|
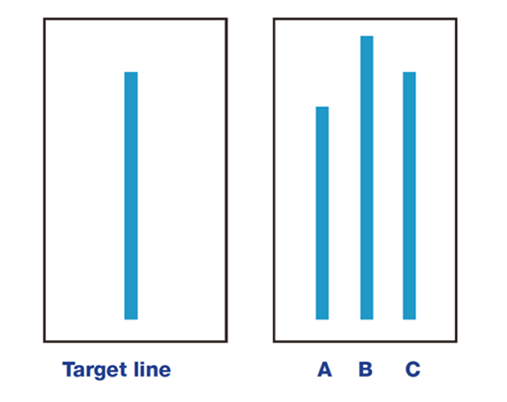
Social Proof
Social proof (or informational social influence) is a psychological and social phenomenon wherein people copy the actions of others in choosing how to behave in a given situation. The term was coined by Robert Cialdini in his 1984 book '' Influence: Science and Practice''. Social proof is used in ambiguous social situations where people are unable to determine the appropriate ''mode of behavior'', and is driven by the assumption that the surrounding people possess more knowledge about the current situation. The effects of social influence can be seen in the tendency of large groups to conform. This is referred to in some publications as the '' herd behavior''. Although social proof reflects a rational motive to take into account the information possessed by others, formal analysis shows that it can cause people to converge too quickly upon a single distinct choice, so that decisions of even larger groups of individuals may be grounded in very little information (see information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laugh Track
A laugh track (or laughter track) is an audio recording consisting of laughter (and other audience reactions) usually used as a separate soundtrack for comedy productions. The laugh track may contain live audience reactions or artificial laughter (canned laughter or fake laughter) made to be inserted into the show, or a combination of the two. The use of canned laughter to "sweeten" the laugh track was pioneered by American sound engineer Charles "Charley" Douglass. The Douglass laugh track became a standard in mainstream television in the U.S., dominating most prime-time sitcoms and sketch comedies from the late 1950s to the late 1970s. Use of the Douglass laughter decreased by the 1980s upon the development of stereophonic laughter. In addition, single-camera sitcoms eliminated audiences altogether. Canned laughter is used to encourage the viewer to laugh. History in the United States Radio Before radio and television, audiences experienced live comedy performances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference Falsification
Preference falsification is the act of misrepresenting a preference under perceived public pressure. It involves the selection of a publicly expressed preference that differs from the underlying privately held preference (or simply, a public preference at odds with one’s private preference). People frequently convey to each other preferences that differ from what they would communicate privately under credible cover of anonymity (such as in opinion surveys to researchers or pollsters). Techniques such as list experiments can be used to uncover preference falsification. The term was coined by Timur Kuran in a 1987 article, "Chameleon voters and public choice." On controversial matters that induce preference falsification, he showed there, widely disliked policies may appear popular. The distribution of public preferences, which Kuran defines as public opinion, may differ greatly from private opinion, which is the distribution of private preferences known only to individuals thems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Pressure
Peer pressure is a direct or indirect influence on peers, i.e., members of social groups with similar interests and experiences, or social statuses. Members of a peer group are more likely to influence a person's beliefs, values, religion and behavior. A group or individual may be encouraged and want to follow their peers by changing their Attitude (psychology), attitudes, Value (ethics), values or behaviors to conform to those of the influencing group or individual. For the individual affected by peer pressure, this can have both a positive or negative effect on them. Social groups include both ''membership groups'' in which individuals hold "formal" membership (e.g. political parties, trade unions, schools) and cliques in which membership is less clearly defined. However, a person does not need to be a member or be seeking membership of a group to be affected by peer pressure. An individual may be in a crowd, a group of many cliques, and still be affected by peer pressure. Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observational Learning
Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. It is a form of Social learning theory, social learning which takes various forms, based on various processes. In humans, this form of learning seems to not need reinforcement to occur, but instead, requires a social model such as a parent, sibling, friend, or teacher with surroundings. Particularly in childhood, a model is someone of authority or higher status in an environment. In animals, observational learning is often based on classical conditioning, in which an instinctive behavior is elicited by observing the behavior of another (e.g. mobbing in birds), but other processes may be involved as well. Human observational learning Many behaviors that a learner observes, remembers, and imitates are actions that models display and display modeling, even though the model may not intentionally try to instill a particular behavior. A child may learn to swear, smack, smoke, and deem other inappropr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge Falsification
Knowledge falsification is the deliberate misrepresentation of what one knows under perceived social pressures. The term was coined by Timur Kuran in his book ''Private Truths, Public Lies: The Social Consequences of Preference Falsification''. Motives According to Kuran's analysis of preference falsification, knowledge falsification is usually undertaken to signal a preference that differs from one's private preference, in other words, to support preference falsification. Successful misrepresentation of one's private preferences requires hiding the knowledge on which they rest. Thus, people engage in preference falsification, or bolster it, by misrepresenting their information, interpretations, and understanding. Such misrepresentation is a response to perceived social, economic, and political pressures. The perceived pressures could be partly, if not fully, imaginary. The pressures may be rooted in speech controls imposed by a state and enforced through state-enforced punish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Cascades
An information cascade or informational cascade is a phenomenon described in behavioral economics and network theory in which a number of people make the same decision in a sequential fashion. It is similar to, but distinct from herd behavior. An information cascade is generally accepted as a two-step process. For a cascade to begin an individual must encounter a scenario with a decision, typically a binary one. Second, outside factors can influence this decision, such as the individual observing others' choices and the apparent outcomes. The two-step process of an informational cascade can be broken down into five basic components: # There is a decision to be made – for example; whether to adopt a new technology, wear a new style of clothing, eat in a new restaurant, or support a particular political position # A limited action space exists (e.g. an adopt/reject decision) # People make the decision sequentially, and each person can observe the choices made by those who acted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herd Mentality
Herd mentality is the tendency for people’s behavior or beliefs to conform to those of the group they belong to. The concept of herd mentality has been studied and analyzed from different perspectives, including biology, psychology and sociology. This psychological phenomenon can have profound impacts on human behavior. Social psychologists study the related topics of collective intelligence, crowd wisdom, groupthink, and deindividuation. History The idea of a "group mind" or " mob behavior" was first put forward by 19th-century social psychologists Gabriel Tarde and Gustave Le Bon. Herd behavior in human societies has also been studied by Sigmund Freud and Wilfred Trotter, whose book '' Instincts of the Herd in Peace and War'' is a classic in the field of social psychology. Sociologist and economist Thorstein Veblen's '' The Theory of the Leisure Class'' illustrates how individuals imitate other group members of higher social status in their consumer behavior. More r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOMO
Fear of missing out (FOMO) is the feeling of apprehension that one is either not in the know about or missing out on information, events, experiences, or life decisions that could make one's life better. FOMO is also associated with a fear of regret, which may lead to concerns that one might miss an opportunity for social interaction, a novel experience, a memorable event, profitable investment, or the comfort of loved ones. It is characterized by a desire to stay continually connected with what others are doing, and can be described as the fear that deciding not to participate is the wrong choice. FOMO could result from not knowing about a conversation, missing a TV show, not attending a wedding or party, or hearing that others have discovered a new restaurant. In recent years, FOMO has been attributed to a number of negative psychological and behavioral symptoms. FOMO has increased in recent times due to advancements in technology. Social networking sites create many opportunit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crowd Psychology
Crowd psychology (or mob psychology) is a subfield of social psychology which examines how the psychology of a group of people differs from the psychology of any one person within the group. The study of crowd psychology looks into the actions and thought processes of both the individual members of the crowd and of the crowd as a collective social entity. The behavior of a crowd is much influenced by deindividuation (seen as a person's loss of responsibility) and by the person's impression of the universality of behavior, both of which conditions increase in magnitude with size of the crowd. Notable theorists in crowd psychology include Gustave Le Bon (1841-1931), Gabriel Tarde (1843-1904), and Sigmund Freud (1856-1939). Many of these theories are today tested or used to simulate crowd behaviors in normal or emergency situations. One of the main focuses in these simulation works aims to prevent crowd crushes and stampedes. Origins According to his biological theory of cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Mass (sociodynamics)
In social dynamics, critical mass is a sufficient number of adopters of a new idea, technology or innovation in a social system so that the rate of adoption becomes self-sustaining and creates further growth. The point at which critical mass is achieved is sometimes referred to as a threshold within the threshold model of statistical modeling. The term " critical mass" is borrowed from nuclear physics, where it refers to the amount of a substance needed to sustain a chain reaction. Within social sciences, critical mass has its roots in sociology and is often used to explain the conditions under which reciprocal behavior is started within collective groups, and how reciprocal behavior becomes self-sustaining. Recent technology research in platform ecosystems shows that apart from the quantitative notion of a “sufficient number”, critical mass is also influenced by qualitative properties such as reputation, interests, commitments, capabilities, goals, consensuses, and decisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Wisdom
The conventional wisdom or received opinion is the body of ideas or explanations generally accepted by the public and/or by experts in a field. History The term "conventional wisdom" dates back to at least 1838, as a synonym for "commonplace knowledge". It was used in a number of works, occasionally in a benign''E.g.,'1 Nahum Capen, ''The History of Democracy'' (1874), page 477("millions of all classes alike are equally interested and protected by the practical judgment and conventional wisdom of ages"). or neutral''E.g.,'"Shallow Theorists", ''American Educational Monthly'' 383 (Oct. 1866)("What is the result? Just what conventional wisdom assumes it would be."). sense, but more often pejoratively.''E.g.,'Joseph Warren Beach, ''The Technique of Thomas Hardy'' (1922), page 152("He has not the colorless monotony of the business man who follows sure ways to success, who has conformed to every rule of conventional wisdom, and made himself as featureless as a potato field, as tame as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |