|
Small-headed Cod
The small-headed cod (''Lepidion microcephalus'') or the long-finned cod is a deepwater fish belonging to the morid cod family ( Moridae), and related to the true cods (genus ''Gadus''). It is found in the Tasman Sea, including the Bass Strait. It is commercially harvested by both Australia and New Zealand. It has been found on the continental shelf, but typically its depth range is from . It grows to in total length. The second common name is because its first dorsal fin is made up of long, filamentous rays. The pelvic fin Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hi ... is long, thin, and scythe-like, and it has a pronounced chin barbel. The colour is grey-brown with a faint red tint on the body and black-edged median fins. References * * * Tony Ayling & Geoffrey Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moridae
The Moridae are a family of cod-like fishes, known as codlings, hakelings, and moras. Morids are marine fishes found throughout the world, and may be found at depths to , although most prefer shallower waters. In appearance, they greatly resemble the typical cods, from which can only be distinguished by their skeletal features and the structure of the swim bladder. They grow up to long (red codling The red codling or hoka (''Pseudophycis bachus'') is a morid cod of the genus ''Pseudophycis'', restricted to New Zealand, from the surface to 700 m. A closely related species, ''Pseudophycis barbata'', is found in Australia. It reaches lengths u ..., ''Pseudophycis bachus''). The earliest fossil member of the group is '' Eophycis'' from the Early Oligocene of Europe. References * Euteleostei families {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 was the first known person to cross it. British explorer Lieutenant James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s during his three voyages of exploration. The Māori people of New Zealand call this sea ''Te Moana-a-Rehua'' meaning 'the sea of Rehua' which clashes with the Pacific waters named ''Te Tai-o-Whitirea'' ('the sea of Whitirea') – after Whitirea, Rehua's lover – at Cape Reinga, the northernmost tip of North Island. Climate The south of the sea is passed over by depressions going from west to east. The northern limit of these westerly winds is near to 40th parallel south, 40°S. During the southern winter, from April to October, the northern branch of these winds from the west changes its direction toward th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria (Australia), Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterway between the Great Australian Bight and the Tasman Sea, and is also the only maritime route into the economically prominent Port Phillip Bay. Formed 8,000 years ago by rising sea levels at the end of the last glacial period, the strait was named after English explorer and physician George Bass (1771–1803) by History of Australia (1788–1850), European colonists. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of Bass Strait as follows: :''On the west.'' The eastern limit of the Great Australian Bight [being a line from Cape Otway, Australia, to King Island (Tasmania), King Island and thence to Cape Grim, the northwest extreme of Tasmania]. :''On the east.'' The western li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an "''insular shelf''." The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
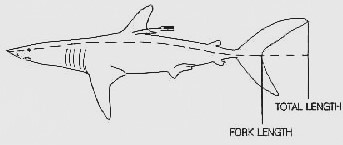
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods, which evolved from lobe-finned fish during the Middle Devonian. Structure and function Structure In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two endochondrally-derived bony girdles attached to bony radials. Dermal fin rays ( lepidotrichia) are positioned distally from the radials. There are three pairs of muscles each on the dorsal and ventral side of the pelvic fin girdle that abduct and adduct the fin from the body. Pelvic fin structures can be extremely specialized in actinopterygians. Gobiids and lumpsuckers modify their pelvic fins into a sucker disk that allow them to adhere to the substrate or climb structures, such as waterfalls. In priapiumfish, males have modified their pelvic structures into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbel (anatomy)
In fish anatomy and turtle anatomy, a barbel is a slender, whisker like sensory organ near the mouth (sometimes called whiskers or tendrils). Fish that have barbels include the catfish, the carp, the goatfish, the hagfish, the sturgeon, the zebrafish, the black dragonfish and some species of shark such as the sawshark. Barbels house the taste buds of such fish and are used to search for food in murky water. The word ''barbel'' comes from Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ... ''barbula'' 'little beard'. Barbels are sometimes erroneously referred to as '' barbs'', which are found in bird feathers for flight. Barbels may be located in a variety of locations on the head of a fish. "Maxillary barbels" refers to barbels on either side of the mouth. Barbels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of Victoria (state)
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |