|
Siege Of Antwerp (1584–1585)
The Fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces. Under the terms agreed, all Protestants were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam, which became the capital of the Dutch Republic. Apart from losing a high proportion of its mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt up to 1795. Background At the time Antwerp, in modern Belgium, was not only the largest Dutch city, but was also the cultural, economic, and financial centre of the Seventeen Provinces and of north-western Europe. On 4 November 1576, unpaid Spanish soldiery mutinied: they plundered and burnt the city during what was called the Spanish Fury. Thousands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed his armies and regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the general rebellion failed to sustain itself. Despite Governor of Spanish Netherlands and General for Spain, the Duke of Parma's steady military and diplomatic successes, the Union of Utr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Austria
John of Austria ( es, Juan, link=no, german: Johann; 24 February 1547 – 1 October 1578) was the natural son born to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V late in life when he was a widower. Charles V met his son only once, recognizing him in a secret codicil to his will. John became a military leader in the service of his half-brother, King Philip II of Spain, Charles V's legitimate heir, and is best known for his role as the admiral of the Holy Alliance fleet at the Battle of Lepanto. Life Early years Born in the Free imperial city of Regensburg, Upper Palatinate, John of Austria was the product of a brief liaison between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (a widower since 1539) and Barbara Blomberg, a burgher's daughter and singer. In the summer of 1554, the boy was taken to the castle of Luis de Quijada in Villagarcía de Campos, Valladolid. Magdalena de Ulloa, the wife of Luis de Quijada, took charge of his education, assisted by the Latin teacher Guillén Prieto, the chaplain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspar De Robles
Caspar de Robles or Gaspard di Robles (1527, Madrid, Spain – 1585, Antwerp), also known as ''Billy'' in Artois, was Stadholder of Friesland and Groningen at the beginning of the Eighty Years' War (reign: 1568 to 1576). Family Robles was the son of Dońa María de Leyte, probably the wet nurse for Philip II of Spain, and João Lopes of Robles.Profile ; accessed 26 December 2014. In 1558 he married Jeanne de Saint-Quentin, baroness of Billy, their son was Jean de Roblès, 1st Count of Annappes. They are considered to be the founders of the Flemish branch of the house and became owner of the castle and lands in |
List Of The Largest Artificial Non-nuclear Explosions
There have been many extremely large explosions, accidental and intentional, caused by modern high explosives, boiling liquid expanding vapour explosions (BLEVEs), older explosives such as gunpowder, volatile petroleum-based fuels such as gasoline, and other chemical reactions. This list contains the largest known examples, sorted by date. An unambiguous ranking in order of severity is not possible; a 1994 study by historian Jay White of 130 large explosions suggested that they need to be ranked by an overall effect of power, quantity, radius, loss of life and property destruction, but concluded that such rankings are difficult to assess. The weight of an explosive does not directly correlate with the energy or destructive impact of an explosion, as these can depend upon many other factors such as containment, proximity, purity, preheating, and external oxygenation (in the case of thermobaric weapons, gas leaks and BLEVEs). In this article, explosion means "the sudden conversio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Match
Slow match, also called match cord, is the slow-burning cord or twine fuse used by early gunpowder musketeers, artillerymen, and soldiers to ignite matchlock muskets, cannons, shells, and petards. Slow matches were most suitable for use around black-powder weapons because a slow match could be roughly handled without going out, and only presented a small glowing tip instead of a large flame that risked igniting nearby gunpowder. Slow match of various types was one of the first kinds of artillery fuse. Slow matches were also used in the drilling and blasting of rock to ignite charges of gunpowder. Design and use The slow match attached to the lock of the matchlock gun was usually a length of hemp or flax cord that had been chemically treated to make it burn slowly and consistently for an extended period. In Japan, however, match cord was made from braiding together strands of bark from the Japanese cypress. The rate of burning was approximately 1 ft (305mm) per hour. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federigo Giambelli
Federigo Giambelli (or Gianibelli; also given as Genebelli or Genibelli in contemporary English texts), was an Italian military and civil engineer who worked in Spain, the Spanish Netherlands and England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. Early life and Spanish service Giambelli was born at Mantua about the middle of the 16th century. Having had some experience as a military engineer in Italy, he went to Spain to offer his services to Philip II. However, his proposals were given a lukewarm reception, and as he could obtain no immediate employment from the king, he moved to Antwerp, where he soon gained considerable reputation for his knowledge in various departments of science. He is said to have married while living there. The Siege of Antwerp Giambelli is said to have vowed to be revenged for his rebuff at the Spanish court; and when Antwerp was besieged by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma in 1584, he offered his services to Elizabeth I of England, who, having satisfied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
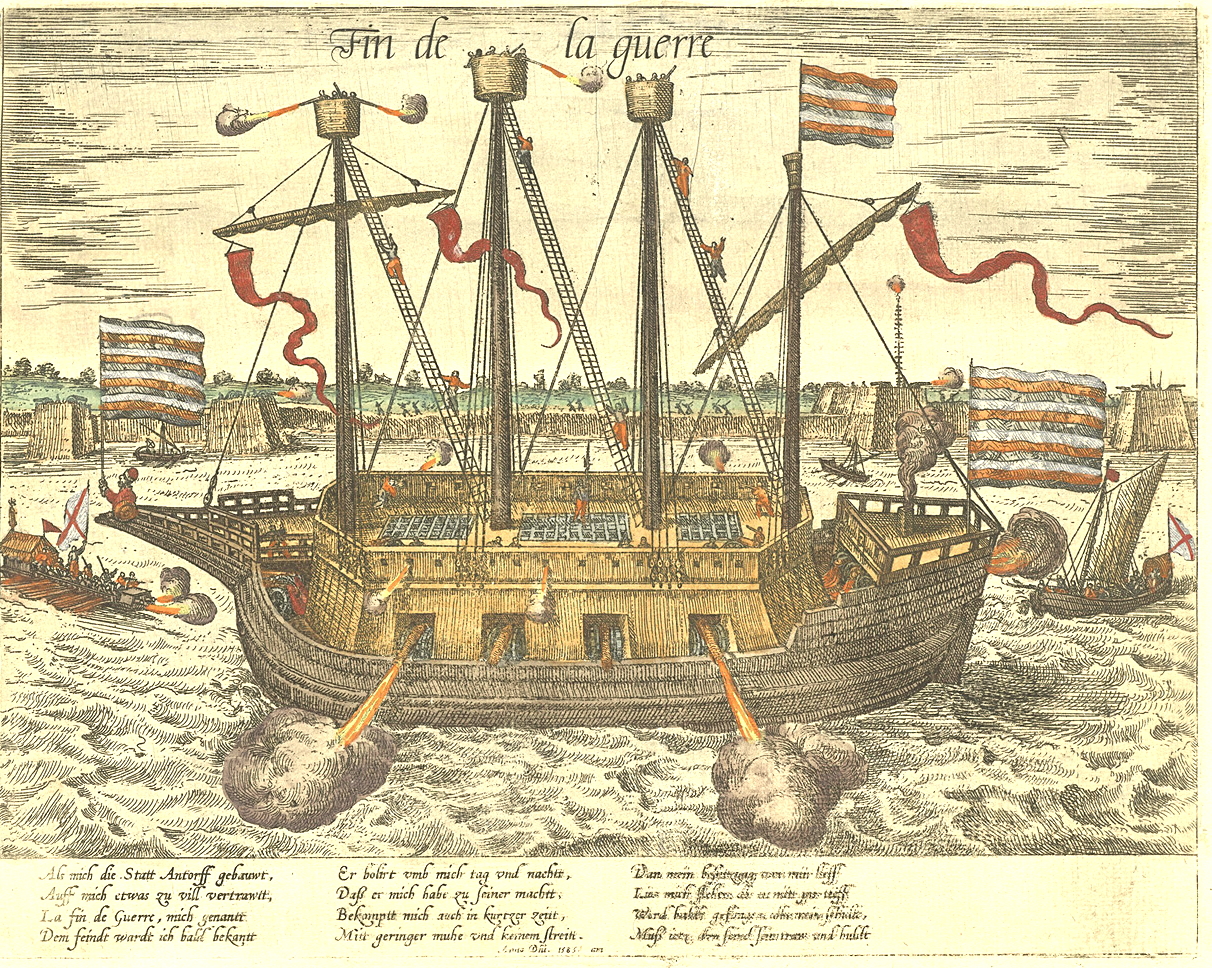
Hellburners
Hellburners ( Dutch: ''hellebranders'') were specialised fireships used in the Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) during the Eighty Years' War between the Dutch rebels and the Habsburgs. They were floating bombs, also called "Antwerp fire", and did immense damage to the Spanish besiegers. Hellburners have been described as an early form of weapons of mass destruction. First use against Antwerp ship bridge The hellburners were constructed by the Italian engineer Federigo Giambelli, who had been hired and subsidised by Elizabeth I of England, unofficially supporting the rebels, to assist the city. In the winter of 1585, Antwerp was besieged by the army of Alexander Farnese, the commander of the Habsburg forces in the Spanish Netherlands, who had constructed a ship bridge over the River Scheldt near Kalloo between Antwerp and the sea, to starve the population by blockade; it had been completed on 25 February. To supply the city it was imperative to destroy the ship bridge. Giamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Lillo
Fort Lillo is a former military fort built as part of the Antwerp Defence Line on the right bank of the Schelde, and completely surrounded by the industrial port of Antwerp. History Built between 1579–82 on the orders of William the Silent to defend Antwerp, in 1809 during the Napoleonic Wars the fort was attacked by the British while under occupation by the forces of Napoleon. Along with Fort Liefkenshoek on the opposite bank of the Scheldt these heavily armed defences proved a formidable obstacle to attacking forces. Of the three towns that formerly comprised the village of Lillo, Fort Lillo is the only one to survive, the other two - Oud Lillo (lit. "Old Lillo") and Lillo-Kruisweg (lit. "Lillo Crossroads") were evacuated in 1958 then demolished and razed to allow the expansion of the port of Antwerp. Fort Lillo shared the fate of three other polder A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old English ' ("shallow"), Modern English ''shoal'', Low German ''schol'', West Frisian ''skol'', and Swedish (obsolete) ''skäll'' ("thin"). Course The headwaters of the Scheldt are in Gouy, in the Aisne department of northern France. It flows north through Cambrai and Valenciennes, and enters Belgium near Tournai. Ghent developed at the confluence of the Lys, one of its main tributaries, and the Scheldt, which then turns east. Near Antwerp, the largest city on its banks, the Scheldt flows west into the Netherlands toward the North Sea. Originally there were two branches from that point: the Oosterschelde (Eastern Scheldt); and the Westerschelde (Western Scheldt). In the 19th century, however, the Dutch built a dyke that cuts the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Road
The Spanish Road (Spanish: ''Camino Español'', German: ''Spanische Straße'') was a military road and trade route in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, linking the Duchy of Milan, the Franche-Comté and the Spanish Netherlands, all of which were at the time territories of the Spanish Empire under the Habsburgs. It was also known as the Road of the Spaniards (''Camino de los Españoles''), Road of the Spanish Tercios (''Camino de los Tercios Españoles''), or Sardinian Corridor (''Corredor Sardo'') in Spanish. The Spanish Road was created under Philip II as a vital artery for the Spanish war effort during the Eighty Years' War against the Dutch Republic. For Spain, it would have been much quicker to ship troops and supplies directly from Spain to the Low Countries – a sailing ship of the time could usually cover about a day, whereas the average pace of soldiers marching on the Spanish Road was only a day. However, Spanish vessels sailing up the English Channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_1.jpg)



