, number of candidates, and of any strategies used by the voters. It was initially developed in 1984 by Samuel Merrill III, along with Social utility efficiency. A related, generalized measure is Smith efficiency, which measures how often a voting method elects a candidate in the Smith set. Except in elections where the Smith set includes all candidate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Ballot
The random ballot, single stochastic vote, or lottery voting is an electoral system in which an election is decided on the basis of a single randomly selected ballot. It is closely related to random dictatorship; the latter is a general rule for social choice, while random ballot is an application of this general rule for electing candidates in multi-constituency bodies. Whilst appearing superficially chaotic, the system has the potential to retain the most attractive characteristics of both first past the post and proportional representation systems in elections to multi-constituency bodies. Random dictatorship was first described in 1977 by Allan Gibbard. Its application to elections was first described in 1984 by Akhil Reed Amar,. Method and properties In an election or referendum, the ballot of a single voter is selected at random, and that ballot decides the result of the election. In this way, each candidate or option wins with a probability exactly equal to the fraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Regret
In stochastic game theory, Bayesian regret is the expected difference ("regret") between the utility of a Bayesian strategy and that of the optimal strategy (the one with the highest expected payoff). The term ''Bayesian'' refers to Thomas Bayes Thomas Bayes ( ; 1701 7 April 1761) was an English statistician, philosopher and Presbyterian minister who is known for formulating a specific case of the theorem that bears his name: Bayes' theorem. Bayes never published what would become his ... (1702–1761), who proved a special case of what is now called Bayes' theorem, who provided the first mathematical treatment of a non-trivial problem of statistical data analysis using what is now known as Bayesian inference. Economics This term has been used to compare a random buy-and-hold strategy to professional traders' records. This same concept has received numerous different names, as the New York Times notes: "In 1957, for example, a statistician named James Hanna called his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax Condorcet Method
In voting systems, the Minimax Condorcet method (often referred to as "the Minimax method") is one of several Condorcet methods used for tabulating votes and determining a winner when using ranked voting in a single-winner election. It is sometimes referred to as the Simpson–Kramer method, and the successive reversal method. Minimax selects as the winner the candidate whose greatest pairwise defeat is smaller than the greatest pairwise defeat of any other candidate: or, put another way, "the only candidate whose support never drops below percent" in any pairwise contest. Description of the method The Minimax Condorcet method selects the candidate for whom the greatest pairwise score for another candidate against him or her is the least such score among all candidates. Formal definition Formally, let \operatorname(X,Y) denote the pairwise score for X against Y. Then the candidate, W selected by minimax (aka the winner) is given by: : W = \arg \min_X \left( \max_Y \operator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Score Voting
Score voting or range voting is an electoral system for single-seat elections, in which voters give each candidate a score, the scores are added (or averaged), and the candidate with the highest total is elected. It has been described by various other names including evaluative voting, utilitarian voting, interval measure voting, the point system, ratings summation, 0-99 voting, average voting and utility voting. It is a type of cardinal voting electoral system, and aims to implement the utilitarian social choice rule. Score voting should be distinguished from positional voting systems, such as the Borda count: in score voting, each voter is free to give any score to any candidate; in positional voting, the score that each voter gives to each candidate is uniquely determined by the candidate's rank in the voter's ballot. Usage Political use Combined approval voting, a 3-rank form of score voting, is used to determine which candidates represent the parties in Latvia's Saei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranked Pairs
Ranked pairs (sometimes abbreviated "RP") or the Tideman method is an electoral system developed in 1987 by Nicolaus Tideman that selects a single winner using votes that express preferences. The ranked-pairs procedure can also be used to create a sorted list of winners. If there is a candidate who is preferred over the other candidates, when compared in turn with each of the others, the ranked-pairs procedure guarantees that candidate will win. Because of this property, the ranked-pairs procedure complies with the Condorcet winner criterion (and is a Condorcet method). Procedure The ranked-pairs procedure operates as follows: # Tally the vote count comparing each pair of candidates, and determine the winner of each pair (provided there is not a tie) # Sort (rank) each pair, by strength of victory, from largest first to smallest last.In fact, there are different ways how the ''strength of a victory'' is measured. This article uses Tideman's original method based on margins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAR Voting
STAR voting is an electoral system for single-seat elections. Variations also exist for multi-winner and proportional representation elections. The name (an allusion to star ratings) stands for "Score then Automatic Runoff", referring to the fact that this system is a combination of score voting, to pick two finalists with the highest total scores, followed by a "virtual runoff" in which the finalist who is preferred on more ballots wins. It is a type of cardinal voting electoral system. Method In STAR, voters are given a score, or ratings ballot, on which each voter scores every candidate with a number from 0 to 5, with 0 representing "worst" and 5 representing "best." The scores for each candidate are then summed, and the two highest-scored candidates are selected as finalists. In the automatic-runoff round, the finalist who was given a higher score on a greater number of ballots is selected as the winner. Usage The concept was first proposed in October 2014 by Mark Froh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical Clustering
In data mining and statistics, hierarchical clustering (also called hierarchical cluster analysis or HCA) is a method of cluster analysis that seeks to build a hierarchy of clusters. Strategies for hierarchical clustering generally fall into two categories: * Agglomerative: This is a " bottom-up" approach: Each observation starts in its own cluster, and pairs of clusters are merged as one moves up the hierarchy. * Divisive: This is a "top-down" approach: All observations start in one cluster, and splits are performed recursively as one moves down the hierarchy. In general, the merges and splits are determined in a greedy manner. The results of hierarchical clustering are usually presented in a dendrogram. The standard algorithm for hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC) has a time complexity of \mathcal(n^3) and requires \Omega(n^2) memory, which makes it too slow for even medium data sets. However, for some special cases, optimal efficient agglomerative methods (of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |