|
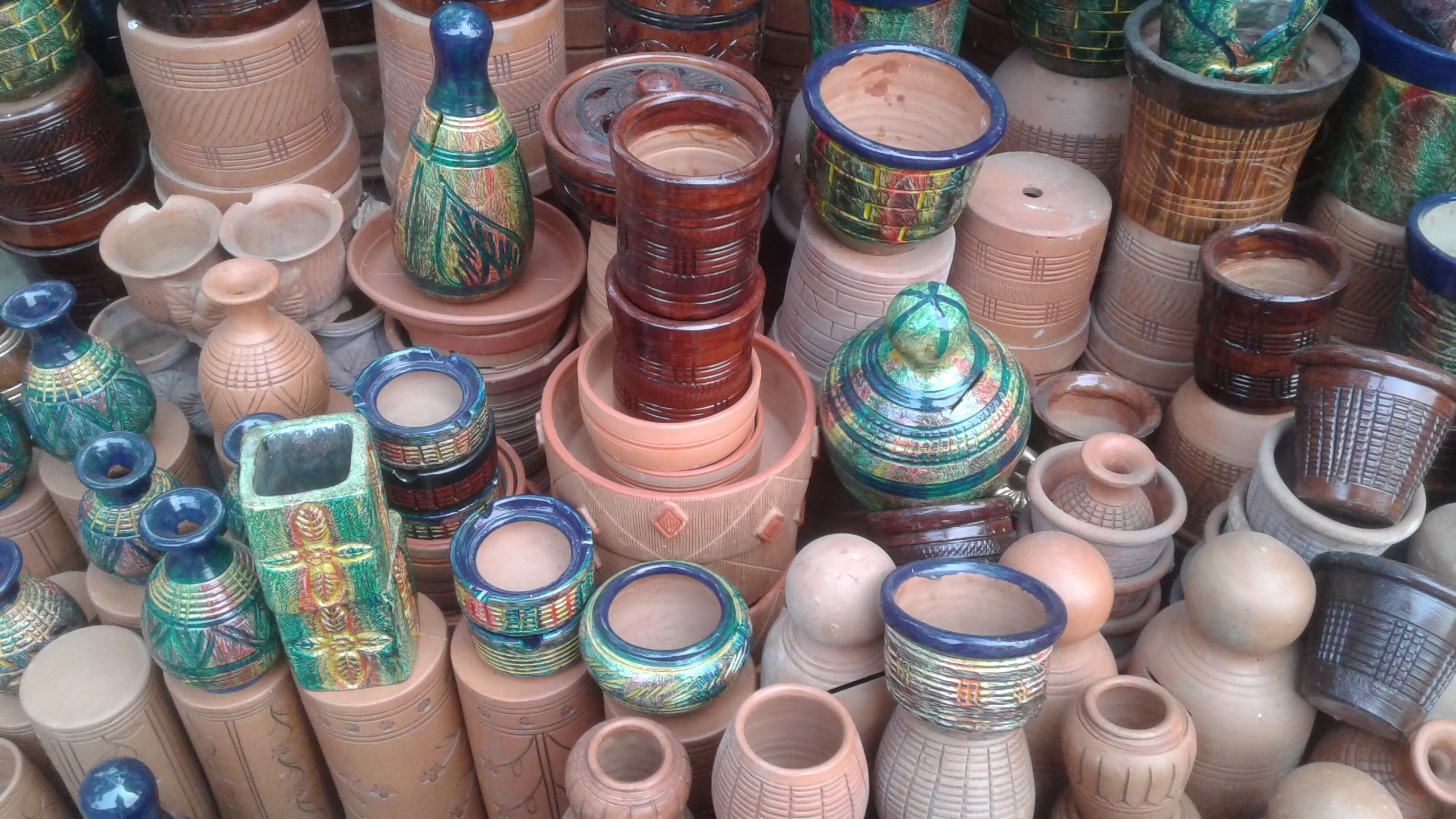
Shepherd's Gourd
A shepherd's gourd (also shepherd's jug} ''(Spanish: botijo de pastor)'' is a container for carrying and holding water, which has a gourd-like body, like the ordinary botijo. It has a widened neck that, allows a rope to be tied to hold it to allow it to be carried or tied to another object. Originally it consisted of a Calabash, small gourd whose interior was emptied and cured, to serve as a vessel for liquids. The shape was later copied by Pottery, potters in the various shapes of vessels, such as botijillas or canteens. Together with the pilgrim's scallop, it is part of the iconography of the pilgrim in general and of the Way of Saint James. Background Other variants of the name are the "shepherd's jug" or "pumpkin jug" (Spanish:''botija de calabaza'') and the calabazo or pilgrim's barrel (Spanish:''barril de peregrino''). This is how Caro Bellido defnes it in his Spanish lexical dictionary, citing in turn Ramón Menéndez Pidal, Menéndez Pidal who defined gourd as an old Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabacilla - Otura - Granada
''Cucurbita radicans'', commonly known in Mexico as calabacilla (little pumpkin/gourd) or calabaza de coyote (coyote gourd), is a species of gourd found growing wild, but also plant cultivation, cultivated, in southern Mexico (specifically in the Federal Districts of Jalisco, State of Mexico, Mexico and Michoacán). The type (biology), type specimen was collected growing in rocks below a mountain near Guadalupe in the vicinity of Mexico City (the exact location is unclear); other specimens were also ubiquitous in the area; in corn fields and gardens, either being cultivated, or as invasive species, invaders. It is a close relative of ''Cucurbita pedatifolia''. References External links ''Cucurbita radicans'' inflorescence from the Institute of Biology at the National Autonomous University of Mexico Flora of Mexico Plants described in 1866 Squashes and pumpkins Cucurbita, radicans {{Cucurbitales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botijo
A botijo, also called ''búcaro'', is a traditional porous clay container designed to contain water. The botijo is a typical element of Spanish culture and may vary in shape, color and material. The botijo has the property that once filled, it cools the water that it contains, acting as an evaporative cooler. The botijo has a wide belly and one or more mouths where it is filled and one or more outputs called ''pitón'' or ''pitorro'' to drink from. The ''búcaro de Indias'' is a special type, made of fragrant clay from Mexico, that was prized in Europe.https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/662163 Operation The operating principle of the botijo is as follows: the stored water is filtered through the pores of the clay and in contact with the outside dry environment (characteristic of Mediterranean climate), it evaporates, producing a cooling (2.219 kilojoules per gram of evaporated water). The key for cooling it, is by the evaporation of bleed water, as the water ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabash
Calabash (; ''Lagenaria siceraria''), also known as bottle gourd, white-flowered gourd, long melon, birdhouse gourd, New Guinea bean, Tasmania bean, and opo squash, is a vine grown for its fruit. It can be either harvested young to be consumed as a vegetable, or harvested mature to be dried and used as a utensil, container, or a musical instrument. When it is fresh, the fruit has a light green smooth skin and white flesh. Calabash fruits have a variety of shapes: they can be huge and rounded, small and bottle-shaped, or slim and serpentine, and they can grow to be over a metre long. Rounder varieties are typically called calabash gourds. The gourd was one of the world's first cultivated plants grown not primarily for food, but for use as containers. The bottle gourd may have been carried from Asia to Africa, Europe, and the Americas in the course of human migration, or by seeds floating across the oceans inside the gourd. It has been proven to have been globally domesticated (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim's Scallop
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve mollusks in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related families within the superfamily Pectinoidea, which also includes the thorny oysters. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family of bivalves found in all of the world's oceans, although never in fresh water. They are one of the very few groups of bivalves to be primarily "free-living", with many species capable of rapidly swimming short distances and even migrating some distance across the ocean floor. A small minority of scallop species live cemented to rocky substrates as adults, while others attach themselves to stationary or rooted objects such as seagrass at some point in their lives by means of a filament they secrete called a byssal thread. The majority of species, however, live recumbent on sandy substrates, and when they sense the presence of a pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Way Of Saint James
The Camino de Santiago ( la, Peregrinatio Compostellana, "Pilgrimage of Compostela"; gl, O Camiño de Santiago), known in English as the Way of St James, is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle Saint James the Great in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tradition holds that the remains of the apostle are buried. As Pope Benedict XVI said, "It is a way sown with so many demonstrations of fervour, repentance, hospitality, art and culture which speak to us eloquently of the spiritual roots of the Old Continent." Many follow its routes as a form of spiritual path or retreat for their spiritual growth. It is also popular with hiking and cycling enthusiasts and organized tour groups. Created and established after the discovery of the relics of Saint James the Great at the beginning of the 9th century, the Way of St James became a major pilgrimage route of medieval Christianity from the 10th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabacilla De Pastor - Adoración Pastores - Maino
''Cucurbita radicans'', commonly known in Mexico as calabacilla (little pumpkin/gourd) or calabaza de coyote (coyote gourd), is a species of gourd found growing wild, but also cultivated, in southern Mexico (specifically in the Federal Districts of Jalisco, Mexico and Michoacán). The type specimen was collected growing in rocks below a mountain near Guadalupe in the vicinity of Mexico City (the exact location is unclear); other specimens were also ubiquitous in the area; in corn fields and gardens, either being cultivated, or as invaders. It is a close relative of ''Cucurbita pedatifolia''. References External links ''Cucurbita radicans'' inflorescencefrom the Institute of Biology at the National Autonomous University of Mexico The National Autonomous University of Mexico ( es, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, UNAM) is a public research university in Mexico. It is consistently ranked as one of the best universities in Latin America, where it's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal (; 13 March 1869 – 14 November 1968) was a Spanish philologist and historian."Ramon Menendez Pidal", ''Almanac of Famous People'' (2011) ''Biography in Context'', Gale, Detroit He worked extensively on the history of the Spanish language and Spanish folklore and folk poetry. One of his main topics was the history and legend of El Cid. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in 26 separate years, thus, being the most nominated person. Biography Menéndez Pidal was born in A Coruña, Galicia, Spain. His father, Juan Menéndez Fernández, was a lawyer and magistrate from Asturias. His mother was Ramona Pidal, also an Asturian. His older brother, Juan Menéndez Pidal, whom he outlived by more than fifty years, was also a literary scholar of the folk poetry of Asturias. Another older brother, Luis Menéndez Pidal, was a realist painter and professor of art history. He studied at the University of Madrid."Ramon Menendez Pidal", ''Contemporary Authors Online' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Mancha
La Mancha () is a natural and historical region located in the Spanish provinces of Albacete, Cuenca, Ciudad Real, and Toledo. La Mancha is an arid but fertile plateau (610 m or 2000 ft) that stretches from the mountains of Toledo to the western spurs of the hills of Cuenca, and bordered to the south by the Sierra Morena and to the north by the Alcarria region. La Mancha historical comarca constitutes the southern portion of Castilla-La Mancha autonomous community and makes up most of the present-day administrative region. Name The name "La Mancha" is probably derived from the Arabic word المنشأ ''al-mansha'', meaning "birthplace" or "fountainhead". The name of the city of Almansa in Albacete shares that origin. The word ''mancha'' in Spanish literally means ''spot'', ''stain'', or ''patch'', but no apparent link exists between this word and the name of the region. Geography The largest plain in Spain, La Mancha is made up of a plateau averaging 500 to 600 metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vieira Camino De Santiago
Vieira is a Portuguese and Galician term which in Portuguese and Galician stands for the Great Pilgrim Mussel from the scallop family (Pectinidae). The term derives its use as a place and family name. History The use of the term can be traced, according to current knowledge, to the beginning of the 13th century in northwestern Portugal. The historical writing form of the term ''Vieira'' was ''Vyeyra''. It is assumed that the term as a name originated independently in different places (e.g. Vieira do Minho and Vieira de Leiria). As a surname, the term is first found in northwestern Portugal in the province of Minho in the era of Kings D. Afonso II and D. Sancho II of Portugal around 1220 A.D. The historically common spelling Vyeyra is still found at least until the end of the Middle Ages in the mid-16th century. The modern Portuguese alphabet basically does not recognise the letter Y alongside the K and W, only the 23 letters of the Latin alphabet A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery Of America
The prehistory of the Americas (North, South, and Central America, and the Caribbean) begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have been isolated from the people of the "Old World" until the coming of Europeans in the 10th century from Iceland led by Leif Erikson and in 1492 with the voyages of Christopher Columbus. While this was the prevailing theory for quite sometime, new genetic and anthropological evidence suggests contact with Polynesian and South East Asian groups, while not confirmed to be frequent, happened with some regularity prior to the arrival of European colonizers as evidenced by cultural and linguistic trade, domesticated crops and livestock, and analysis of DNA from east Peruvian and Andean cultures as well as some sites suggested to be permanent settlements of Oceanic and Polynesian sailors. Some anthropologists also suggest that contact with West African, Chinese, and even som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)