|
Siege Of Grave (1674)
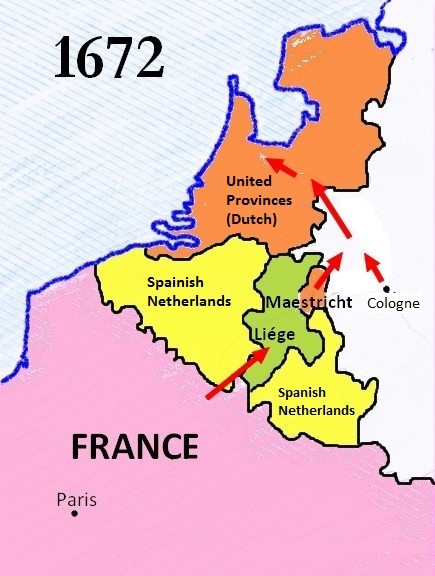
The Siege of Grave took place from 25 July to 27 October in 1674 during the Franco-Dutch War of 1672 to 1678, when a Dutch army captured the Dutch fortress town of Grave, Netherlands, Grave (De Graaf) in what is now North Brabant. Grave had been occupied by the French since the summer of 1672 when an army under Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, Viscount of Turenne, Turenne forced the town to surrender. Prelude In May 1672, following the outbreak of the Franco-Dutch War and its peripheral conflict the Third Anglo-Dutch War, Kingdom of France, France, supported by Bishopric of Münster, Münster and Electorate of Cologne, Cologne, invaded and nearly overran the Dutch Republic. At the same time, it faced the threat of an Kingdom of England, Anglo-French naval blockade, though that attempt was abandoned following the Battle of Solebay. Grave, a strong fortress town, strategically placed along the Meuse river was captured by the French on 5 July 1672 without much difficulty. French advances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the ''Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, retaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norman (1066–1154), Plantagenet (1154–1485), Tudor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raam (river)
The Raam is a small river in the eastern part of North Brabant, Netherlands. It flows into the Meuse ( nl, Maas) at the old town Grave A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as grave .... Rivers of North Brabant Rivers of the Netherlands Tributaries of the Meuse {{Netherlands-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment (military)
Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort (or town) with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced. A contravallation is a line of fortifications, built by the attackers around the besieged fortification facing towards an enemy fort to protect the besiegers from sorties by its defenders and to enhance the blockade. The contravallation can be used as a base to launch assaults against the besieged city or to construct further earthworks nearer to the city. A circumvallation may be constructed if the besieging army is threatened by a field army allied to an enemy fort. It is a second line of fortifications outside the contravallation that faces away from an enemy fort. The circumvallation protects the besiegers from attacks by allies of the city's defenders and enhances the blockade of an enemy fort by making it more difficult to smuggle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehog Defence
The hedgehog defence is a military tactic in which a defending army creates mutually supporting strongpoints in a defence in depth, designed to sap the strength and break the momentum of an attacking army. The strongpoints are designed to be expensive for an attacker to assault. Although the defending positions are intended to be bypassed, doing so exposes the attacker's rear echelons and line of communications to counterattack. Description In warfare, it is a military tactic to defend against a mobile armoured attack, or blitzkrieg. The defenders deploy in depth in heavily fortified positions suitable for all-around defence. The attackers can penetrate between the "hedgehogs", but each position continues to fight on when it is surrounded. That keeps large numbers of attacking troops tied up, attacking the well-defended strongpoints, and it allows the defenders to counterattack against the units that bypass the strongpoints with their own armored reserves, by cutting them off f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beleg Van Grave Door Willem III, 1674 Belegeringh Der Stadt Graef (titel Op Object) 't Veroveren Der Stercke Stadt Graef, Door Sijn Hoogheyt Den Heer Prins Van Orangien, Op Den 25 October 1674, RP-P-OB-82
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavriel Kay. It tells of Eä, a fictional universe that includes the Blessed Realm of Valinor, the once-great region of Beleriand, the sunken island of Númenor, and the continent of Middle-earth, where Tolkien's most popular works—'' The Hobbit'' and '' The Lord of the Rings''—are set. After the success of ''The Hobbit'', Tolkien's publisher Stanley Unwin requested a sequel, and Tolkien offered a draft of the writings that would later become ''The Silmarillion''. Unwin rejected this proposal, calling the draft obscure and "too Celtic", so Tolkien began working on a new story that eventually became ''The Lord of the Rings''. ''The Silmarillion'' has five parts. The first, '' Ainulindalë'', tells in mythic style of the creation of Eä, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse ( nl, Maas), at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (''Sint-Pietersberg'') is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is about 175 km south east of the capital Amsterdam and 65 km from Eindhoven; it is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège and Hasselt. Maastricht developed from a Roman settlement (''Trajectum ad Mosam'') to a medieval religious centre. In the 16th century it became a garrison town and in the 19th century an early industrial centre. Today, the city is a thriving cultural and regional hub. It beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon , father = Louis XIII , mother = Anne of Austria , birth_date = , birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France , death_date = , death_place = Palace of Versailles, Versailles, France , burial_date = 9 September 1715 , burial_place = Basilica of Saint-Denis , religion = Catholicism (Gallican Rite) , signature = Louis XIV Signature.svg Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign in history whose date is verifiable. Although Louis XIV's France was emblematic of the age of absolutism in Europe, the King surrounded himself with a variety of significant political, military, and cultural figures, such as Bossuet, Colbert, Le Brun, Le Nôtre, Lully, Mazarin, Molière, Racine, Turenne, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Bonn (1673)
The siege of Bonn took place from 3 to 12 November 1673 in Bonn, Germany, during the Franco-Dutch War. Having forced the armies of Louis XIV to retreat, the Dutch in 1673 went on the offensive. At Bonn, a garrison consisting of troops from France and the Electorate of Cologne was besieged by a force from the Dutch Republic (commanded by stadtholder William III), the Holy Roman Empire (commanded by Raimondo Montecuccoli), and Spain. The allied forces captured the garrison following a nine-day siege. In 1689 Bonn was again the site of a major siege. Notes References * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Siege of Bonn (1673) Bonn The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr r ... 1673 in Europe Bonn 1673 Bonn 1673 Bonn 1673 Bonn 1673 History of Bonn 1673 in the Holy Roman Empire Bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Naarden (1673)
The siege of Naarden took place from 6 to 13 September 1673 during the Franco-Dutch War of 1672 to 1678, when a Dutch army captured the Dutch fortress town of Naarden. Naarden had been occupied by the French since the previous year. Prelude In May 1672, following the outbreak of the Franco-Dutch War and its peripheral conflict the Third Anglo-Dutch War, Kingdom of France, France, supported by Bishopric of Münster, Münster and Electorate of Cologne, Cologne, invaded and nearly overran the Dutch Republic. At the same time, it faced the threat of an Kingdom of England, Anglo-French naval blockade, though that attempt was abandoned following the Battle of Solebay. Naarden, which is positioned close to Amsterdam, was captured by the French on 20 June 1672 and further French advances into the province of County of Holland, Holland were only halted due too the Dutch Water Line. A stalemate followed. By August 1673 the French had diverted manpower and recources away from the Dutch Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy. It was founded in 959 following the division of Lotharingia into two separate duchies: Upper and Lower Lorraine, the westernmost parts of the Holy Roman Empire. The Lower duchy was quickly dismantled, while Upper Lorraine came to be known as simply the Duchy of Lorraine. The Duchy of Lorraine was coveted and briefly occupied by the dukes of Burgundy and the kings of France. In 1737, the duchy was given to Stanisław Leszczyński, the former king of Poland, who had lost his throne as a result of the War of the Polish Succession, with the understanding that it would fall to the French crown on his death. When Stanisław died on 23 February 1766, Lorraine was annexed by France and reorganized as a province. History Lotharingia Lorraine's predecessor, Lotharingia, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |