|
Small Cajal Body Specific RNA 15
Small Cajal body specific RNA 15 (also known as SCARNA15 or ACA45) is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies and believed to be involved in the pseudouridylation (isomerisation of uridine to pseudouridine) of U1 spliceosomal RNA. scaRNAs are a specific class of small nucleolar RNAs that localise to the Cajal bodies and guide the modification of RNA polymerase II transcribed spliceosomal A spliceosome is a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) and numerous proteins. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules bind to speci ... RNAs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U12. ACA45 belongs to the H/ACA box class of guide RNAs as it has the predicted hairpin-hinge-hairpin-tail structure, the conserved H/ACA-box motifs and is found associated with GAR1. ACA45 is predicted to guide the pseudouridylation of residue U37 of the U2 spliceosomal snRNA. It has been shown that human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types The most common secondary st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U2 Spliceosomal RNA
U2 spliceosomal snRNAs are a species of small nuclear RNA ( snRNA) molecules found in the major spliceosomal (Sm) machinery of virtually all eukaryotic organisms. ''In vivo'', U2 snRNA along with its associated polypeptides assemble to produce the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), an essential component of the major spliceosomal complex. The major spliceosomal-splicing pathway is occasionally referred to as U2 dependent, based on a class of Sm intron—found in mRNA primary transcripts—that are recognized exclusively by the U2 snRNP during early stages of spliceosomal assembly. In addition to U2 dependent intron recognition, U2 snRNA has been theorized to serve a catalytic role in the chemistry of pre-RNA splicing as well. Similar to ribosomal RNAs ( rRNAs), Sm snRNAs must mediate both RNA:RNA and RNA:protein contacts and hence have evolved specialized, highly conserved, primary and secondary structural elements to facilitate these types of interactions. Shortly after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
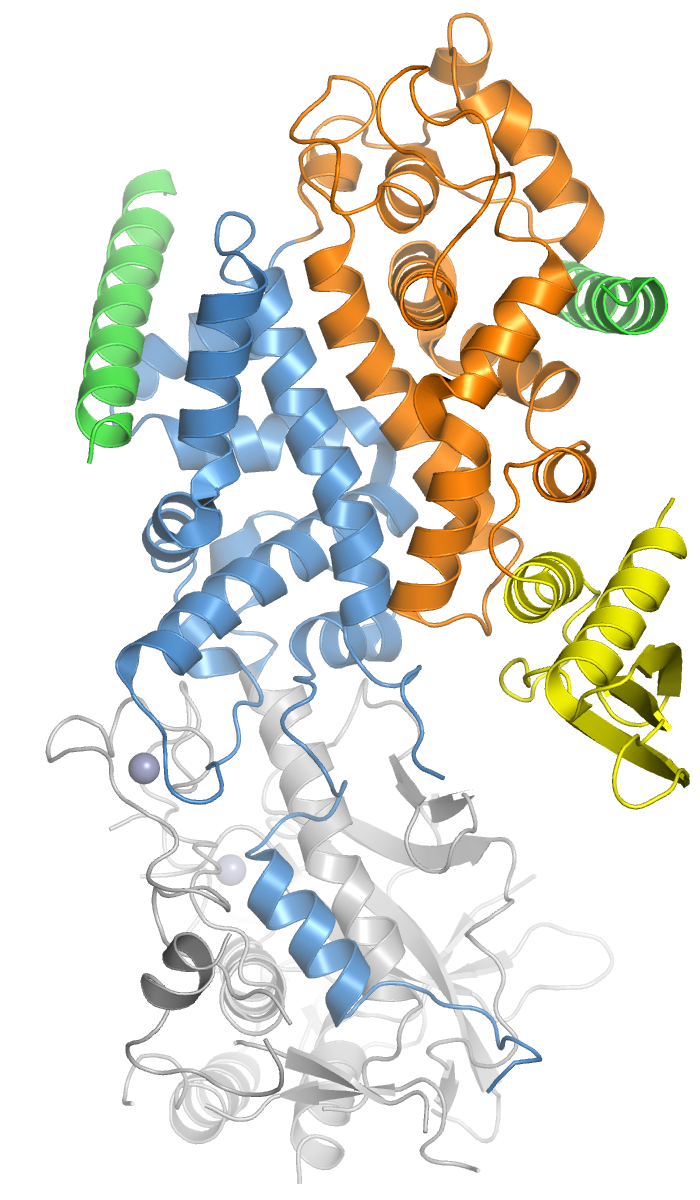
Drosha
Drosha is a Class 2 ribonuclease III enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DROSHA'' (formerly ''RNASEN'') gene. It is the primary nuclease that executes the initiation step of miRNA processing in the nucleus. It works closely with DGCR8 and in correlation with Dicer. It has been found significant in clinical knowledge for cancer prognosisSlack FJ, Weidhaas JB (December 2008). "MicroRNA in cancer prognosis". ''The New England Journal of Medicine.'' 359 (25): 2720-2. and HIV-1 replication.Swaminathan, G., Navas-Martín, S., & Martín-García, J. (2014). MicroRNAs and HIV-1 infection: antiviral activities and beyond. ''Journal of molecular biology'', ''426''(6), 1178-1197. History Human Drosha was cloned in 2000 when it was identified as a nuclear dsRNA ribonuclease involved in the processing of ribosomal RNA precursors. The other two human enzymes that participate in the processing and activity of miRNA are the Dicer and Argonaute proteins. Recently, proteins like Drosha ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoribonuclease
An endoribonuclease is a ribonuclease endonuclease. It cleaves either single-stranded or double-stranded RNA, depending on the enzyme. Example includes both single proteins such as RNase III, RNase A, RNase T1, RNase T2 and RNase H and also complexes of proteins with RNA such as RNase P and the RNA-induced silencing complex. Further examples include endoribonuclease XendoU found in frogs (''Xenopus ''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-kno ...''). External links * {{Nucleases EC 3.1 Ribonucleases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiRBase
In bioinformatics, miRBase is a biological database that acts as an archive of microRNA sequences and annotations. As of September 2010 it contained information about 15,172 microRNAs. This number has risen to 38,589 by March 2018. The miRBase registry provides a centralised system for assigning new names to microRNA genes. miRBase grew from the microRNA registry resource set up by Sam Griffiths-Jones in 2003. According to Ana Kozomara and Sam Griffiths-Jones miRBase has five aims: # To provide a consistent naming system for microRNAs # To provide a central place collecting all known microRNA sequences # To provide human and computer readable information for each microRNA # To provide primary evidence for each microRNA # To aggregate and link to microRNA target information MiRBase contains miRNAs belonging of various species belonging to Alveolata, Chromalveolata, Metazoa, Mycetozoa, Viridiplantae and Viruses. For the Viridiplantae, in release 21 (2014) data is available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicer
Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into short double-stranded RNA fragments called small interfering RNA and microRNA, respectively. These fragments are approximately 20–25 base pairs long with a two-base overhang on the 3′-end. Dicer facilitates the activation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is essential for RNA interference. RISC has a catalytic component Argonaute, which is an endonuclease capable of degrading messenger RNA (mRNA). Discovery Dicer was given its name in 2001 by Stony Brook PhD student Emily Bernstein while conducting research in Gregory Hannon's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Bernstein sought to discover the enzyme responsible for generating small RNA fragments from double-stranded RNA. Dicer's ability to generate around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase III
Ribonuclease III (RNase III or RNase C)(BREND3.1.26.3 is a type of ribonuclease that recognizes dsRNA and cleaves it at specific targeted locations to transform them into mature RNAs. These enzymes are a group of endoribonucleases that are characterized by their ribonuclease domain, which is labelled the RNase III domain. They are ubiquitous compounds in the cell and play a major role in pathways such as RNA precursor synthesis, RNA Silencing, and the ''pnp'' autoregulatory mechanism. Types of RNase III The RNase III superfamily is divided into four known classes: 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each class is defined by its domain structure.Liang Y-H, Lavoie M, Comeau M-A, Elela SA, Ji X. Structure of a Eukaryotic RNase III Post-Cleavage Complex Reveals a Double- Ruler Mechanism for Substrate Selection. Molecular cell. 2014;54(3):431-444. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.006. Class 1 RNase III *Class 1 RNase III enzymes have a homodimeric structure whose function is to cleave dsRNA into multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SnoRNA
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes. snoRNA guided modifications After transcription, nascent rRNA molecules (termed pre-rRNA) undergo a series of processing steps to generate the mature rRNA molecule. Prior to cleavage by exo- and endonucleases, the pre-rRNA undergoes a complex pattern of nucleoside modifications. These include methylations and pseudouridylations, guided by snoRNAs. *Methylation is the attachment or substitution of a methyl group onto various substrates. The rRNA of humans contain approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U12 Minor Spliceosomal RNA
U12 minor spliceosomal RNA is formed from U12 small nuclear (snRNA), together with U4atac/ U6atac, U5, and U11 snRNAs and associated proteins, forms a spliceosome that cleaves a divergent class of low-abundance pre-mRNA introns. Although the U12 sequence is very divergent from that of U2, the two are functionally analogous. Structure The predicted secondary structure of U12 RNA is published,. However, the alternative single hairpin in the 3' end shown here seems to better match the alignment of divergent ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' sequences. The sequences U12 introns that are spliced out are collected in a biological database called the U12 intron database U12 Intron Database (U12DB) is a biological database of containing the sequence of eukaryotic introns that are spliced out by a specialised minor spliceosome that contains U12 minor spliceosomal RNA U12 minor spliceosomal RNA is formed from U12 sm .... References External links * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U5 Spliceosomal RNA
U5 snRNA is a small nuclear RNA (snRNA) that participates in RNA splicing as a component of the spliceosome. It forms the U5 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein'') by associating with several proteins including Prp8 - the largest and most conserved protein in the spliceosome, Brr2 - a helicase Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separat ... required for spliceosome activation, Snu114, and the 7 Sm proteins. U5 snRNA forms a coaxially-stacked series of helices that project into the active site of the spliceosome. Loop 1, which caps this series of helices, forms 4-5 base pairs with the 5'-exon during the two chemical reactions of splicing. This interaction appears to be especially important during step two of splicing, exon ligation. References Further reading * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |