|
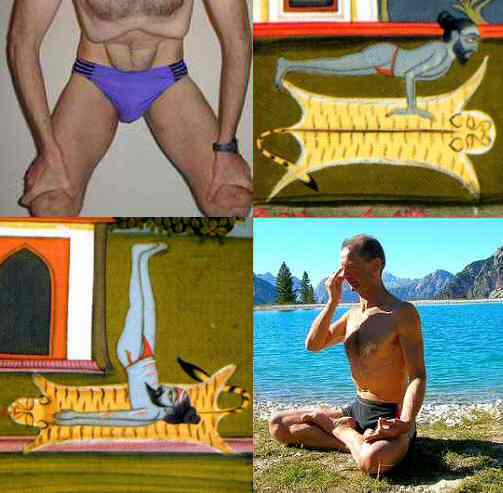
Siddhasana
Siddhasana (; ) or Accomplished Pose is an ancient seated asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise suitable for meditation. The names Muktasana (, Liberated Pose) and Burmese position are sometimes given to the same pose, sometimes to an easier variant, Ardha Siddhasana. Svastikasana has each foot tucked as snugly as possible into the fold of the opposite knee. Siddhasana is one of the oldest asanas. It is described as a meditation seat in the early Hatha Yoga text, the 10th century '' Goraksha Sataka''. This states that Siddhasana ranks alongside Padmasana (lotus position) as the most important of the asanas, opening the way to liberation. The 15th-century ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' similarly suggests that all other asanas are unnecessary once Siddhasana has been mastered. Etymology The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''siddha'' () meaning both "perfect" and "adept", and () meaning "posture" or "seat". The name Muktasana comes from meaning "liberation". Ann Swa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asana
An āsana (Sanskrit: आसन) is a body posture, originally and still a general term for a sitting meditation pose,Verse 46, chapter II, "Patanjali Yoga sutras" by Swami Prabhavananda, published by the Sri Ramakrishna Math p. 111 and later extended in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise, to any type of position, adding reclining, standing, inverted, twisting, and balancing poses. The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' define "asana" as " position thatis steady and comfortable". Patanjali mentions the ability to sit for extended periods as one of the eight limbs of his system. Patanjali '' Yoga sutras'', Book II:29, 46 Asanas are also called yoga poses or yoga postures in English. The 10th or 11th century '' Goraksha Sataka'' and the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' identify 84 asanas; the 17th century '' Hatha Ratnavali'' provides a different list of 84 asanas, describing some of them. In the 20th century, Indian nationalism favoured physical culture in response t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hatha Yoga
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Itihasa, Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amritasiddhi, Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a Tantra, tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Meditation Posture
Meditative postures or meditation seats are the body positions or asanas, usually sitting but also sometimes standing or reclining, used to facilitate meditation. Best known in the Buddhist and Hindu traditions are the lotus and kneeling positions; other options include sitting on a chair, with the spine upright. Meditation is sometimes practiced while walking, such as kinhin, doing simple repetitive tasks, as in Zen samu, or work which encourages mindfulness. Postures in the ''Yoga Sutras'' The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' describe yoga as having eight limbs, one being asana, the meditation seat. The sutras do not name any asanas, merely specifying the characteristics of a good asana, stating: The ''Sutras'' are embedded in the ''Bhasya'' commentary, which scholars including Philipp Maas now believe are by the same author; it names 12 seated meditation asanas, possibly all cross-legged, including Padmasana, Virasana, Bhadrasana (now called Baddha Konasana), and Svasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hatha Yoga
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Itihasa, Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amritasiddhi, Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a Tantra, tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
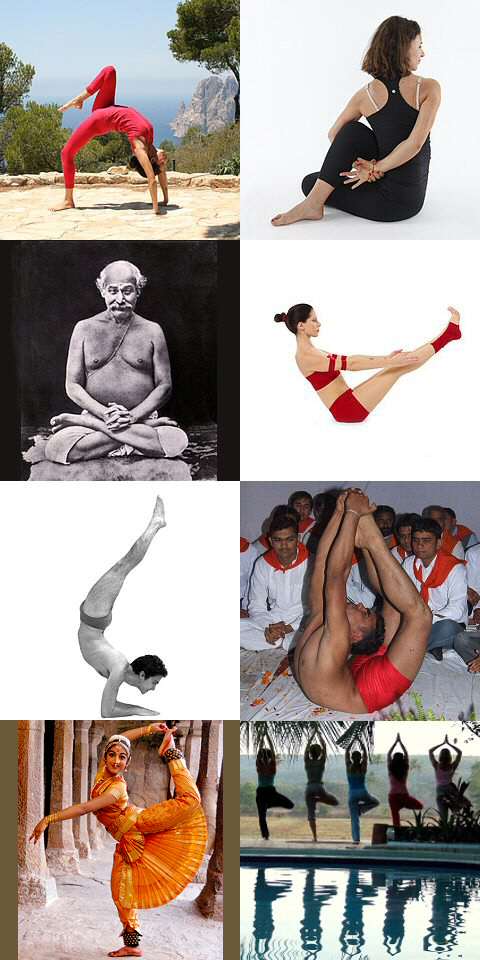
Yoga As Exercise
Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of asana, postures, often connected by vinyasa, flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by pranayama, breathing exercises, and frequently ending with savasana, relaxation lying down or meditation. Yoga in this form has become familiar across the world, especially Yoga in the United States, in the US and Europe. It is derived from medieval Haṭha yoga, which made use of similar postures, but it is generally simply called "yoga". Academic research has given yoga as exercise a variety of names, including modern postural yoga and transnational anglophone yoga. Postures were not central in any of the older traditions of yoga; posture practice was revived in the 1920s by yoga gurus including Yogendra and Kuvalayananda, who emphasised its health benefits. The flowing sequences of Surya Namaskar (Salute to the Sun) were pioneered by the Rajah of Aundh State, Aundh, Bhawanrao Shrinivasrao Pant Pratinidhi, in the 1920s. It and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gheranda Samhita
''Gheranda Samhita'' (IAST: gheraṇḍasaṁhitā, घेरंडसंहिता, meaning “Gheranda's collection”) is a Sanskrit text of Yoga in Hinduism. It is one of the three classic texts of hatha yoga (the other two being the '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' and the '' Shiva Samhita''), and one of the most encyclopedic treatises in yoga.B. Heimann (1937)Review: The Ǧheraṇda Saṁhitā. A Treatise on Haṭha Yoga by Śrīś Chandra Vasu The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, Cambridge University Press, No. 2 (Apr., 1937), pp. 355-357 Fourteen manuscripts of the text are known, which were discovered in a region stretching from Bengal to Rajasthan. The first critical edition was published in 1933 by Adyar Library, and the second critical edition was published in 1978 by Digambarji and Ghote. Some of the Sanskrit manuscripts contain ungrammatical and incoherent verses, and some cite older Sanskrit texts. It is likely a late 17th-century te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shambhala Publications
Shambhala Publications is an Independent publisher, independent publishing company based in Boulder, Colorado. According to the company, it specializes in "books that present creative and conscious ways of transforming the individual, the society, and the planet". Many of its titles deal with Buddhism and related topics in Eastern studies, religion, philosophy, and martial arts. The company's name was inspired by the Sanskrit word Shambhala, referring to a mystical kingdom hidden beyond the snowpeaks of the Himalayas, according to the Tibetan Buddhist tradition. Its authors include Chögyam Trungpa, Pema Chödrön, Thomas Cleary, Ken Wilber, Fritjof Capra, A. H. Almaas, John Daido Loori, John Stevens (scholar), John Stevens, Edward Espe Brown and Natalie Goldberg. The company is unaffiliated with Shambhala Buddhism, Shambhala International, or ''Lion's Roar (magazine), Lion's Roar'' (previously entitled ''Shambhala Sun'') magazine. History Shambhala was founded in 1969 by Samue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
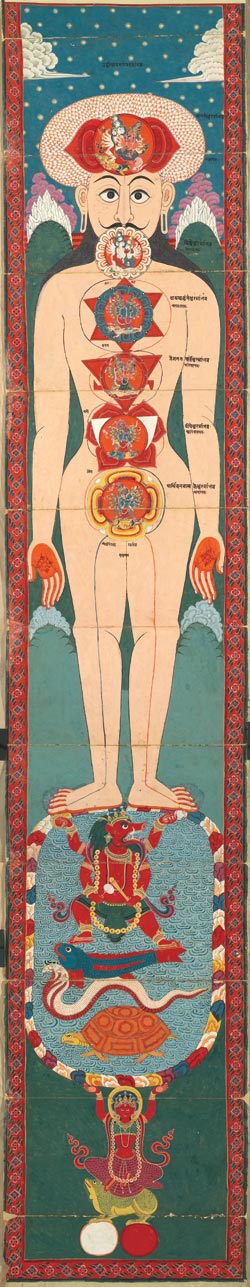
Nadi (yoga)
() is a term for the channels through which, in traditional Indian medicine and spiritual theory, the energies such as prana of the physical body, the subtle body and the causal body are said to flow. Within this philosophical framework, the nadis are said to connect at special points of intensity, the chakras. All nadis are said to originate from one of two centres; the heart and the ''kanda'', the latter being an egg-shaped bulb in the pelvic area, just below the navel. The three principal nadis run from the base of the spine to the head, and are the ida on the left, the sushumna in the centre, and the pingala on the right. Ultimately the goal is to unblock these nadis to bring liberation. Overview Nadi is an important concept in Hindu philosophy, mentioned and described in the sources, some as much as 3,000 years old. The number of nadis of the human body is claimed to be up to hundreds-of-thousands and even millions. The '' Shiva Samhita'' treatise on yoga states, for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subtle Body
A subtle body is a "quasi material" aspect of the human body, being neither solely physical nor solely spiritual, according to various Western esotericism, esoteric, occultism, occult, and mysticism, mystical teachings. This contrasts with the mind–body dualism that has dominated Western thought. The subtle body is important in the Taoism of China and Indian religions, Dharmic religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, mainly in the branches that focus on tantra and yoga, where it is known as the ''Sūkṣma-śarīra'' (). However, while mostly associated with Asian cultures, non-dualistic approaches to the mind and body are found in many parts of the world. Subtle body concepts and practices can be identified as early as 2nd century BCE in Taoist texts found in the Mawangdui tombs. It was "evidently present" in Indian thought as early as the 4th to 1st century BCE when the Taittiriya Upanishad described the Panchakoshas, a series of five interpenetrating sheaths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Light On Yoga
''Light on Yoga: Yoga Dipika'' (Sanskrit: योग दीपिका, "Yoga Dīpikā") is a 1966 book on the Iyengar Yoga style of modern yoga as exercise by B. K. S. Iyengar, first published in English. It describes more than 200 yoga postures or asanas, and is illustrated with some 600 monochrome photographs of Iyengar demonstrating these. The book has been described as the 'bible of modern yoga', and its presentation of the asanas has been called "unprecedented" and "encyclopedic". It has been translated into at least 23 languages and has sold over three million copies. Context Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices from ancient India, forming one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophical traditions. In the Western world, however, yoga is often taken to mean a modern form of medieval Hatha yoga, practised mainly for exercise, consisting largely of the postures called asanas. B. K. S. Iyengar (1918-2014) was born in a poor fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |