|
Smith Gun
The Smith Gun was an ''ad hoc'' anti-tank artillery piece used by the British Army and Home Guard during the Second World War. With a German invasion of Great Britain seeming likely after the defeat in the Battle of France, most available weaponry was allocated to the regular British Army, leaving the Home Guard short on supplies, particularly anti-tank weaponry. The Smith Gun was designed by retired Army Major William H. Smith as a makeshift anti-tank weapon, and was put into production in 1941 following a demonstration to the Prime Minister, Winston Churchill. The weapon consisted of a smooth-bore barrel approximately long mounted on a carriage and capable of firing both modified 3-inch mortar anti-tank and anti-personnel rounds. Despite the promising-sounding nature of the weapon, which at trials in ideal conditions achieved a ''maximum range'' of , it was generally regarded as a short-range weapon with an accepted effective range of between . Furthermore, it was heavy an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Nelson, Portsmouth
Fort Nelson, in the civil parish of Boarhunt in the English county of Hampshire, is one of five defensive forts built on the summit of Portsdown Hill in the 1860s, overlooking the important naval base of Portsmouth. It is now part of the Royal Armouries, housing their collection of artillery, and a Grade I Listed Building. Description Fort Nelson is a typical Polygonal or Palmerston Fort. It is six-sided with a deep ditch protected by three caponiers. Above each caponier is a well-protected emplacement for 13-inch mortars. It was originally entered by two Guthrie rolling bridges and has a barrack block for 172 officers and other ranks, protected by a V-shaped redan. A large open parade ground gives access to the magazines 40 feet underneath it. There are open emplacements on the ramparts for 64 pounder rifled muzzle-loading guns and RML 6.6-inch howitzers. There are also three Haxo casemates for 7 inch rifled breech-loaders. The Nelson Monument, which gave the fort its n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk Evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the north of France, between 26 May and 4 June 1940. The operation commenced after large numbers of Belgian, British, and French troops were cut off and surrounded by German troops during the six-week Battle of France. In a speech to the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this "a colossal military disaster", saying "the whole root and core and brain of the British Army" had been stranded at Dunkirk and seemed about to perish or be captured. In his " We shall fight on the beaches" speech on 4 June, he hailed their rescue as a "miracle of deliverance". After Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, France and the British Empire declared war on Germany and imposed an economic blockade. The British Expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery By Type
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a layman term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We Know Our Onions
"We Know Our Onions" is the fourth episode of the sixth series of the British comedy series '' Dad's Army''. It was originally transmitted on 21 November 1973. Synopsis The platoon take part in a Home Guard efficiency test. If the men pass with flying colours, they will be graded a 12-star platoon. Plot The platoon are examining their new Smith Gun (an artillery piece unique to the Home Guard), which they have to take on a Home Guard efficiency test for the weekend. Wilson is told off by Mainwaring when he complains "do we have to drag that gun about, what an awful fag". Godfrey and his sisters have made an inappropriate cover for the gun out of a flowery old sofa cover. They are going to the test in Jones' van, but Walker has been using it to fulfil a blackmarket order for Warden Hodges, the greengrocer, and has half a ton of onions. These cause the platoon (especially Pike) some discomfort on the journey and Hodges is so incensed about the non-delivery of the onions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
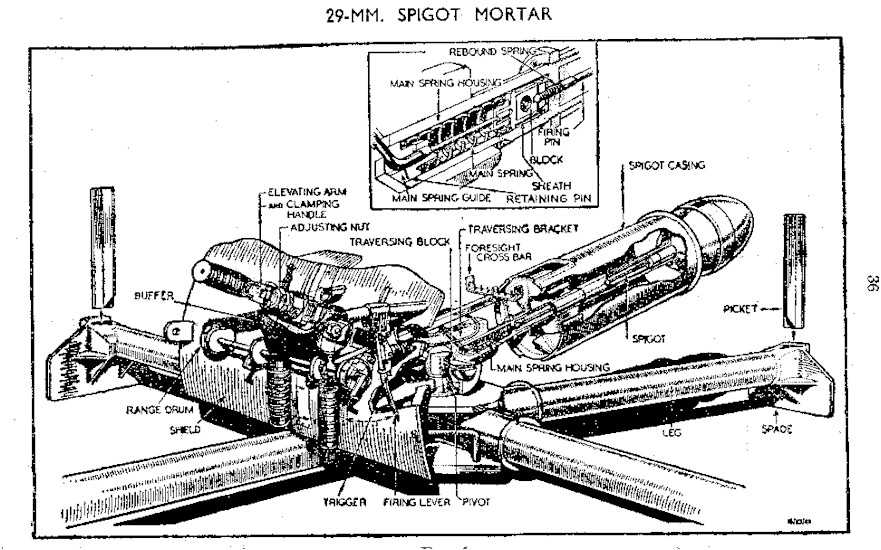
Blacker Bombard
The Blacker Bombard, also known as the 29-mm Spigot Mortar, was an infantry anti-tank weapon devised by Lieutenant-Colonel Stewart Blacker in the early years of the Second World War. Intended as a means to equip Home Guard units with an anti-tank weapon in case of German invasion, at a time of grave shortage of weapons, it was accepted only after the intervention of Churchill. Although there were doubts about the effectiveness of the Bombard, many were issued. Few, if any, saw combat. Development With the end of the Battle of France and the evacuation of the British Expeditionary Force from the port of Dunkirk between 26 May and 4 June 1940, a German invasion of Great Britain seemed likely. However, the British Army was not well-equipped to defend the country in such an event; in the weeks after the Dunkirk evacuation it could field only twenty-seven divisions.Lampe, p. 3 (The German Army had more than 100 divisions at that time.) The Army was particularly short of anti-tank g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northover Projector
The Projector, 2.5 inch—more commonly known as the Northover Projector—was an ''ad hoc'' anti-tank weapon used by the British Army and Home Guard during the Second World War. With a German invasion of Great Britain seeming likely after the defeat in the Battle of France, most available weaponry was diverted to the regular British Army, leaving the Home Guard short on supplies, particularly anti-tank weaponry. The Northover Projector was designed by Home Guard officer Robert Harry Northover to act as a makeshift anti-tank weapon, and was put into production in 1940 following a demonstration to the Prime Minister, Winston Churchill. The weapon consisted of a hollow metal tube attached to a tripod, with a rudimentary breech at one end. Rounds were fired with the use of black powder ignited by a standard musket percussion cap, and it had an effective range of between 100 and 150 yards. Although it was cheap and easy to manufacture, it did have several problems; it was diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821) are published by Times Newspapers, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', which do not share editorial staff, were founded independently and have only had common ownership since 1966. In general, the political position of ''The Times'' is considered to be centre-right. ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, such as '' The Times of India'', ''The New York Times'', and more recently, digital-first publications such as TheTimesBlog.com (Since 2017). In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as , or as , although the newspaper is of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bren Carrier
The Bren gun was a series of light machine guns (LMG) made by Britain in the 1930s and used in various roles until 1992. While best known for its role as the British and Commonwealth forces' primary infantry LMG in World War II, it was also used in the Korean War and saw service throughout the latter half of the 20th century, including the 1982 Falklands War. Although fitted with a bipod, it could also be mounted on a tripod or be vehicle-mounted. The Bren gun was a licensed version of the Czechoslovak ZGB 33 light machine gun which, in turn, was a modified version of the ZB vz. 26, which British Army officials had tested during a firearms service competition in the 1930s. The later Bren gun featured a distinctive top-mounted curved box magazine, conical flash hider, and quick change barrel. The name ''Bren'' was derived from Brno, the Czechoslovak city in Moravia, where the Zb vz. 26 was designed (in the Zbrojovka Brno Factory) and Enfield, site of the British Royal Small A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Smith Three Inch Mobile Gun H18832
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
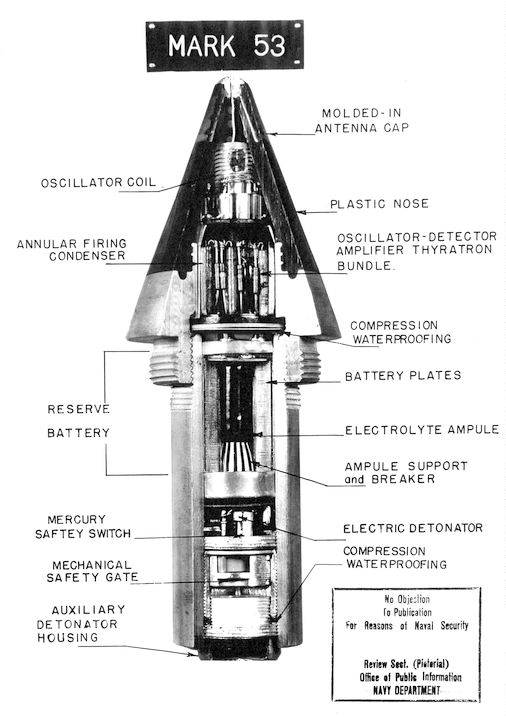
Fuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toggle Rope
A toggle rope was part of the standard equipment of British commandos and the Parachute Regiment during World War II. It was long, and had a toggle at one end in a tightly fitting eye splice, with a larger eye at the other end. This enabled them to be fastened together to create an ersatz An ersatz good () is a substitute good, especially one that is considered inferior to the good it replaces. It has particular connotations of wartime usage. Etymology ''Ersatz'' is a German word literally meaning ''substitute'' or ''replacement' ... rope ladder, or to secure around a bundle for hauling, among other uses. The ropes were carried around the commandos' waists while not in use. External links * * World War II infantry weapons of the United Kingdom {{Mil-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major
Major ( commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and '' sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)