|
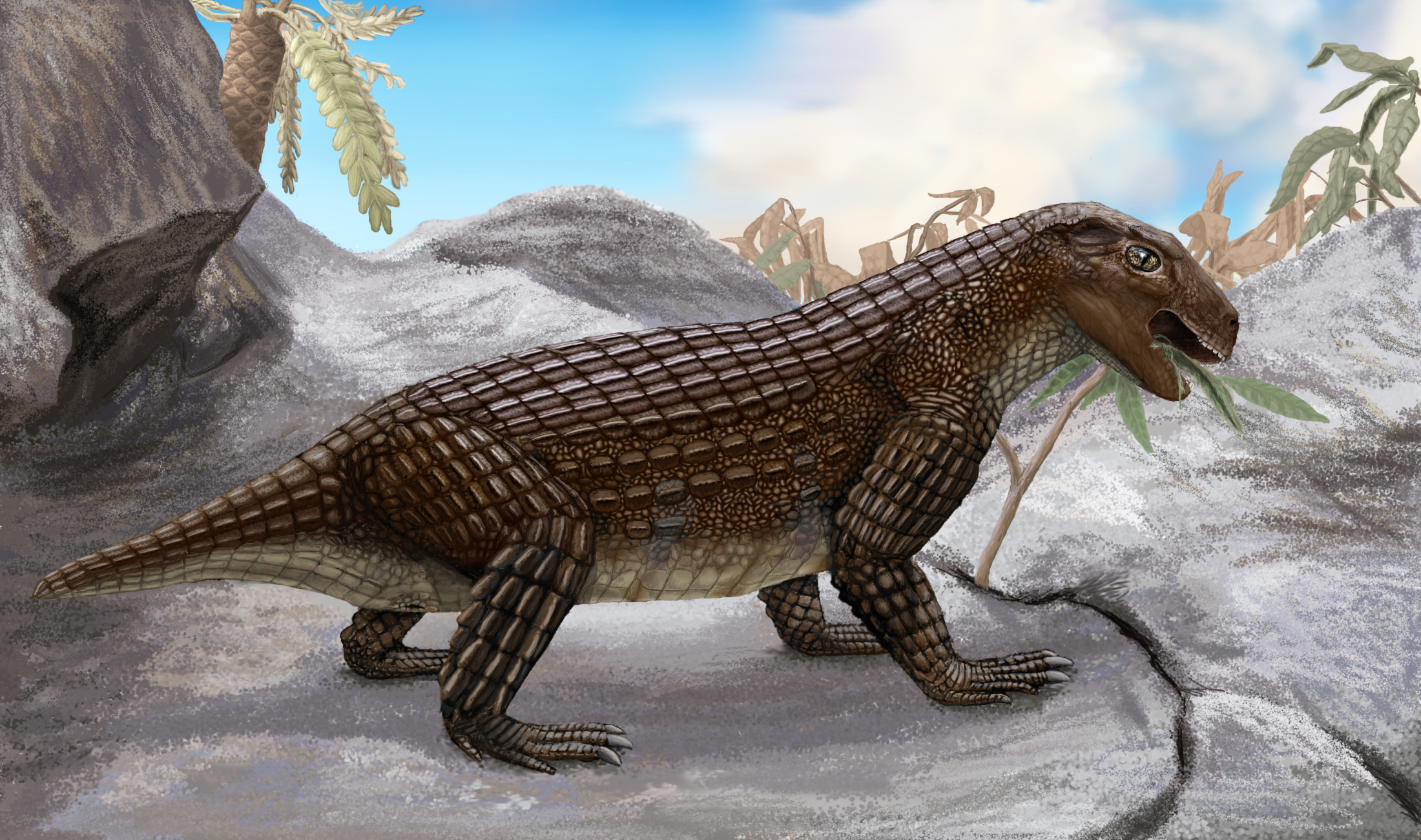
Simosuchus Clarki
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about in length. The type species is ''Simosuchus clarki'', found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of ''S. clarki'' were shaped like maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs. In fact, these features have led many palaeontologists to consider it a herbivore. Description ''Simosuchus'' was small, about long based on the skeletons of mature individuals. In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, ''Simosuchus'' has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means "pug-nosed crocodile" in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simosuchus
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about in length. The type species is ''Simosuchus clarki'', found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of ''S. clarki'' were shaped like maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs. In fact, these features have led many palaeontologists to consider it a herbivore. Description ''Simosuchus'' was small, about long based on the skeletons of mature individuals. In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, ''Simosuchus'' has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means "pug-nosed crocodile" in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simosuchus Scale
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek (language), Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about in length. The type species is ''Simosuchus clarki'', found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of ''S. clarki'' were shaped like Maple leaf, maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs. In fact, these features have led many palaeontologists to consider it a herbivore. Description ''Simosuchus'' was small, about long based on the skeletons of mature individuals. In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, ''Simosuchus'' has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 ''Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herba' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel. as a function of axial position ../nowiki>" Spherical coordinates In a spherical coordinate system, the radius describes the distance of a point from a fixed origin. Its position if further defined by the polar angle measured between the radial direction and a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuth angle, the angle between the orthogonal projection of the radial direction on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, and a fixed reference direction in that plane. See also *Bend radius *Filling radius in Riemannian geometry *Radius of convergence * Radius of convexity *Radius of curvature *Radius of gyration ''Radius of gyration'' or gyradius of a body about the axis of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condyle (anatomy)
A condyle (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. la, , from el, kondylos; κόνδυλος knuckle) is the round prominence at the end of a , most often part of a joint – an articulation with another bone. It is one of the markings or features of bones, and can refer to: * On the , in the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
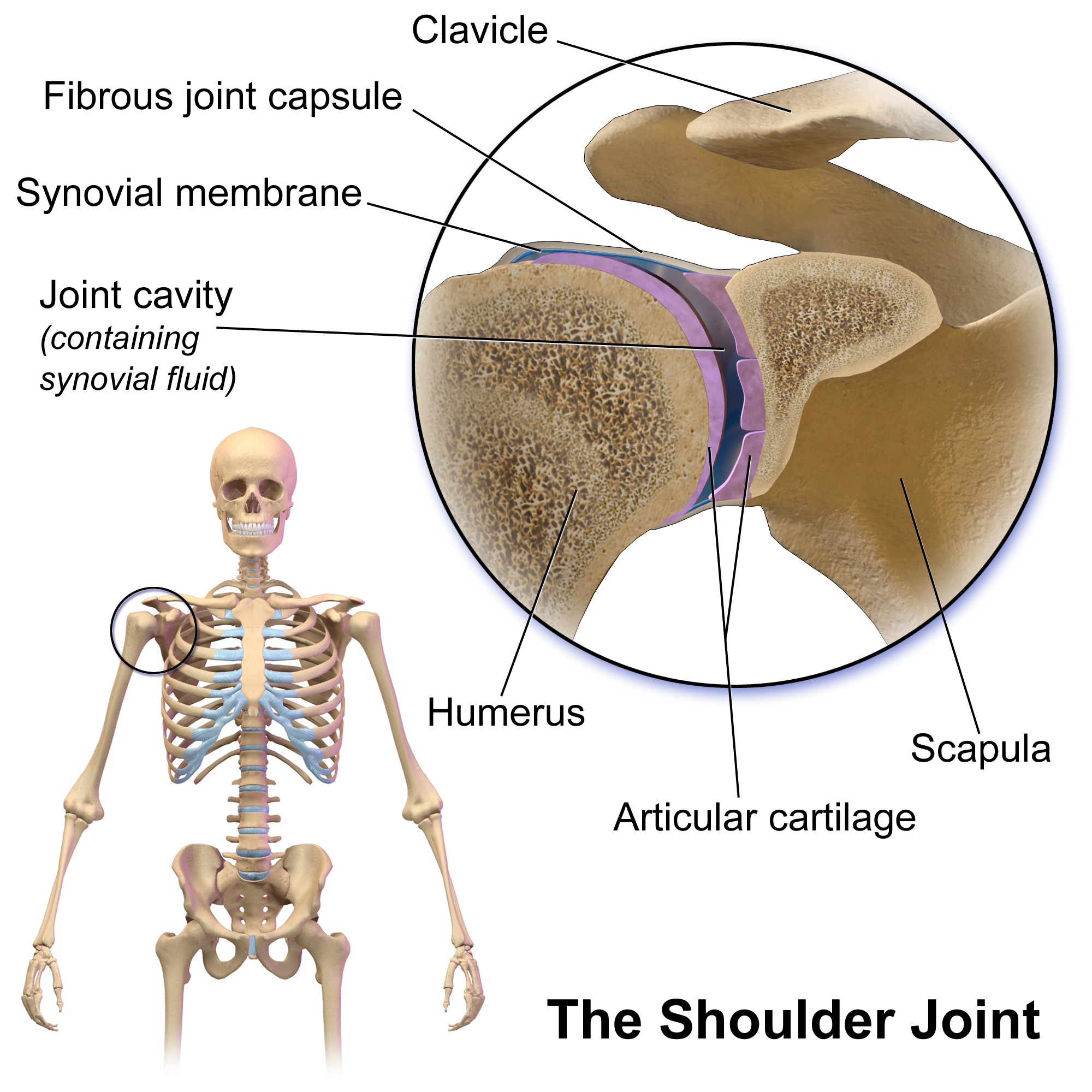
Glenohumeral Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to the focal taxon (which may be a species, family or in general any clade). It can therefore be considered an apomorphy in relation to a single taxon. The word ''autapomorphy'', first introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig, is derived from the Greek words αὐτός, ''autos'' "self"; ἀπό, ''apo'' "away from"; and μορφή, ''morphḗ'' = "shape". Discussion Because autapomorphies are only present in a single taxon, they do not convey information about relationship. Therefore, autapomorphies are not useful to infer phylogenetic relationships. However, autapomorphy, like synapomorphy and plesiomorphy is a relative concept depending on the taxon in question. An autapomorphy at a given level may well be a synapomorphy at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)