|
Short Message Service Technical Realisation (GSM)
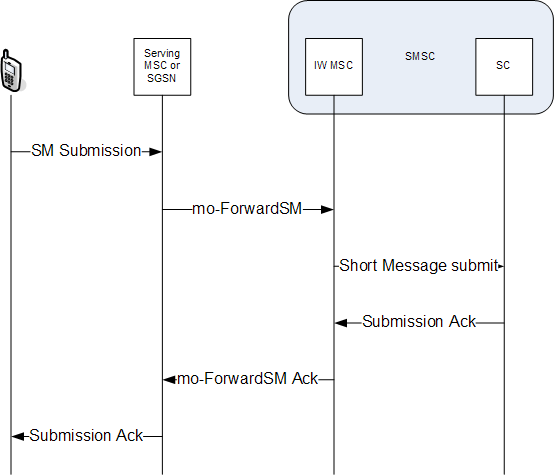
The Short Message Service is realised by the use of the Mobile Application Part (MAP) of the SS7 protocol, with Short Message protocol elements being transported across the network as fields within the MAP messages.Mobile Application Part specification, 3GPP TS 29.002, availablhere/ref> These MAP messages may be transported using "traditional" TDM based signalling, or over IP using SIGTRAN and an appropriate adaptation layer. Protocol The Short Message protocol itself is defined b3GPP TS 23.040for the ''Short Message Service - Point to Point (SMS-PP)'',SMS Point to Point specification, 3GPP TS 23.040, availabl/ref> anfor the ''Cell Broadcast Service (CBS)''.Cell Broadcast Service specification 3GPP TS 23.041, availabl/ref> Four MAP procedures are defined for the control of the Short Message Service: * Mobile Originated (MO) short message service transfer; * Mobile Terminated (MT) short message service transfer; * Short message alert procedure; * Short message waiting data set pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Message Service
Short Message/Messaging Service, commonly abbreviated as SMS, is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile devices exchange short text messages. An intermediary service can facilitate a text-to-voice conversion to be sent to landlines. SMS technology originated from radio telegraphy in radio memo pagers that used standardized phone protocols. These were defined in 1986 as part of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) series of standards.GSM Doc 28/85 "Services and Facilities to be provided in the GSM System" rev2, June 1985 The first SMS message was sent on 3 December 1992, when Neil Papworth, a test engineer for Sema Group, sent "Merry Christmas" to the Orbitel 901 phone of colleague Richard Jarvis. SMS rolled out commercially on many cellular networks that decade and became hugely popular worldwide as a method of text communication. By the end of 2010, SMS w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concatenated SMS
In the cellular phone industry, mobile phones and their networks sometimes support concatenated short message service (or concatenated SMS) to overcome the limitation on the number of characters that can be sent in a single SMS text message transmission (which is usually 160). Using this method, long messages are split into smaller messages by the sending device and recombined at the receiving end. Each message is then billed separately. When the feature works properly, it is nearly transparent to the user, appearing as a single long text message. Previously, due to incompatibilities between providers and lack of support in some phone models, there was not widespread use of this feature. In the late 2000s to early 2010s, this feature was adopted more widely. Not only do many handsets support this feature, but support for the feature also exists amongst SMS gateway providers. The way concatenation works in GSM and UMTS networks is specified in SMS Point to Point specification, 3GPP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Location Register
Network switching subsystem (NSS) (or GSM core network) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location. The NSS originally consisted of the circuit-switched core network, used for traditional GSM services such as voice calls, SMS, and circuit switched data calls. It was extended with an overlay architecture to provide packet-switched data services known as the GPRS core network. This allows mobile phones to have access to services such as WAP, MMS and the Internet. Mobile switching center (MSC) Description The mobile switching center (MSC) is the primary service del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visitor Location Register
Network switching subsystem (NSS) (or GSM core network) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location. The NSS originally consisted of the circuit-switched core network, used for traditional GSM services such as voice calls, SMS, and circuit switched data calls. It was extended with an overlay architecture to provide packet-switched data services known as the GPRS core network. This allows mobile phones to have access to services such as WAP, MMS and the Internet. Mobile switching center (MSC) Description The mobile switching center (MSC) is the primary service del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failed Short Message Delivery
Failure is the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One person might consider a failure what another person considers a success, particularly in cases of direct competition or a zero-sum game. Similarly, the degree of success or failure in a situation may be differently viewed by distinct observers or participants, such that a situation that one considers to be a failure, another might consider to be a success, a qualified success or a neutral situation. It may also be difficult or impossible to ascertain whether a situation meets criteria for failure or success due to ambiguous or ill-defined definition of those criteria. Finding useful and effective criteria, or heuristics, to judge the success or failure of a situation may itself be a significant task. In American history Cultural histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Land Mobile Network
In telecommunication, a public land mobile network (PLMN) is a combination of wireless communication services offered by a specific operator in a specific country.3GPP TS 21.905 https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_tr/121900_121999/121905/15.00.00_60/tr_121905v150000p.pdf A PLMN typically consists of several cellular technologies like GSM/ 2G, UMTS/ 3G, LTE/ 4G, offered by a single operator within a given country, often referred to as a cellular network. PLMN code A PLMN is identified by a globally unique PLMN code, which consists of a MCC (Mobile Country Code) and MNC (Mobile Network Code). Hence, it is a five- to six-digit number identifying a country, and a mobile network operator in that country, usually represented in the form 001-01 or 001–001. A PLMN is part of a: * Location Area Identity (LAI) (PLMN and Location Area Code) * Cell Global Identity (CGI) (LAI and Cell Identifier) * IMSI (see PLMN code and IMSI) Leading zeros in PLMN codes Note that an MNC can be of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sms Home Routing
SMS Home Routing is a modification to the original GSM specifications that changed the way inbound (off-net) SMS messages are treated by mobile telecommunications networks. Adopted by the 3GPP in 2007, Home Routing was devised to enable mobile networks to offer a full range of advanced services on both inbound and outbound SMS, giving more utility to phone users and enabling operators to generate additional revenue. The roots of the problem The original GSM specifications provided for all outbound and cross-network messaging to pass through the home network message entity, but inbound messages generated on other networks to be sent directly to target handsets under the control of the sending network, not the home network. This inconsistency arose from the fact that SMS was conceived as a voicemail alert system, not a person-to-person messaging system, and it put SMS out of step with most other forms of communication including voice telephony, email and MMS where the home entity ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol Data Unit
In telecommunications, a protocol data unit (PDU) is a single unit of information transmitted among peer entities of a computer network. It is composed of protocol-specific control information and user data. In the layered architectures of communication protocol stacks, each layer implements protocols tailored to the specific type or mode of data exchange. For example, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) implements a connection-oriented transfer mode, and the PDU of this protocol is called a ''segment'', while the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) uses datagrams as protocol data units for connectionless communication. A layer lower in the Internet protocol suite, at the Internet layer, the PDU is called a packet, irrespective of its payload type. Packet-switched data networks In the context of packet switching data networks, a protocol data unit (PDU) is best understood in relation to a service data unit (SDU). The features or services of the network are implemented in dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Application Part
The Mobile Application Part (MAP) is an SS7 protocol that provides an application layer for the various nodes in GSM and UMTS mobile core networks and GPRS core networks to communicate with each other in order to provide services to users. The Mobile Application Part is the application-layer protocol used to access the Home Location Register, Visitor Location Register, Mobile Switching Center, Equipment Identity Register, Authentication Centre, Short message service center and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN). Facilities provided The primary facilities provided by MAP are: * Mobility Services: location management (to support roaming), authentication, managing service subscription information, fault recovery, * Operation and Maintenance: subscriber tracing, retrieving a subscriber's IMSI * Call Handling: routing, managing calls whilst roaming, checking that a subscriber is available to receive calls * Supplementary Services * Short Message Service * Packet Data Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |