|
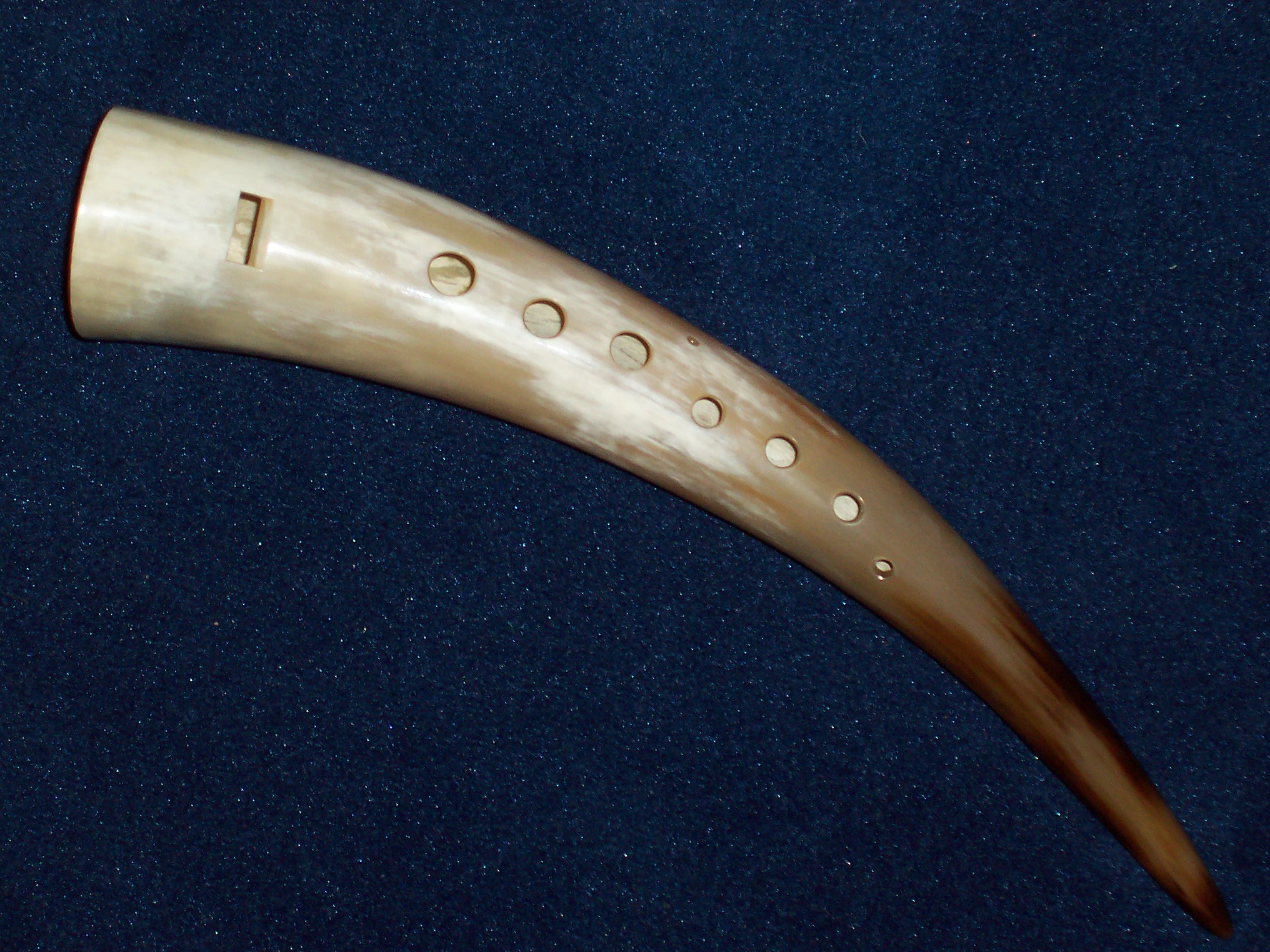
Shepherd's Whistle
A shepherd's whistle is a specialized, modulatable, variable-pitch whistle used to train and transmit commands to working dogs and other animals. Unlike other whistles, they are placed inside the mouth. The pitch is controlled by the placement of the tongue; physically, shepherd's whistles are vessel flutes with the tongue forming one side of the resonating chamber, and controlling its size. Like tin whistles, while simple, they can be used as musical instruments in their own right. Purpose A shepherd's whistle is traditionally used for communicating commands to a sheepdog to aid in herding. They are typically seen used at sheepdog trials, but are also used for other working dogs including gundogs, and for falconry. Shepherd's whistles are used to communicate clearly, and at distances up to , the commands of the owner to their working dog. They produce clear, high-frequency tones of an easily modulated and variable pitch, allowing the shepherd to communicate a variety of comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendant
A pendant is a loose-hanging piece of jewellery, generally attached by a small loop to a necklace, which may be known as a "pendant necklace". A pendant earring is an earring with a piece hanging down. Its name stems from the Latin word ''pendere'' and Old French word ''pendr'', both of which translate to "to hang down". In modern French, ''pendant'' is the gerund form of ''pendre'' ("to hang") and also means "during". The extent to which the design of a pendant can be incorporated into an overall necklace makes it not always accurate to treat them as separate items. In some cases, though, the separation between necklace and pendant is far clearer. Overview Pendants are among the oldest recorded types of bodily adornment. Stone, shell, pottery, and more perishable materials were used. Ancient Egyptians commonly wore pendants, some shaped like hieroglyphs. Pendants can have several functions, which may be combined: * Award (i.e., Scouting Ireland Chief Scout's Award, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Communication
Animal communication is the transfer of information from one or a group of animals (sender or senders) to one or more other animals (receiver or receivers) that affects the current or future behavior of the receivers. Information may be sent intentionally, as in a courtship display, or unintentionally, as in the transfer of scent from predator to prey. Information may be transferred to an "audience" of several receivers. Animal communication is a rapidly growing area of study in disciplines including animal behavior, sociology, neurology and animal cognition. Many aspects of animal behavior, such as symbolic name use, emotional expression, learning and sexual behavior, are being understood in new ways. When the information from the sender changes the behavior of a receiver, the information is referred to as a "signal". Signalling theory predicts that for a signal to be maintained in the population, both the sender and receiver should usually receive some benefit from the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vessel Flutes
Vessel(s) or The Vessel may refer to: Biology *Blood vessel, a part of the circulatory system and function to transport blood throughout the body *Lymphatic vessel, a thin walled, valved structure that carries lymph *Vessel element, a narrow water transporting tube in plant Containers *Bowl (vessel), a common open-top container *Drinking vessel, for holding drinkable liquids *Pressure vessel, designed to hold fluids at a pressure different from the ambient pressure Watercraft *Watercraft, also known as water vessel, craft designed for transportation on water **Sailing ship or sailing vessel, watercraft that uses sails and wind power for movement Arts and entertainment Film and television * ''Vessel'' (film), a 2014 documentary film by Diana Whitten * ''The Vessel'' (film), a 2016 film starring Martin Sheen * ''The Vessel'' (web series), a 2012 British comedy web series * "The Vessel" (''The Outer Limits''), a television episode Music Performers *Vessels (band), a British post- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Training And Behavior
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Dogs were the first species to be domesticated by hunter-gatherers over 15,000 years ago before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have expanded to a large number of domestic individuals and gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other canids. The dog has been selectively bred over millennia for various behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes. Dog breeds vary widely in shape, size, and color. They perform many roles for humans, such as hunting, herding, pulling loads, protection, assisting police and the military, companionship, therapy, and aiding disabled people. Over the millennia, dogs became uniquely adapted to human behavior, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistles
Whistling without the use of an artificial whistle is achieved by creating a small opening with one's lips, usually after applying moisture (licking one's lips or placing water upon them) and then blowing or sucking air through the space. The air is moderated by the lips, curled tongue, teeth or fingers (placed over the mouth or in various areas between pursed lips) to create turbulence, and the curled tongue acts as a resonant chamber to enhance the resulting sound by acting as a type of Helmholtz resonator. By moving the various parts of the lips, fingers, tongue and epiglottis, one can then manipulate the types of whistles produced. Techniques Pucker whistling is the most common form in much Western music. Typically, the tongue tip is lowered, often placed behind the lower teeth, and pitch altered by varying the position of the tongue. Although varying the degree of pucker will change the pitch of a pucker whistle, expert pucker whistlers will generally only make small var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vessel Flute
A vessel flute is a type of flute with a body which acts as a Helmholtz resonator. The body is vessel-shaped, not tube- or cone-shaped; that is, the far end is closed. Most flutes have cylindrical or conical bore (examples: concert flute, shawm). Vessel flutes have more spherical hollow bodies. The air in the body of a vessel flute resonates as one, with air moving alternately in and out of the vessel, and the pressure inside the vessel increasing and decreasing. This is unlike the resonance of a tube or cone of air, where air moves back and forth along the tube, with pressure increasing in part of the tube while it decreases in another. Blowing across the opening of empty bottle produces a basic edge-blown vessel flute. Multi-note vessel flutes include the ocarina.For a linguistic analysis of the possible origins of the word ''ocarina'', cf. Perono Cacciafoco, Francesco. (2019). A Prehistoric 'Little Goose': A New Etymology for the Word 'Ocarina'. ''Annals of the Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
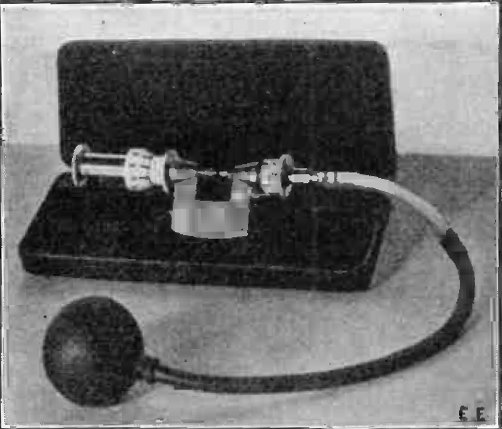
Dog Whistle
A dog whistle (also known as silent whistle or Galton's whistle) is a type of whistle that emits sound in the ultrasonic range, which humans cannot hear but some other animals can, including dogs and domestic cats, and is used in their training. It was invented in 1876 by Francis Galton and is mentioned in his book ''Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development'',Galton, Francis (1883) ''Inquiries into Human Faculty and Its Development'' pp. 26-27. in which he describes experiments to test the range of frequencies that could be heard by various animals, such as a house cat. The upper limit of the human hearing range is about 20 kilohertz (kHz) for children, declining to 15–17 kHz for middle-age adults. The top end of a dog's hearing range is about 45 kHz, while a cat's is 64 kHz. It is thought that the wild ancestors of cats and dogs evolved this higher hearing range in order to hear high-frequency sounds made by their preferred prey, small rodents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–animal Communication
Human–animal communication is the communication observed between humans and other animals, ranging from non-verbal cues and vocalizations to the use of language. Some human–animal communication may be observed in casual circumstances, such as the interactions between pets and their owners, which can reflect a form of spoken, while not necessarily verbal dialogue. A dog being scolded is able to grasp the message by interpreting cues such as the owner's stance, tone of voice, and body language. This communication is two-way, as owners can learn to discern the subtle differences between barks or meows, and there is a clear difference between the bark of an angry dog defending its home and the happy bark of the same animal while playing. Communication (often nonverbal) is also significant in equestrian activities such as dressage. One scientific study has found that 30 bird species and 29 mammal species share the same pattern of pitch and speed in basic messages. Therefore, hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Resonance
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration (its '' resonance frequencies''). The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to narrow mechanical resonance to the frequency range of human hearing, but since acoustics is defined in general terms concerning vibrational waves in matter, acoustic resonance can occur at frequencies outside the range of human hearing. An acoustically resonant object usually has more than one resonance frequency, especially at harmonics of the strongest resonance. It will easily vibrate at those frequencies, and vibrate less strongly at other frequencies. It will "pick out" its resonance frequency from a complex excitation, such as an impulse or a wideband noise excitation. In effect, it is filtering out all frequencies other than its resonance. Acoustic resonance is an important consideration for instrument builders, as most acoustic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Box
A sound box or sounding box (sometimes written soundbox) is an open chamber in the body of a musical instrument which modifies the sound of the instrument, and helps transfer that sound to the surrounding air. Objects respond more strongly to vibrations at certain frequencies, known as resonances. The frequency and strength of the resonances of the body of a musical instrument have a significant impact on the tone quality it produces. The air inside the chamber has its own resonances, and these interact with the resonances of the body, altering the resonances of the instrument as a whole. The sound box typically adds resonances at lower frequencies, enhancing the lower-frequency response of the instrument. The distinctive sound of an instrument with a sound box owes a lot to the alteration made to the tone. A sound box is found in most string instruments. The most notable exceptions are some electrically amplified instruments like the solid body electric guitar or the electric v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fipple
The term fipple specifies a variety of end-blown flute that includes the flageolet, recorder, and tin whistle. The Hornbostel–Sachs system for classifying musical instruments places this group under the heading "Flutes with duct or duct flutes." The label "fipple flute" is frequently applied to members of the subgroup but there is no general agreement about the structural detail of the sound-producing mechanism that constitutes the fipple, itself. Nomenclature The accompanying illustration of the mouthpiece of a recorder shows a wooden block (A) with a channel carved into the body of the instrument (B), together forming a duct that directs a ribbon of air across an opening toward a sharp edge (C). The edge splits the air in a manner that alternately directs it into and outside of the tube, setting the contained column of air into periodic vibration. This flow-controlled "air reed" is a definitive characteristic of all flutes, which therefore all have an edge or equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_great-egret-8243-web_(324180866).jpg)