|
Simmonds' Test
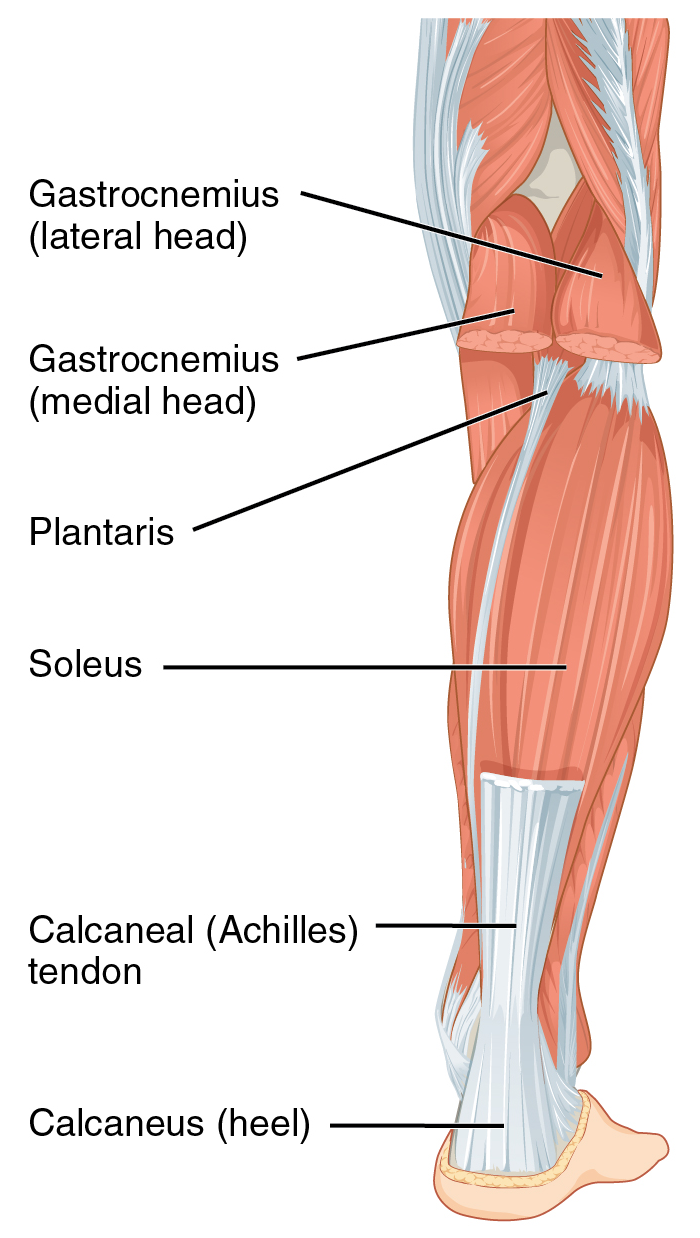
The Thompson test (also called Simmonds' test or Simmonds-Thompson test) is used in lower limb examination to test for the Achilles tendon rupture, rupture of the Achilles tendon. The patient lies face down with feet hanging off the edge of the bed. If the test is positive, there is no movement of the foot (normally plantarflexion) on squeezing the corresponding calf, signifying likely rupture of the Achilles tendon. Interpretation of results Recent research has indicated that while the test is an accurate detector of achilles rupture, it is unable to distinguish between partial tear (tear of the gastrocnemius or soleal portion only) and a complete tear of both portions. History The test is named after Franklin Adin Simmonds (1910-1983), an English Orthopedic surgeon, orthopaedic surgeon at the Rowley Bristow Hospital, Surrey. References {{Orthopedic examination, state=autocollapse Medical signs Musculoskeletal examination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles Tendon Rupture
Achilles tendon rupture is when the Achilles tendon, at the back of the ankle, breaks. Symptoms include the sudden onset of sharp pain in the heel. A snapping sound may be heard as the tendon breaks and walking becomes difficult. Rupture typically occurs as a result of a sudden bending up of the foot when the calf muscle is engaged, direct trauma, or long-standing tendonitis. Other risk factors include the use of fluoroquinolones, a significant change in exercise, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or corticosteroid use. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and examination and supported by medical imaging. Prevention may include stretching before activity and gradual progression of exercise intensity. Treatment may consist of surgical repair or conservative management. Quick return to weight bearing (within 4 weeks) appears okay and is often recommended. While surgery traditionally results in a small decrease in the risk of re-rupture, the risk of other complications is greater. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantarflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simmonds Test
Simmonds as a surname may refer to: * Ann Simmonds, English pentathlete * Ellie Simmonds (born 1994), British Paralympic swimmer * Henry Simmonds, Canada sailor at the 1932 Olympics * Kaleb Simmonds, Canadian singer, ''Canadian Idol'' contestant * Kennedy Simmonds, Saint Kitts and Nevis politician * Kim Simmonds, Welsh guitarist * Lizzie Simmonds, born Elizabeth Simmonds, English swimmer * Megan Simmonds, Jamaican athlete * Mark Simmonds, British politician * Matthew Simmonds, British demoscene musician * Millicent Simmonds, American deaf actor * Morris Simmonds (1855-1925), Virgin Islands-born German physician * Posy Simmonds, British cartoonist * Reece Simmonds, Australian rugby league player * Robert Simmonds, Canadian police commissioner * Samantha Simmonds, British television presenter * Stuart Simmonds, English Cricketer and author * Troy Simmonds, Australian rules footballer * Wayne Simmonds, Canadian ice hockey player * William Simmonds (other), various people, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Adin Simmonds
Franklin Adin Simmonds F.R.C.S. (31 October 1910 - 14 July 1983; also known as Sam Simmonds) was a British orthopaedic surgeon for whom the Simmonds' test on rupture of the Achilles tendon is named. He also worked with the pioneering surgeon John Charnley on hip replacement surgery and became an expert in this field. He very much disliked his given names and in adult life was universally known as Sam. Career After education at Sherborne School in Dorset he studied at Pembroke College, Cambridge, and St Thomas's Hospital London. From 1939 to 1941 he worked with W. Rowley Bristow at St Nicholas's Hospital Pyrford (subsequently renamed Rowley Bristow Hospital Pyrford), and when Rowley Bristow became Brigadier in charge of orthopaedic services of the British Army, he recruited Simmonds into the Royal Army Medical Corps. Lt Col Simmonds commanded base hospitals in North Africa, Sicily, France and the Far East. After the war he returned to Pyrford and worked there and at The Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Surgeon
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rowley Bristow Hospital
Pyrford is a village in the borough of Woking in Surrey, England. It is on the left bank of the River Wey, around east of the town of Woking and just south of West Byfleet; the M25 motorway is northeast of the edge of the former parish. The village sits on raised mixed heath soil, and has historical links with the abbey at Westminster, in whose possession it remained between the Norman conquest in 1066 and the Dissolution of the Monasteries nearly five hundred years later. Geography At the foot of slopes in the south of the area are agricultural flood plain pasture meadows bisected by the River Wey Navigation; the actual border is the River Wey itself (though slightly inaccurate as based on meanders as they were before 1820). Roads passing through the village include the B367 (Upshott Lane/Church Hill) and B382 (Old Woking Road). Open areas in the south and east of the village are designated Metropolitan Green Belt. History and use in the arts The current village name 'Py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Signs
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |