|
Short-circuit Test
The purpose of a short-circuit test is to determine the series branch parameters of the equivalent circuit of a transformer. Method The test is conducted on the high-voltage (HV) side of the transformer where the low-voltage (LV) side (or the secondary) is short-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary side. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is the same as the voltmeter reading. Now with the help of a variac, the applied voltage is slowly increased until the ammeter gives a reading equal to the rated current of the HV side. After reaching the rated current of the HV side, all three instruments reading (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and wattmeter readings) are recorded. The ammeter reading gives the primary equivalent of full load current IL. As the voltage applied for full load current in short circuit test on transformer is quite small compared to the rated primary voltage of the transformer, the iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit Test
Short may refer to: Places * Short (crater), a lunar impact crater on the near side of the Moon * Short, Mississippi, an unincorporated community * Short, Oklahoma, a census-designated place People * Short (surname) * List of people known as the Short Arts, entertainment, and media * Short film, a cinema format (also called film short or short subject) * Short story, prose generally readable in one sitting * ''The Short-Timers'', a 1979 semi-autobiographical novel by Gustav Hasford, about military short-timers in Vietnam Brands and enterprises * Short Brothers, a British aerospace company * Short Brothers of Sunderland, former English shipbuilder Computing and technology * Short circuit, an accidental connection between two nodes of an electrical circuit * Short integer, a computer datatype Finance * Short (finance), stock-trading position * Short snorter, a banknote signed by fellow travelers, common during World War II Foodstuffs * Short pastry, one which is rich in butte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response. A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signal-processing circuits. Since the invention of the first constant-potential transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an " open circuit", which is an infinite resistance between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same voltage. In an 'ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattmeter
The wattmeter is an instrument for measuring the electric active power (or the average of the rate of flow of electrical energy) in watts of any given circuit. Electromagnetic wattmeters are used for measurement of utility frequency and audio frequency power; other types are required for radio frequency measurements. A wattmeter reads the average value of the product ''v(t)i(t) = p(t)'', where ''v(t)'' is the voltage with positive reference polarity at the ± terminal with respect to the other terminal of the potential coil, and ''i(t)'' is the current with reference direction flowing into the ± terminal of the current coil. The wattmeter reads ''P = (1/T) ∫0T v(t)i(t) dt'', which in sinusoidal steady-state reduces to ''V''rms ''I''rms cos(φ), where ''T'' is the period of ''p(t)'' and φ is the angle by which the current lags the voltage. History On 14 August 1888, Oliver B. Shallenberge patented a watt-hour meter. The Hungarian Ottó Bláthy patented his AC wattmeter. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured. An ammeter usually has low resistance so that it does not cause a significant voltage drop in the circuit being measured. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as ''milliammeters'' or ''microammeters''. Early ammeters were laboratory instruments that relied on the Earth's magnetic field for operation. By the late 19th century, improved instruments were designed which could be mounted in any position and allowed accurate measurements in electric power systems. It is generally represented by letter 'A' in a circuit. History The relation between electric current, magnetic fields and physical forces was first noted by Hans Christian Ør ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series And Parallel Circuits
Two-terminal components and electrical networks can be connected in series or parallel. The resulting electrical network will have two terminals, and itself can participate in a series or parallel topology. Whether a two-terminal "object" is an electrical component (e.g. a resistor) or an electrical network (e.g. resistors in series) is a matter of perspective. This article will use "component" to refer to a two-terminal "object" that participate in the series/parallel networks. Components connected in series are connected along a single "electrical path", and each component has the same current through it, equal to the current through the network. The voltage across the network is equal to the sum of the voltages across each component. Components connected in parallel are connected along multiple paths, and each component has the same voltage across it, equal to the voltage across the network. The current through the network is equal to the sum of the currents through each c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage measured and can be built from a galvanometer and series resistor. Meters using amplifiers can measure tiny voltages of microvolts or less. Digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog-to-digital converter. Voltmeters are made in a wide range of styles, some separately powered (e.g. by battery), and others powered by the measured voltage source itself. Instruments permanently mounted in a panel are used to monitor generators or other fixed apparatus. Portable instruments, usually equipped to also measure current and resistance in the form of a multimeter, are standard test instruments used in electrical and electronics work. Any measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotransformer
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. The " auto" (Greek for "self") prefix refers to the single coil acting alone, not to any kind of automatic mechanism. In an autotransformer, portions of the same winding act as both the primary winding and secondary winding sides of the transformer. In contrast, an ordinary transformer has separate primary and secondary windings which have no metallic conducting path between them. The autotransformer winding has at least three taps where electrical connections are made. Since part of the winding does "double duty", autotransformers have the advantages of often being smaller, lighter, and cheaper than typical dual-winding transformers, but the disadvantage of not providing electrical isolation between primary and secondary circuits. Other advantages of autotransformers include lower leakage reactance, lower losses, lower excitation current, and increased VA rating for a given size and mass. An example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-circuit Test
The open-circuit test, or no-load test, is one of the methods used in electrical engineering to determine the no-load impedance in the excitation branch of a transformer. The no load is represented by the open circuit, which is represented on the right side of the figure as the "hole" or incomplete part of the circuit. Method The secondary of the transformer is left open-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is the same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary. If the applied voltage is normal voltage then normal flux will be set up. Since iron loss is a function of applied voltage, normal iron loss will occur. Hence the iron loss is maximum at rated voltage. This maximum iron loss is measured using the wattmeter. Since the impedance of the series winding of the transformer is very small compared to that of the excitation branch, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blocked Rotor Test
A blocked rotor test is conducted on an induction motor. It is also known as short-circuit test (because it is the mechanical analogy of a transformer short-circuit test), locked rotor test or stalled torque test. From this test, short-circuit current at normal voltage, power factor on short circuit, total leakage reactance, and starting torque of the motor can be found. It is very important to know a motor's starting torque since if it is not enough to overcome the initial friction of its intended load then it will remain stationary while drawing an excessive current and rapidly overheat. The test may be conducted at lower voltage because at the normal voltage the current through the windings would be high enough to rapidly overheat and damage them. The test may still be conducted at full voltage if it is brief enough to avoid overheating the windings or overloading the starting circuits, but requires much more care to be taken while performing the test. The ''blocked rotor torqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
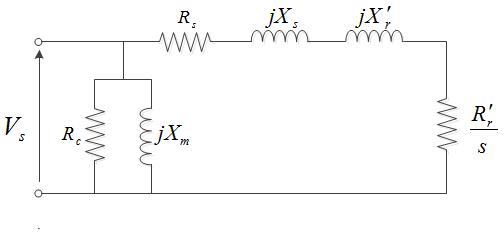
Circle Diagram
First conceived by A.heyland in 1894 and B.A. Behrend in 1895, the circle diagram is the graphical representation of the performance of the electrical machine drawn in terms of the locus of the machine's input voltage and current. The circle diagram can be drawn for alternators, synchronous motors, transformers, induction motors. The Heyland diagram is an approximate representation of circle diagram applied to induction motors, which assumes that stator input voltage, rotor resistance and rotor reactance are constant and stator resistance and core loss are zero. Another common circle diagram form is as described in the two constant air-gap induction motor images shown here, where, * Rs, Xs: Stator resistance and leakage reactance * Rr', Xr', s: Rotor resistance and leakage reactance referred to the stator and rotor slip * Rc, Xm, : Core and mechanical losses, magnetization reactance * Vs, Impressed stator voltage * I0 = OO', IBL = OA, I1 =OV: No load current, blocked rotor curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |