|
Sheet Erosion
Sheet erosion or sheet wash is the even erosion of substrate along a wide area. It occurs in a wide range of settings such as coastal plains, hillslopes, floodplains, beaches, savanna plains and semi-arid plains. Water moving fairly uniformly with a similar thickness over a surface is called sheet flow, and is the cause of sheet erosion. Sheet erosion implies that any flow of water that causes the erosion is not canalized. If a hillslope surface contains many irregularities, sheet erosion may give way to erosion along small channels called rills, which can then converge forming gullies. However, sheet erosion may occur despite some limited unevenness in the sheet flow arising from clods of earth, rock fragments, or vegetation. Sheet erosion occurs in two steps. First, rainsplash dislodges small particles of the substrate and then the particles are carried away, usually short distances, by a thin and uniform layer of water known as sheetflow. Transport by the sheetflow is usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coastal Plain of North America extends northwards from the Gulf of Mexico along the Lower Mississippi River to the Ohio River, which is a distance of about . The Atlantic Coastal Plain runs from the New York Bight to Florida. The Coastal Plains of India lie on either side of the Deccan Plateau, along the western and eastern coasts of India. They extend for about 6,150 km from the Rann of Kutch in the west to West Bengal in the east. They are broadly divided into the Western Coastal Plains and the Eastern Coastal Plains. The two coastal plains meet at Kanyakumari, the southernmost tip of the Indian mainland. The eastern coastal plain is located between The Bay of Bengal and the eastern Ghats and the western coastal plain is located between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, air (wind), plants, and animals (including humans). In accordance with these agents, erosion is sometimes divided into water erosion, glacial erosion, snow erosion, wind (aeolean) erosion, zoogenic erosion and anthropogenic erosion such as tillage erosion. Soil erosion may be a slow process that continues relatively unnoticed, or it may occur at an alarming rate causing a serious loss of topsoil. The loss of soil from farmland may be reflected in reduced crop production potential, lower surface water quality and damaged drainage networks. Soil erosion could also cause sinkholes. Human activities have increased by 10–50 times the rate at which erosion is occurring world-wide. Excessive (or accelerated) erosion causes both "on-site" and "off-site" problems. On- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment (geology)
A pediment, also known as a concave slope or waning slope, is a very gently sloping (0.5°-7°) inclined bedrock surface. It is typically a concave surface sloping down from the base of a steeper retreating desert cliff, escarpment, or surrounding a monadnock or inselberg, but may persist after the higher terrain has eroded away. Pediments are erosional surfaces. A pediment develops when sheets of running water (sheet floods) wash over it in intense rainfall events. It may be thinly covered with fluvial gravel that has washed over it from the foot of mountains produced by cliff retreat erosion. A pediment is not to be confused with a bajada, which is a merged group of alluvial fans. Bajadas also slope gently from an escarpment, but are composed of material eroded from canyons in the escarpment and redeposited on the bajada, rather than of bedrock with a thin veneer of gravel. Description Pediments were originally recognized as the upper part of smoothly sloping (0.5°-7°) co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillslope Evolution
Hillslope evolution is the changes in the erosion rates, erosion styles and form of slopes of hills and mountains over time. Conceptual models During most of the 20th century three models of hillslope evolution were widely diffused: slope decline, slope replacement and parallel slope retreat. Until the 1950s models of hillslope form evolution were central in geomorphology. The modern understanding is that the evolution of slopes is much more complex than the classical models of decline, replacement and retreat imply. Slope decline Slope decline was proposed by William Morris Davis in his cycle of erosion theory. It consists of a gradual decrease in slope angle as stream incision slows down. This is accompaigned as slopes becomes more gentle they accumulate with fine-grained regolith stemming from weathering. Slope replacement Slope replacement was first proposed by Walther Penck challenging Davis' ideas on slope development. Slope replacement describes an evolution of slopes tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
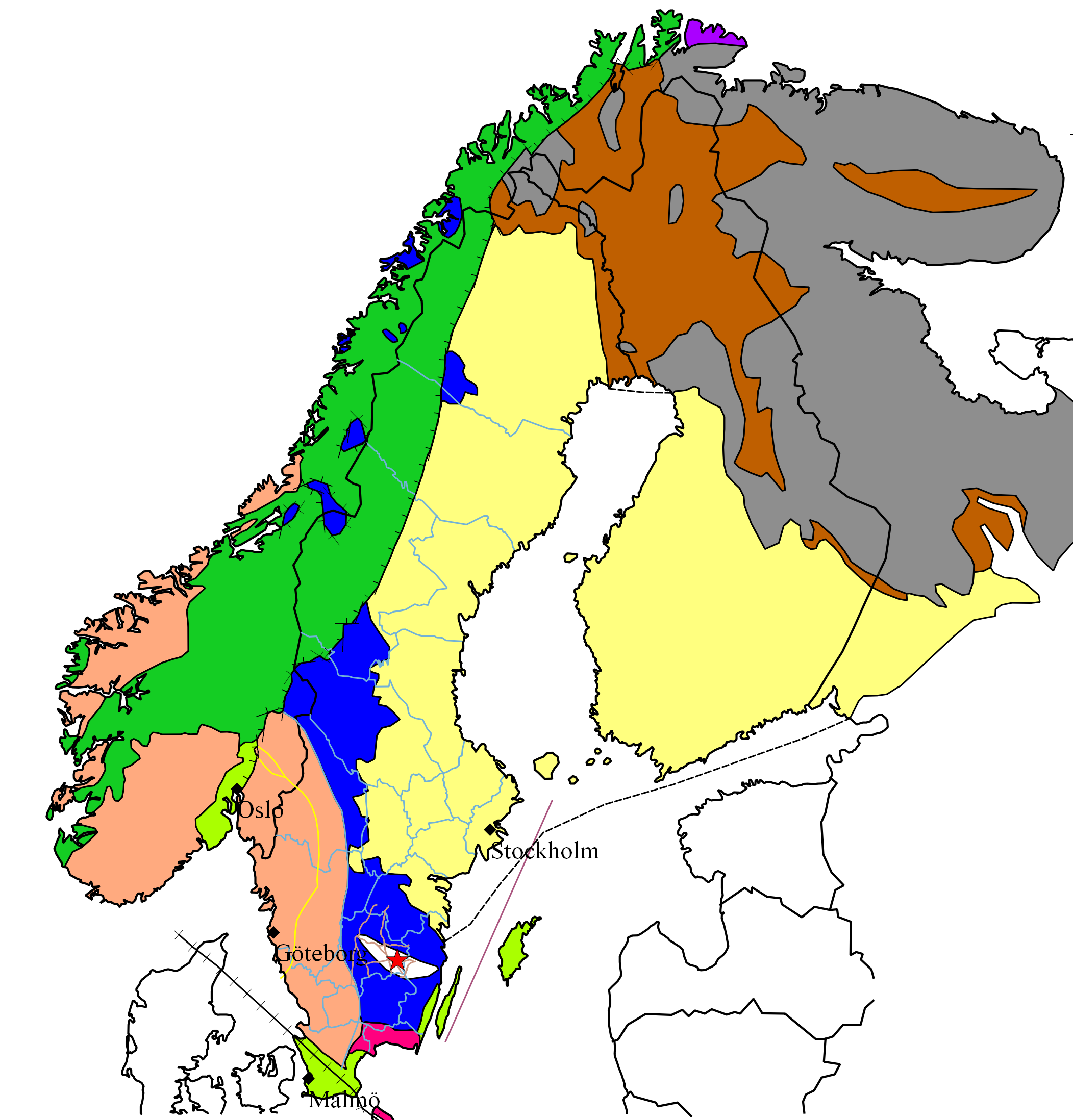
Baltic Shield
The Baltic Shield (or Fennoscandian Shield) is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstone which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity. It contains the oldest rocks of the European continent with a thickness of 250–300 km. The Baltic Shield is divided into five ''provinces'': the Svecofennian and Sveconorwegian (or Southwestern gneiss) provinces in Fennoscandia, and the Karelian, Belomorian and Kola provinces in Russia. The latter three are divided further into several ''blocks'' and ''complexes'' and contain the oldest of the rocks, at 2500-3100 Ma (million years) old. The youngest rocks belong to the Sveconorwegian province, at 900-1700 Ma old. Thought to be formerly part of an ancient continent, the Baltic Shield grew in size through collisions with n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Cambrian Peneplain
The sub-Cambrian peneplain is an ancient, extremely flat, erosion surface (peneplain) that has been exhumed and exposed by erosion from under Cambrian strata over large swathes of Fennoscandia. Eastward, where this peneplain dips below Cambrian and other Lower Paleozoic cover rocks. The exposed parts of this peneplain are extraordinarily flat with relief of less than 20 m. The overlying cover rocks demonstrate that the peneplain was flooded by shallow seas during the Early Paleozoic. Being the oldest identifiable peneplain in its area the Sub-Cambrian peneplain qualifies as a primary peneplain. The surface was first identified by Arvid Högbom in a 1910 publication, with Sten Rudberg publishing the first extensive map in 1954. This mapping has been improved upon by Karna Lidmar-Bergström since the 1980s. Extent The Sub-Cambrian peneplain extends as an almost continuous belt along the eastern coast of Sweden for some 700 km from north to south. Near Stockholm and Hudiksvall the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian Research
''Precambrian Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the geology of the Earth and its planetary neighbors. It is published by Elsevier and, , the editors-in-chief are V. Pease (Stockholm University) and G.C. Zhao (University of Hong Kong). It was established in 1974. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2013 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 6.023. References External links * * Geology journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Publications established in 1974 {{geology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary History Of Plants
The evolution of plants has resulted in a wide range of complexity, from the earliest algal mats, through multicellular marine and freshwater green algae, terrestrial bryophytes, lycopods and ferns, to the complex gymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants) of today. While many of the earliest groups continue to thrive, as exemplified by red and green algae in marine environments, more recently derived groups have displaced previously ecologically dominant ones; for example, the ascendance of flowering plants over gymnosperms in terrestrial environments. There is evidence that cyanobacteria and multicellular photosynthetic eukaryotes lived in freshwater communities on land as early as 1 billion years ago, and that communities of complex, multicellular photosynthesizing organisms existed on land in the late Precambrian, around . Evidence of the emergence of embryophyte land plants first occurs in the mid-Ordovician (~), and by the middle of the Devonian (~), many of the featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago. It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic Era and succeeded by the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The most severe glaciation known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian, when ice sheets may have reached the equator and formed a " Snowball Earth". The earliest fossils of complex multicellular life are found in the Ediacaran Period. These organisms make up the Ediacaran biota, including the oldest definitive animals in the fossil record. According to Rino and co-workers, the sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. Geology At the onset of the Neoproterozoic the supercontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texa ... and United States customary units#Units of area, US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the International yard and pound, international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainstorm
Rain is liquid water in the form of droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then become heavy enough to fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems, as well as water for hydroelectric power plants and crop irrigation. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |