|
Singar Mosque
The Singar Mosque ( bn, সিঙ্গাইর মসজিদ)Transliterations vary. Signage on site spells it Singair. Perween Hasan uses Shingria and ''Banglapedia'' uses Singria, whereas most other sources use Singair. is a 15th-century mosque which is part of the Mosque City of Bagerhat, a World Heritage Site in south-western Bangladesh. It is a single-domed, square building of exposed brick with terracotta decorations. Location The Singar Mosque is part of the Mosque City of Bagerhat in south-western Bangladesh. It is situated on the south side of the Bagerhat-Khulna Highway, about south-east of the Sixty Dome Mosque. History The mosque has no inscription by which it can be dated. Architect Abu Sayeed M Ahmed estimates that it is from the 15th century. Other experts believe, based on the known ages of stylistically similar local buildings, that it was built in the mid-15th century. There is archaeological evidence that at one time the mosque compound was surrounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions. According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad left no successor and the participants of the Saqifah event appointed Abu Bakr as the next-in-line (the first caliph). This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor. The adherents of Sunni Islam are referred to in Arabic as ("the people of the Sunnah and the community") or for short. In English, its doctrines and practices are sometimes called ''Sunnism'', while adherents are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, Sunnites and Ahlus Sunnah. Sunni Islam is sometimes referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Society Of Bangladesh
The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh is a non political and non profit research organisation registered under both Society Act of 1864 and NGO Bureau, Government of Bangladesh. The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh was established as the Asiatic Society of East Pakistan in Dhaka in 1952 by a number of Muslim leaders, and renamed in 1972. Ahmed Hasan Dani, a noted Muslim historian and archaeologist of Pakistan played an important role in founding this society. He was assisted by Muhammad Shahidullah, a Bengali linguist. The society is housed in Nimtali, walking distance from the Curzon Hall of Dhaka University, locality of Old Dhaka. Publications The society's publications include: * ''Banglapedia, the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh'' (edition 2, 2012) * ''Encyclopedia of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh'' (2010, 28 volumes) * ''Cultural Survey of Bangladesh, a documentation of the country's cultural history, tradition and heritage'' (2008, 12 volumes) * ''Children’s Banglapedia'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaeological Sites In Bangladesh
This is a list of archaeological sites in Bangladesh: Dhaka Division * Sat Gambuj Mosque * Khan Mohammad Mridha Mosque * Bara Katra * Lalbagh Fort * Chhota Katra * Shahbaz Khan Mosque * Musa Khan Mosque * Northbrook Hall * Ruplal House * Rose Garden Palace * Bhajahari Lodge * Panam Nagar * Sonakanda Fort * Hajiganj Fort * Baliati Zamindari * Idrakpur Fort * Baba Adam's Mosque * Wari-Bateshwar ruins * Pathrail Mosque Chittagong Division * Shalban Vihara * Bariura Old Bridge Sylhet Division * Ghayebi Dighi Masjid * Shankarpasha Shahi Masjid Barisal Division * Nasrat Gazi Mosque * Qasba Mosque * Mahilara Sarkar Math * Kamalapur Mosque * Miah Bari Mosque * Bibi Chini Mosque * Collectorate Bhaban, Barishal Rajshahi Division * Bagha Mosque * Kismat Maria Mosque * Bara Anhik Mandir * Puthia Rajbari * Chota Anhik Mandir * Pancha Ratna Shiva Temple * Dol-Mandir * Pancha Ratna Govinda Temple * Somapura Mahavihara * Halud Vihara * Kusumba Mosque * Jagaddala Mahavihara * Utt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mosques In Bangladesh
Mosques Dhaka Division Dhaka District Faridpur District Gazipur District Kishoreganj District Munshiganj District Narayanganj District Tangail District Barisal Division Barisal District Jhalokati District Chittagong Division Brahmanbaria District Chandpur District Chittagong District Comilla District Feni District Lakshmipur District Noakhali District Khulna Division Jessore District Jhenaidah District Satkhira District Bagerhat District Please add TEN DOME MOSQUE,ranabijopur, bagerhat as number one oldest mosque in Bangladesh. Mymensingh Division Rajshahi Division Naogaon District Nawabganj District Pabna District Rajshahi District Rangpur Division Dinajpur District Gaibandha District Kurigram District Rangpur District Sylhet Division Habiganj District Moulvibazar District Sunamganj District Sylhet District Eidgahs References External links * {{Architecture of Bangladesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
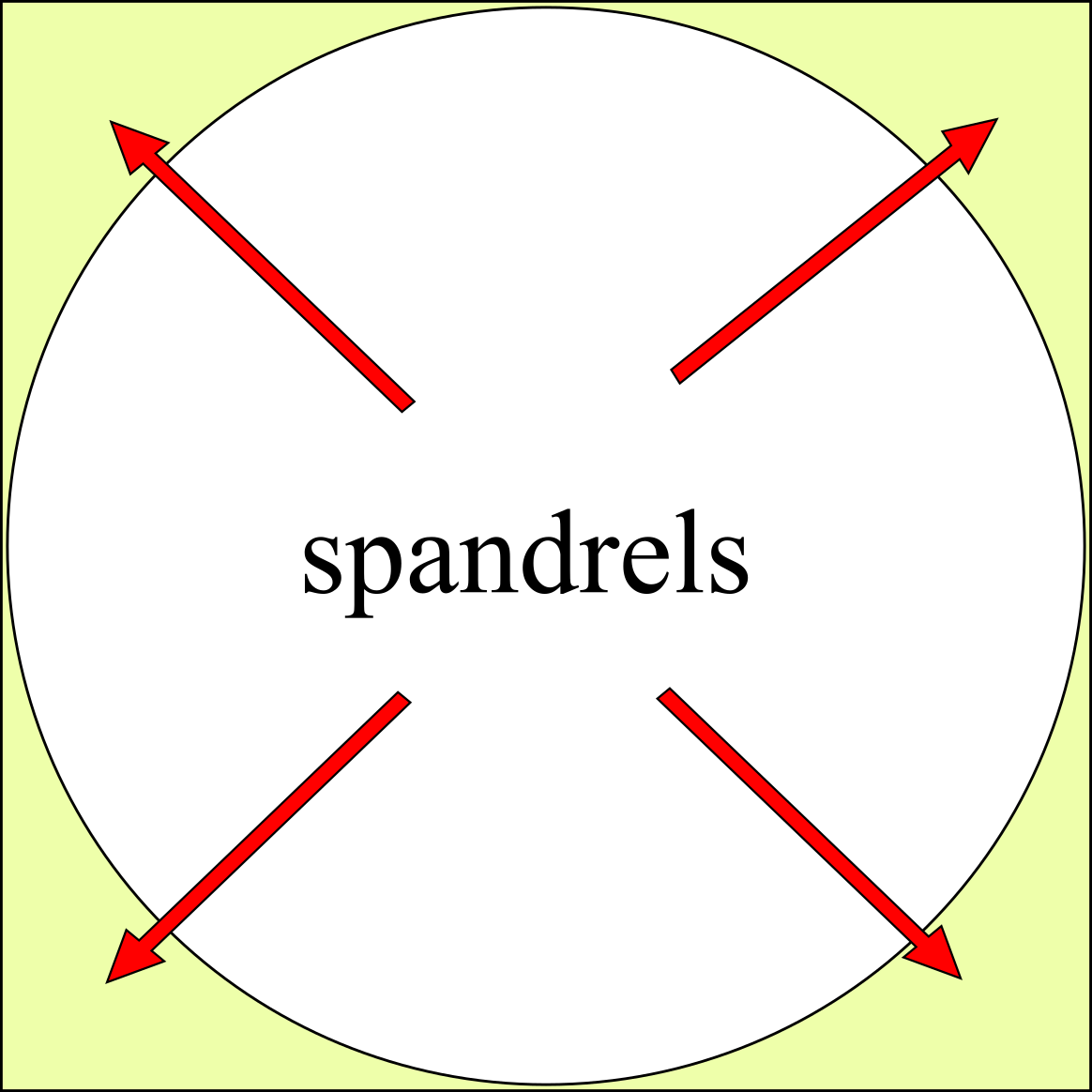
Spandrels
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multifoil Arch
A multifoil arch (or polyfoil arch), also known as a cusped arch, polylobed arch, or scalloped arch, is an arch characterized by multiple circular arcs or leaf shapes (called foils, lobes, or cusps) that are cut into its interior profile or intrados. The term ''foil'' comes from the old French word for "leaf." A specific number of foils is indicated by a prefix: trefoil (three), quatrefoil (four), cinquefoil (five), sexfoil (six), octofoil (eight). The term multifoil or scalloped is specifically used for arches with more than five foils. The multifoil arch is characteristic of Islamic art and architecture; particularly in the Moorish architecture of al-Andalus (Iberian Peninsula) and North Africa and in Mughal architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Variants of the multifoil arch, such as the trefoil arch, are also common in other architectural traditions such as Gothic architecture. Origins The first multifoil arches were developed by the Umayyads and can be found in a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the salah. In Islam, the Kaaba is believed to be a sacred site built by prophets Abraham and Ishmael, and that its use as the qibla was ordained by Allah in several verses of the Quran revealed to Muhammad in the second Hijri year. Prior to this revelation, Muhammad and his followers in Medina faced Jerusalem for prayers. Most mosques contain a '' mihrab'' (a wall niche) that indicates the direction of the qibla. The qibla is also the direction for entering the ''ihram'' (sacred state for the hajj pilgrimage); the direction to which animals are turned during ''dhabihah'' (Islamic slaughter); the recommended direction to make ''dua'' (supplications); the direction to avoid when relieving oneself or spitting; and the direction to which the deceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla wall". The ''minbar'', which is the raised platform from which an imam (leader of prayer) addresses the congregation, is located to the right of the mihrab. Etymology The origin of the word ''miḥrāb'' is complicated and multiple explanations have been proposed by different sources and scholars. It may come from Old South Arabian (possibly Sabaic) ''mḥrb'' meaning a certain part of a palace, as well as "part of a temple where ''tḥrb'' (a certain type of visions) is obtained," from the root word ''ḥrb'' "to perform a certain religious ritual (which is compared to combat or fighting and described as an overnight retreat) in the ''mḥrb'' of the temple." It may also possibly be related to Ethiopic ''məkʷrab'' "temple, sanctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Archaeology (Bangladesh)
Department of Archaeology ( bn, বাংলাদেশ প্রত্নতত্ত্ব অধিদপ্তর, ) is one of the government agency of Bangladesh. By the ''Laws of Archaeology 1964'' (amended in 1976) this agency maintains the conservation and preservation of archaeological sites in the country. Since 2013, the department has been running its activities from the Administration Building situated in Agargaon in Dhaka. History The organization was first founded in 1861 as a part of the Archaeological Survey of India. After the independence of Bangladesh its office was established in Dhaka.Department of Archaeology, Bangladesh', Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. Retrieved 29 June 2013. In 1983 regional offices were established in the then 4 divisions including Dhaka as the headquarter by divisional rearrangement. Agency Functions Department of Archaeology (Bangladesh) compiles and also conserves the list of archaeological sites and artifac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Sayeed M Ahmed
Abu Sayeed Mostaque Ahmed is an architect and architectural conservation specialist from Bangladesh. Career Ahmed passed the SSC exam from Comilla District School in 1974 and HSC exam from Comilla Victoria College in 1976. Later, he was admitted to the architecture department of Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET). He obtained a Bachelor of Architecture degree from there. After four years of service at the ECBL consultancy firm, he moved to Germany to do a master's degree. There he passed his M.Arch from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and PhD from the same university. Ahmed served as the president of Institute of Architects Bangladesh (IAB) for its 21st Executive Council (2015-2016). and President of Architects Regional Council of Asia (ARCASIA) for 2021-22 Ahmed is the dean of the School of Environmental Science and Design and Head of the Department of Architecture in University of Asia Pacific University of Asia Pacific ( bn, ইউনিভার্ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)
