|
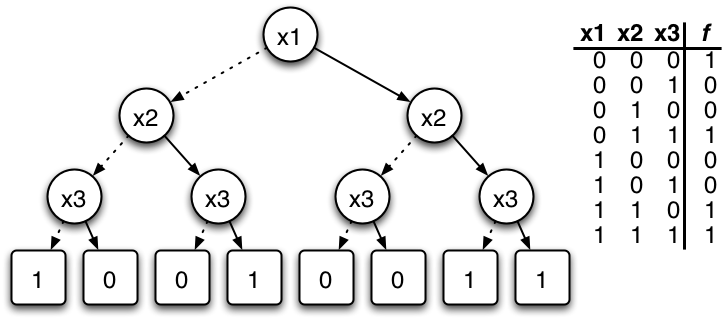
Shannon Expansion
Boole's expansion theorem, often referred to as the Shannon expansion or decomposition, is the identity: F = x \cdot F_x + x' \cdot F_, where F is any Boolean function, x is a variable, x' is the complement of x, and F_xand F_ are F with the argument x set equal to 1 and to 0 respectively. The terms F_x and F_ are sometimes called the positive and negative Shannon cofactors, respectively, of F with respect to x. These are functions, computed by restrict operator, \operatorname(F, x, 0) and \operatorname(F, x, 1) (see valuation (logic) and partial application). It has been called the "fundamental theorem of Boolean algebra". Besides its theoretical importance, it paved the way for binary decision diagrams (BDDs), satisfiability solvers, and many other techniques relevant to computer engineering and formal verification of digital circuits. In such engineering contexts (especially in BDDs), the expansion is interpreted as a if-then-else, with the variable x being the condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity (mathematics)
In mathematics, an identity is an equality relating one mathematical expression ''A'' to another mathematical expression ''B'', such that ''A'' and ''B'' (which might contain some variables) produce the same value for all values of the variables within a certain range of validity. In other words, ''A'' = ''B'' is an identity if ''A'' and ''B'' define the same functions, and an identity is an equality between functions that are differently defined. For example, (a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2 and \cos^2\theta + \sin^2\theta =1 are identities. Identities are sometimes indicated by the triple bar symbol instead of , the equals sign. Common identities Algebraic identities Certain identities, such as a+0=a and a+(-a)=0, form the basis of algebra, while other identities, such as (a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab +b^2 and a^2 - b^2 = (a+b)(a-b), can be useful in simplifying algebraic expressions and expanding them. Trigonometric identities Geometrically, trigonometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unate Function
A unate function is a type of boolean function which has monotonic properties. They have been studied extensively in switching theory. A function f(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n) is said to be positive unate in x_i if for all possible values of x_j, j\neq i :f(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_,1,x_,\ldots,x_n) \ge f(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_,0,x_,\ldots,x_n).\, Likewise, it is negative unate in x_i if :f(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_,0,x_,\ldots,x_n) \ge f(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_,1,x_,\ldots,x_n).\, If for every x_i ''f'' is either positive or negative unate in the variable x_i then it is said to be unate (note that some x_i may be positive unate and some negative unate to satisfy the definition of unate function). A function is binate if it is not unate (i.e., is neither positive unate nor negative unate in at least one of its variables). For example, the logical disjunction function ''or'' with boolean values used for true (1) and false (0) is positive unate. Conversely, Exclusive or Exclusive or or exclusive disjunction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed–Muller Expansion
In Boolean logic, a Reed–Muller expansion (or Davio expansion) is a decomposition of a Boolean function. For a Boolean function f(x_1,\ldots,x_n) : \mathbb^n \to \mathbb we call : \begin f_(x) & = f(x_1,\ldots,x_,1,x_,\ldots,x_n) \\ f_(x)& = f(x_1,\ldots,x_,0,x_,\ldots,x_n) \end the positive and negative cofactors of f with respect to x_i, and : \begin \frac & = f_(x) \oplus f_(x) \end the boolean derivation of f with respect to x_i, where denotes the XOR operator. Then we have for the Reed–Muller or positive Davio expansion: : f = f_ \oplus x_i \frac. Description This equation is written in a way that it resembles a Taylor expansion of f about x_i=0. There is a similar decomposition corresponding to an expansion about x_i=1 (negative Davio expansion): : f = f_ \oplus \overline_i \frac. Repeated application of the Reed–Muller expansion results in an XOR polynomial in x_1,\ldots,x_n: : f = a_1 \oplus a_2 x_1 \oplus a_3 x_2 \oplus a_4 x_1 x_2 \oplus \ldots \oplu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell System Technical Journal
The ''Bell Labs Technical Journal'' is the in-house scientific journal for scientists of Nokia Bell Labs, published yearly by the IEEE society. The managing editor is Charles Bahr. The journal was originally established as the ''Bell System Technical Journal'' (BSTJ) in New York by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1922, published under this name until 1983, when the breakup of the Bell System placed various parts of the system into separate companies. The journal was devoted to the scientific fields and engineering disciplines practiced in the Bell System for improvements in the wide field of electrical communication. After the restructuring of Bell Labs in 1984, the journal was renamed to ''AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal''. In 1985, it was published as the ''AT&T Technical Journal'' until 1996, when it was renamed to ''Bell Labs Technical Journal''. History The ''Bell System Technical Journal'' was published by AT&T in New York City through its I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications, Inc
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many illegal migrant crossings during the English channel migrant crisis. The Port of Dover provides mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of 2^n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output. A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean functions of multiple variables. Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device taking a single input and selecting signals of the output of the compatible mux, which is connected to the single input, and a shared selection line. A multiplexer is often used with a compleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switching Circuit Theory
Switching circuit theory is the mathematical study of the properties of networks of idealized switches. Such networks may be strictly combinational logic, in which their output state is only a function of the present state of their inputs; or may also contain sequential elements, where the present state depends on the present state and past states; in that sense, sequential circuits are said to include "memory" of past states. An important class of sequential circuits are state machines. Switching circuit theory is applicable to the design of telephone systems, computers, and similar systems. Switching circuit theory provided the mathematical foundations and tools for digital system design in almost all areas of modern technology. In an 1886 letter, Charles Sanders Peirce described how logical operations could be carried out by electrical switching circuits. During 1880–1881 he showed that NOR gates alone (or alternatively NAND gates alone) can be used to reproduce the funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decision Diagrams
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression. Similar data structures include negation normal form (NNF), Zhegalkin polynomials, and propositional directed acyclic graphs (PDAG). Definition A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed, acyclic graph, which consists of several (decision) nodes and two terminal nodes. The two terminal nodes are labeled 0 (FALSE) and 1 (TRUE). Each (decision) node u is labeled by a Boolean variable x_i and has two child nodes called low child and high child. The edge from node u to a low (or high) child represents an assignment of the value FALSE (or TRUE, respectively) to variable x_i. Such a BDD is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, and cryptographer known as a "father of information theory". As a 21-year-old master's degree student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), he wrote his thesis demonstrating that electrical applications of Boolean algebra could construct any logical numerical relationship. Shannon contributed to the field of cryptanalysis for national defense of the United States during World War II, including his fundamental work on codebreaking and secure telecommunications. Biography Childhood The Shannon family lived in Gaylord, Michigan, and Claude was born in a hospital in nearby Petoskey. His father, Claude Sr. (1862–1934), was a businessman and for a while, a judge of probate in Gaylord. His mother, Mabel Wolf Shannon (1890–1945), was a language teacher, who also served as the principal of Gaylord High School. Claude Sr. was a descendant of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Laws Of Thought
''An Investigation of the Laws of Thought on Which are Founded the Mathematical Theories of Logic and Probabilities'' by George Boole, published in 1854, is the second of Boole's two monographs on algebraic logic. Boole was a professor of mathematics at what was then Queen's College, Cork (now University College Cork), in Ireland. Review of the contents The historian of logic John Corcoran wrote an accessible introduction to ''Laws of Thought''George Boole. 1854/2003. ''The Laws of Thought'', facsimile of 1854 edition, with an introduction by J. Corcoran. Buffalo: Prometheus Books (2003). Reviewed by James van Evra in Philosophy in Review.24 (2004) 167–169. and a point by point comparison of ''Prior Analytics'' and ''Laws of Thought''.John Corcoran, Aristotle's Prior Analytics and Boole's Laws of Thought, ''History and Philosophy of Logic'', 24 (2003), pp. 261–288. According to Corcoran, Boole fully accepted and endorsed Aristotle's logic. Boole's goals were “to go und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Boole
George Boole (; 2 November 1815 – 8 December 1864) was a largely self-taught English mathematician, philosopher, and logician, most of whose short career was spent as the first professor of mathematics at Queen's College, Cork in Ireland. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, and is best known as the author of '' The Laws of Thought'' (1854) which contains Boolean algebra. Boolean logic is credited with laying the foundations for the Information Age. Early life Boole was born in 1815 in Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England, the son of John Boole senior (1779–1848), a shoemaker and Mary Ann Joyce. He had a primary school education, and received lessons from his father, but due to a serious decline in business, he had little further formal and academic teaching. William Brooke, a bookseller in Lincoln, may have helped him with Latin, which he may also have learned at the school of Thomas Bainbridge. He was self-taught in modern la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Differential Calculus
Boolean differential calculus (BDC) (German: (BDK)) is a subject field of Boolean algebra discussing changes of Boolean variables and Boolean functions. Boolean differential calculus concepts are analogous to those of classical differential calculus, notably studying the changes in functions and variables with respect to another/others.H. WehlanBoolean Algebra in ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The Boolean differential calculus allows various aspects of dynamical systems theory such as * automata theory on finite automata * Petri net theory * supervisory control theory (SCT) to be discussed in a united and closed form, with their individual advantages combined. History and applications Originally inspired by the design and testing of switching circuits and the utilization of error-correcting codes in electrical engineering, the roots for the development of what later would evolve into the Boolean differential calculus were initiated by works of Irving S. Reed, Dav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |