|
Shared Parenting Marriage
Shared may refer to: * Sharing * Shared ancestry or Common descent * Shared care * Shared-cost service * Shared decision-making in medicine * Shared delusion, various meanings * Shared government * Shared intelligence or collective intelligence * Shared library * Shared morality * Shared ownership * Shared parenting or shared custody * Shared property * Shared reading * Shared secret * Shared services * Shared universe, in fiction * Shared vision planning, in irrigation * Shared workspace Science and technology * Shared medium, in telecommunication * Shared neutral, in electric circuitry * Shared pair, in chemistry *Shared vertex (or shared corner or common corner), point of contact between polygons, polyhedra, etc. *Shared edge, line of contact between polygons, polyhedra, etc. Computing * Shared agenda, in groupware * Shared computing * Shared desktop * Shared data structure * Shared IP address * Shared-memory architecture * Shared memory (interprocess communication) * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharing
Sharing is the joint use of a resource or space. It is also the process of dividing and distributing. In its narrow sense, it refers to joint or alternating use of inherently finite goods, such as a common pasture or a shared residence. Still more loosely, "sharing" can actually mean giving something as an outright gift: for example, to "share" one's food really means to give some of it as a gift. Sharing is a basic component of human interaction, and is responsible for strengthening social ties and ensuring a person’s well-being. Apart from obvious instances, which can be observed in human activity, many examples can be found in nature. When an organism takes in nutrition or oxygen, for instance, its internal organs are designed to divide and distribute the energy taken in, to supply parts of its body that need it. Flowers divide and distribute their seeds. In a broader sense, it can also include free granting of use rights to goods that can be treated as Rivalry (economics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Vision Planning
Shared vision planning was developed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers during the National Drought Study (1989–1993). At the end of the Drought Study, Shared vision planning had three basic elements: (1) an updated version of the systems approach to water resources management developed during the Harvard Water Program; (2) an approach to public involvement called "Circles of Influence"; and (3) collaboratively built computer models of the system to be managed. Alternative dispute resolution methods are often used to bring people in conflict to the table, and to resolve differences that occur during planning. A method of collaborative decision making called "Informed consent" is used to make decisions internally consistent, more defensible and transparent. The three original basic elements Each of the three original elements in shared vision planning has an evolutionary history leading to it. The Harvard Water Program planning approach (documented in a 1962 book, "Design of Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared-memory Architecture
A shared-memory architecture (SM) is a distributed computing Software architecture, architecture in which the nodes share the same memory as well as the same storage.{{Cite web , title=Memory: Shared vs Distributed - UFRC , url=https://help.rc.ufl.edu/doc/Memory:_Shared_vs_Distributed , access-date=2024-03-13 , website=help.rc.ufl.edu It contrasts with shared-nothing architecture, in which each node has distinct memory and storage, and with shared-disk architecture, in which the nodes share the same storage but not the same memory. This is distinct from the use of shared memory between different programs or threads on a single node, with or without multiprocessing. See also * Distributed database * Shared memory References Distributed computing architecture External links *The Case for Shared Nothing. ''www.linkedin.com''. * Garrod, Charlie (2023).Lecture #21: Introduction to Distributed Databases (PDF). ''Carnegie Mellon University - School of Computer Science''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface identification, and location addressing. Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) was the first standalone specification for the IP address, and has been in use since 1983. IPv4 addresses are defined as a 32-bit number, which became too small to provide enough addresses as the internet grew, leading to IPv4 address exhaustion over the 2010s. Its designated successor, IPv6, uses 128 bits for the IP address, giving it a larger address space. Although IPv6 deployment has been ongoing since the mid-2000s, both IPv4 and IPv6 are still used side-by-side . IP addresses are usually displayed in a human-readable notation, but systems may use them in various different computer number formats. CIDR notation can also be used to designate how much of the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Data Structure
In computer science, a concurrent data structure (also called shared data structure) is a data structure designed for access and modification by multiple computing threads (or processes or nodes) on a computer, for example concurrent queues, concurrent stacks etc. The concurrent data structure is typically considered to reside in an abstract storage environment known as shared memory, which may be physically implemented as either a tightly coupled or a distributed collection of storage modules. Basic principles Concurrent data structures, intended for use in parallel or distributed computing environments, differ from "sequential" data structures, intended for use on a uni-processor machine, in several ways. Most notably, in a sequential environment one specifies the data structure's properties and checks that they are implemented correctly, by providing safety properties. In a concurrent environment, the specification must also describe liveness properties which an impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Desktop
Desktop sharing is a common name for technologies and products that allow remote access and remote collaboration on a person's computer desktop through a graphical terminal emulator. The most common two scenarios for desktop sharing are: * Remote login * Real-time collaboration ''Remote log-in'' allows users to connect to their own desktop while being physically away from their computer. Systems that support the X Window System, typically Unix-based ones, have this ability "built in". Windows versions starting from Windows 2000 have a built-in solution for remote access as well in the form of Remote Desktop Protocol and prior to that in the form of Microsoft’s NetMeeting. Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a cross-platform solution accomplished through a common client/server model. The client, or VNC viewer, is installed on a local computer and then connects to the network via a server component, which is installed on a remote computer. In a typical VNC session, all keystr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Computing
Grid computing is the use of widely distributed computer resources to reach a common goal. A computing grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve many files. Grid computing is distinguished from conventional high-performance computing systems such as cluster computing in that grid computers have each node set to perform a different task/application. Grid computers also tend to be more heterogeneous and geographically dispersed (thus not physically coupled) than cluster computers. Although a single grid can be dedicated to a particular application, commonly a grid is used for a variety of purposes. Grids are often constructed with general-purpose grid middleware software libraries. Grid sizes can be quite large. Grids are a form of distributed computing composed of many networked loosely coupled computers acting together to perform large tasks. For certain applications, distributed or grid computing can be seen as a special type o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
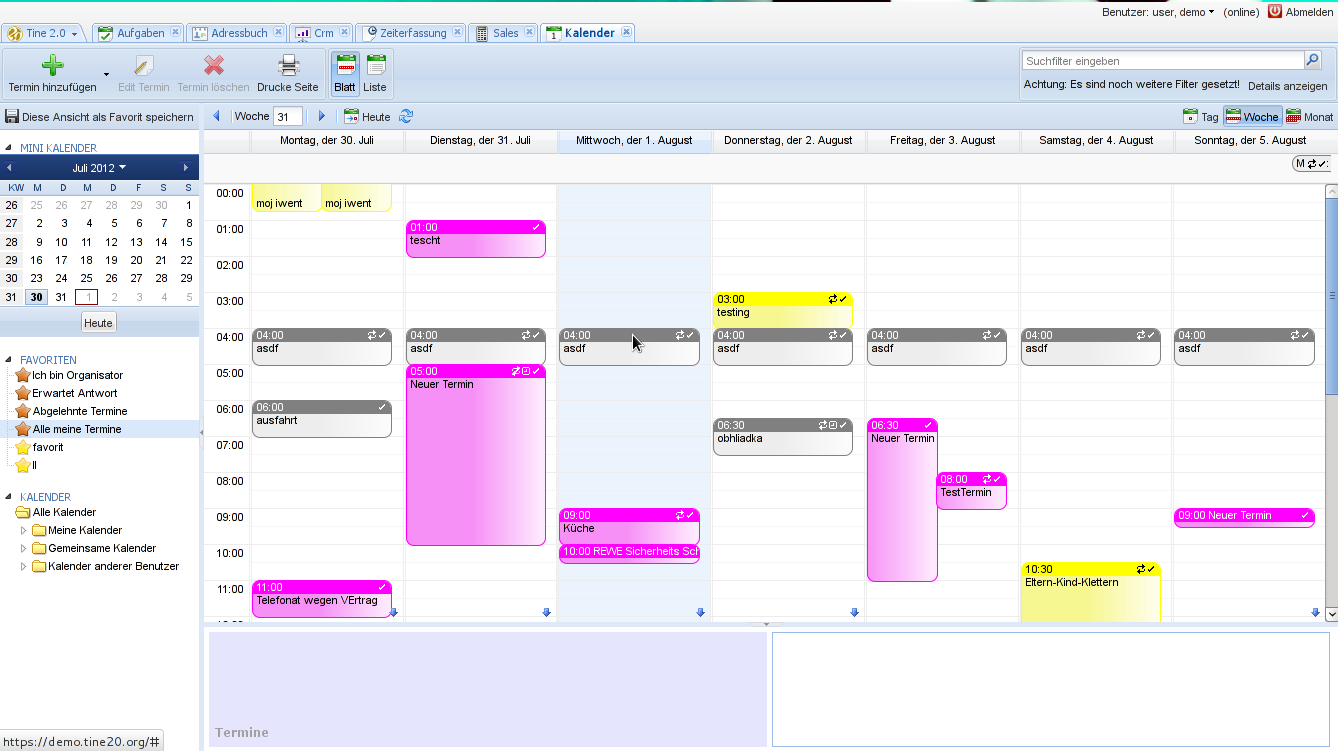
Shared Agenda
A digital calendar is a collaborative or personal time management software with a calendar that can be used to keep track of planned events. The calendar can also contain an appointment book, address book or contact list. Common features of digital calendars are that users can: * Enter their own events * Change the visibility (whether events, groups of events or entire calendars are private, shared with selected users/user groups, or are public) * Subscribe to other calendars * Set up meetings that can be shared or where others can be invited * Different options for setting up reminders There are several varieties of digital calendars. Some have the ability to be connected or synchronized with other calendars across different vendors. The iCalendar 1.0 and 2.0 specifications and its associated standards have been a cornerstone of the standardization and interoperability of calendar software across different vendors. A digital calendar can be viewed as an extension of many of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge (geometry)
In geometry, an edge is a particular type of line segment joining two vertex (geometry), vertices in a polygon, polyhedron, or higher-dimensional polytope. In a polygon, an edge is a line segment on the boundary, and is often called a polygon side. In a polyhedron or more generally a polytope, an edge is a line segment where two Face (geometry), faces (or polyhedron sides) meet. A segment joining two vertices while passing through the interior or exterior is not an edge but instead is called a diagonal. An ''edge'' may also be an infinite line (geometry), line separating two half-planes. The ''sides'' of a plane angle are semi-infinite Half-line (geometry), half-lines (or rays). Relation to edges in graphs In graph theory, an Edge (graph theory), edge is an abstract object connecting two vertex (graph theory), graph vertices, unlike polygon and polyhedron edges which have a concrete geometric representation as a line segment. However, any polyhedron can be represented by its n-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (: vertices or vertexes), also called a corner, is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or line segments Tangency, meet or Intersection (geometry), intersect. For example, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the point where edge (geometry), edges of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra meet are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Pair
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including sigma bond, σ-bonding, pi bond, π-bonding, Metallic bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term "covalence" was introduced by Irving Langmuir in 1919, with Nevil Sidgwick using "co-valent link" in the 1920s. Merriam-Webster dates the specific phrase ''covalent bond'' to 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |