|
Social Inequity Aversion
Inequity is injustice or unfairness or an instance of either of the two. Aversion is "a feeling of repugnance toward something with a desire to avoid or turn from it; a settled dislike; a tendency to extinguish a behavior or to avoid a thing or situation and especially a usually pleasurable one because it is or has been associated with a noxious stimulus". The given definition of inequity aversion is "the preference for fairness and resistance to inequitable outcomes". Clarification through experiment To better understand and breakdown the concept of social inequity aversion would be to use the study done by Sarah Brosnan and Frans de Waal , Henrich, Josephbr>"Animal Behaviour (Communication Arising): Inequity Aversion in Capuchins?"11 March 2004. ''Nature''. Issue 428. Retrieved 3 December 2007. who specialize in social behavior and social cognition. In their experiment, "Monkeys Reject Unequal Pay" five female capuchin monkeys were used and given an unequal distribution of rewa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inequity Aversion
Inequity aversion (IA) is the preference for fairness and resistance to incidental inequalities. The social sciences that study inequity aversion include sociology, economics, psychology, anthropology, and ethology. Human studies Inequity aversion research on humans mostly occurs in the discipline of economics though it is also studied in sociology. Research on inequity aversion began in 1978 when studies suggested that humans are sensitive to inequities in favor of as well as those against them, and that some people attempt overcompensation when they feel "guilty" or unhappy to have received an undeserved reward. A more recent definition of inequity aversion (resistance to inequitable outcomes) was developed in 1999 by Fehr and Schmidt. They postulated that people make decisions so as to minimize inequity in outcomes. Specifically, consider a setting with individuals who receive pecuniary outcomes ''xi''. Then the utility to person ''i'' would be given by :U_i(\) = x_i - \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Brosnan
Sarah Brosnan is a researcher studying the development of cognitive processes that underlie cooperation and reciprocity. The focus of her work has been on how animals perceive "exchanged goods and services," as demonstrated by reciprocal interactions,. She has looked at both human and nonhuman primates as a way of understanding the evolution of cooperative and economic behaviors, specifically the topic of inequity aversion and the cooperative pulling paradigm. She works at Georgia State University in the Department of Psychology, and directs the university's Comparative Economics and Behavioral Studies Laboratory (CEBUS Lab). (Accessed April 2012) Selected publications * * * * < ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frans De Waal
Franciscus Bernardus Maria "Frans" de Waal (born October 29, 1948) is a Dutch primatologist and ethologist. He is the Charles Howard Candler Professor of Primate Behavior in the Department of Psychology at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, director of the Living Links Center at the Yerkes National Primate Research Center at Emory, and author of numerous books including ''Chimpanzee Politics'' (1982) and ''Our Inner Ape'' (2005). His research centers on primate social behavior, including conflict resolution, cooperation, inequity aversion, and food-sharing. He is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. Early life and education De Waal was born in 's-Hertogenbosch on October 29, 1948. He studied at the Dutch universities of Radboud University Nijmegen, University of Groningen, and Utrecht. In 1977, De Waal received his doctorate in biology from Utrecht University after training as a zoologist and ethol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Henrich
Joseph Henrich (born 1968) is an American professor of human evolutionary biology at Harvard University. Prior to arriving at Harvard, Henrich was a professor of psychology and economics at the University of British Columbia. He is interested in the question of how humans evolved from "being a relatively unremarkable primate a few million years ago to the most successful species on the globe", and how culture shaped our species' genetic evolution. Biography Henrich holds bachelor degrees in anthropology and aerospace engineering from the University of Notre Dame, earned in 1991. From 1991 to 1993, he worked as a Test and Evaluation Systems Engineer for General Electric Aerospace (sold to Martin Marietta in 1993) in Springfield, Virginia. In 1995, he earned a master's degree and four years later, a doctorate in anthropology from the University of California at Los Angeles. From 2002 to 2007, Henrich was on the faculty of Emory University in the Department of Anthropology. He be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capuchin Monkey
The capuchin monkeys () are New World monkeys of the subfamily Cebinae. They are readily identified as the " organ grinder" monkey, and have been used in many movies and television shows. The range of capuchin monkeys includes some tropical forests in Central America and South America as far south as northern Argentina. In Central America, where they are called white-faced monkeys ("carablanca"), they usually occupy the wet lowland forests on the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica and Panama and deciduous dry forest on the Pacific coast. Etymology The word "capuchin" derives from a group of friars named the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, an offshoot from the Franciscans, who wear brown robes with large hoods. When Portuguese explorers reached the Americas in the 15th century, they found small monkeys whose coloring resembled these friars, especially when in their robes with hoods down, and named them capuchins. When the scientists described a specimen (thought to be a golden-bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Inequality
Social inequality occurs when resources in a given society are distributed unevenly, typically through norms of allocation, that engender specific patterns along lines of socially defined categories of persons. It posses and creates gender cap between individuals that limits the accessibility that women have within society. the differentiation preference of access of social goods in the society brought about by power, religion, kinship, prestige, race, ethnicity, gender, age, sexual orientation, and class. Social inequality usually implies the lack of equality of outcome, but may alternatively be conceptualized in terms of the lack of equality of access to opportunity. This accompanies the way that inequality is presented throughout social economies and the rights that are skilled within this basis. The social rights include labor market, the source of income, health care, and freedom of speech, education, political representation, and participation. Social inequality is link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
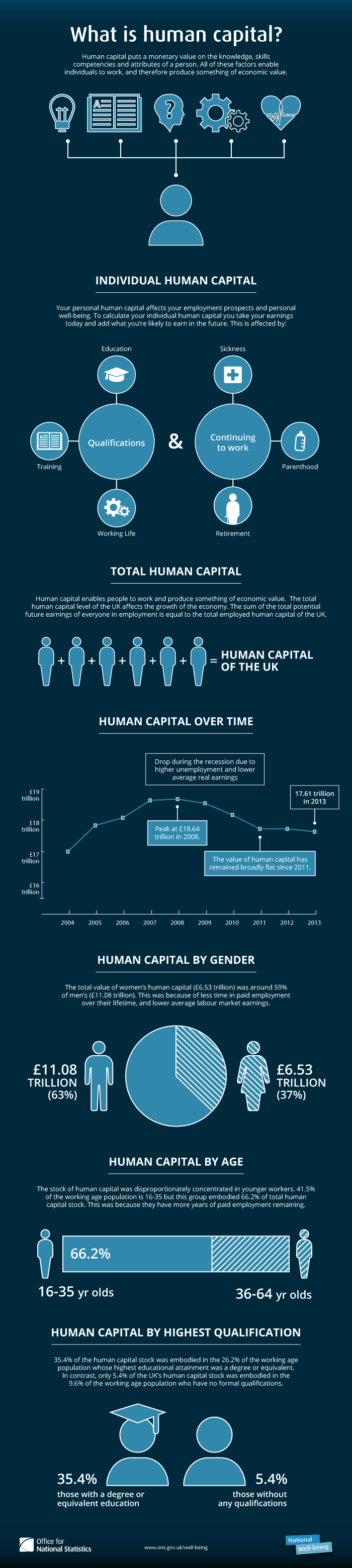
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spite House
A spite house is a building constructed or substantially modified to irritate neighbors or any party with land stakes. Because long-term occupation is not the primary purpose of these houses, they frequently sport strange and impractical structures. Spite houses may create obstructions, such as blocking out light or blocking access to neighboring buildings, or they can be flagrant symbols of defiance. Although, in the US, homeowners generally have no right to views, light, or air, neighbors can sue for a negative easement. In instances regarding a spite build, courts are far more likely to side with the neighboring parties which may have been affected by that build. For example, the Coty v. Ramsey Associates, Inc. case of 1988 ruled that the defendant's spite farm constituted a nuisance, granting the neighboring landowner a negative easement. Spite houses, as well as spite farms, are considerably rarer than spite fences. This is partially attributable to the fact that modern b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Systems
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal Social structure, structure of role and status that can form in a small, stable group. An individual may belong to multiple social systems at once; examples of social systems include nuclear family units, community, communities, City, cities, nations, college campuses, corporations, and Industry (economics), industries. The organization and definition of groups within a social system depend on various shared properties such as location, socioeconomic status, race, religion, societal function, or other distinguishable features. Notable theorists The study of social systems is integral to the fields of sociology and public policy. Social systems have been studied for as long as sociology has existed. Talcott Parsons Talcott Parsons was the first to formulate a systematic theory of social systems, which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Of Wealth
The distribution of wealth is a comparison of the wealth of various members or groups in a society. It shows one aspect of economic inequality or economic heterogeneity. The distribution of wealth differs from the income distribution in that it looks at the economic distribution of ownership of the assets in a society, rather than the current income of members of that society. According to the International Association for Research in Income and Wealth, "the world distribution of wealth is much more unequal than that of income." For rankings regarding wealth, see list of countries by wealth equality or list of countries by wealth per adult. Definition of wealth Wealth of an individual is defined as net worth, expressed as: wealth = assets − liabilities A broader definition of wealth, which is rarely used in the measurement of wealth inequality, also includes human capital. For example, the United Nations definition of '' inclusive wealth'' is a monetary measure which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism (), or equalitarianism, is a school of thought within political philosophy that builds from the concept of social equality, prioritizing it for all people. Egalitarian doctrines are generally characterized by the idea that all humans are equal in fundamental worth or moral status. Egalitarianism is the doctrine that all citizens of a state should be accorded exactly equal rights. Egalitarian doctrines have motivated many modern social movements and ideas, including the Enlightenment, feminism, civil rights, and international human rights. The term ''egalitarianism'' has two distinct definitions in modern English, either as a political doctrine that all people should be treated as equals and have the same political, economic, social and civil rights, or as a social philosophy advocating the removal of economic inequalities among people, economic egalitarianism, or the decentralization of power. Sources define egalitarianism as equality reflecting the natural st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)