|
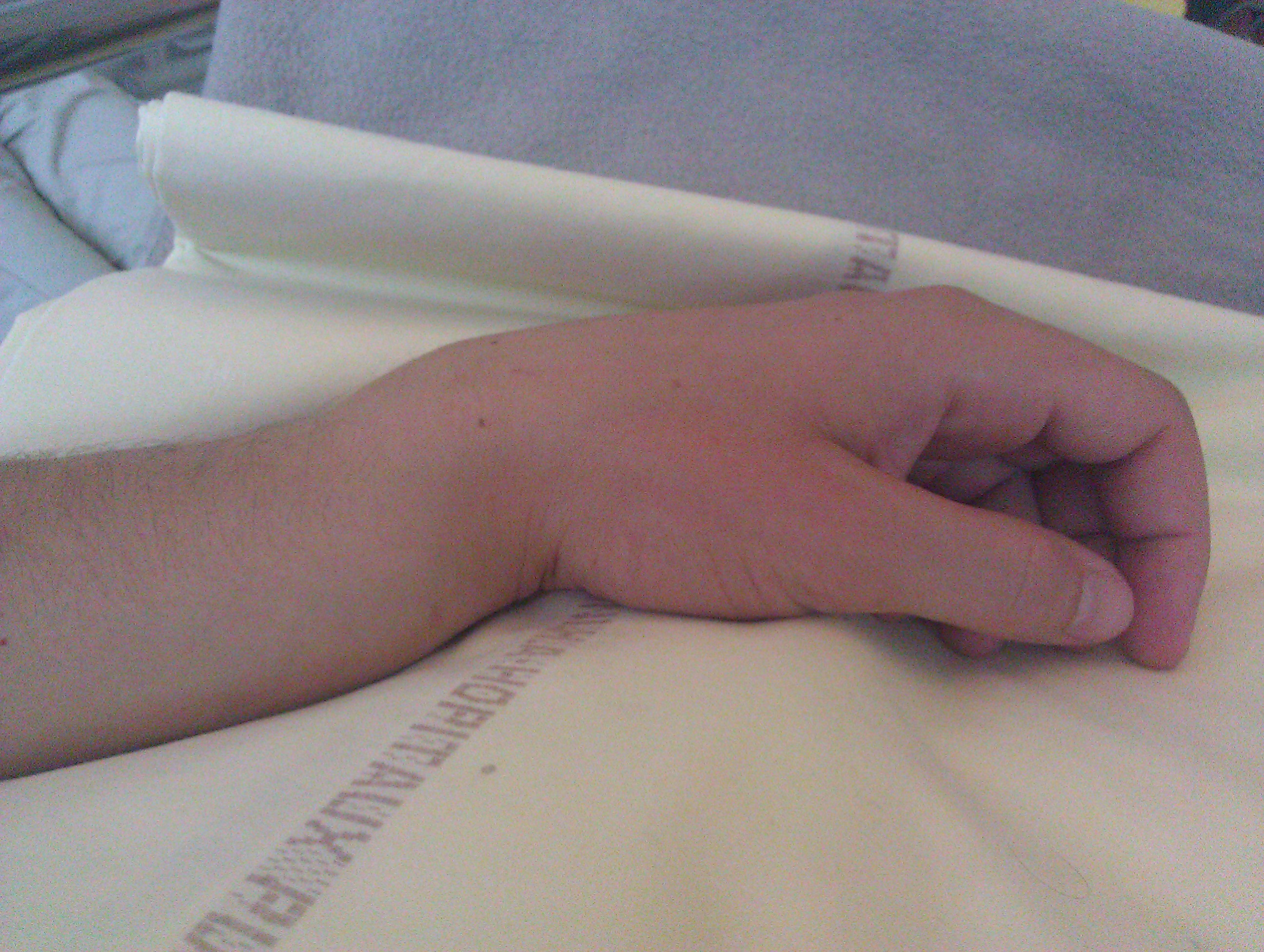
Smith's Fracture
A Smith's fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius. Although it can also be caused by a direct blow to the dorsal forearm or by a fall with the wrist flexed, the most common mechanism of injury for Smith's fracture occurs in a palmar fall with the wrist joint slightly dorsiflexed. Smith's fractures are less common than Colles' fractures. The distal fracture fragment is displaced volarly (ventrally), as opposed to a Colles' fracture which the fragment is displaced dorsally. Depending on the severity of the impact, there may be one or many fragments and it may or may not involve the articular surface of the wrist joint. Classification A commonly used classification of distal radial fractures is the Frykman Classification: * Type I: Extra-articular * Type II: Type I, with fracture of distal ulna * Type III: Radiocarpal joint involvement * Type IV: Type III with fracture of distal ulna * Type V: Distal radioulnar joint involved. * Type VI: Type V with fracture of distal ulna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colles' Fracture
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve. It typically occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand. Risk factors include osteoporosis. The diagnosis may be confirmed via X-rays. The tip of the ulna may also be broken. Treatment may include casting or surgery. Surgical reduction and casting is possible in the majority of cases in people over the age of 50. Pain management can be achieved during the reduction with procedural sedation and analgesia or a hematoma block. A year or two may be required for healing to occur. About 15% of people have a Colles' fracture at some point in their life. They occur more commonly in young adults and older people than in children and middle-aged adults. Women are more frequently affected than men. The fracture is named after Abraham Colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist Joint
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduction (orthopedic Surgery)
Reduction is a surgical procedure to repair a fracture or dislocation to the correct alignment. Description When a bone fractures, the fragments lose their alignment in the form of displacement or angulation. For the fractured bone to heal without any deformity the bony fragments must be re-aligned to their normal anatomical position. Orthopedic surgery attempts to recreate the normal anatomy of the fractured bone by ''reduction'' of the displacement. This sense of the term "reduction" does not imply any sort of removal or quantitative decrease but rather implies a restoration: ''re'' ("back o initial position) + ''ducere'' ("lead"/"bring"), i.e., "bringing back to normal". Because the process of reduction can briefly be intensely painful, it is commonly done under a short-acting anesthetic, sedative A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Surgeon
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert William Smith (surgeon)
Robert William Smith MD FRCSI MRIA (12 October 1807 in Dublin – 28 October 1873) was an Irish surgeon and pathologist who described Smith's fracture in his 1847 book, the first important book on fractures by an Irish author. Biography Smith studied medicine in his native Dublin and he was apprenticed to Richard Carmichael, and he studied professionally in the RCSI Medical School, Trinity College, the Richmond Hospital Schools, and in the House of Industry Hospitals. Smith received his Licentiate of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI) in 1832. He was awarded his MD from Trinity College, Dublin in 1842, and became a Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI) in 1844. He became the first Professor of Surgery at Trinity College in 1847, and a member of the Royal Irish Academy in 1849. He worked as surgeon to the Hospital for the Mentally Ill, Sir Patrick Dun's Hospital and he taught surgery and forensic medicine at the Richmond Hospital. He co-fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |