|
Shahin Missile System
The Shahin ( fa, شاهین) missile is an Iranian supersonic mid-range low to mid-altitude surface-to-air missile. It is an Iranian version of the American MIM-23 Hawk and is thus designed for use with the Mersad air defense system. Unveiling and testing The shahin missiles were developed as part of a domestic weapons program that Iran started in 1992 as a response to increasing American sanctions against Iran. The Shahin missiles were first unveiled in April 2010. They were then tested on November 16, 2010 along with the Mersad air defense system during the war games Defenders of the Sky of the Velayat III, the maneuvers were themselves carried out to prepare for a hypothetical Israeli assault on Iranian nuclear facilities. The missile was tested again on 13 June 2011 shortly before entering service. Characteristics The missile is considered low to mid-altitude and mid-range low with a range of 70-150 km. The missile is also suggested to be supersonic by various sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Wings
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ). Although long studied, it did not find significant applications until the Jet Age, when it proved suitable for high-speed subsonic and supersonic flight. At the other end of the speed scale, the Rogallo flexible wing proved a practical design for the hang glider and other ultralight aircraft. The delta wing form has unique aerodynamic characteristics and structural advantages. Many design variations have evolved over the years, with and without additional stabilising surfaces. General characteristics Structure The long root chord of the delta wing and minimal structure outboard make it structurally efficient. It can be built stronger, stiffer and at the same time lighter than a swept wing of equivalent lifting capability. Because of this it is easy and relatively inexpensive to build – a substantial factor in the success of the MiG-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missiles Of Iran
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
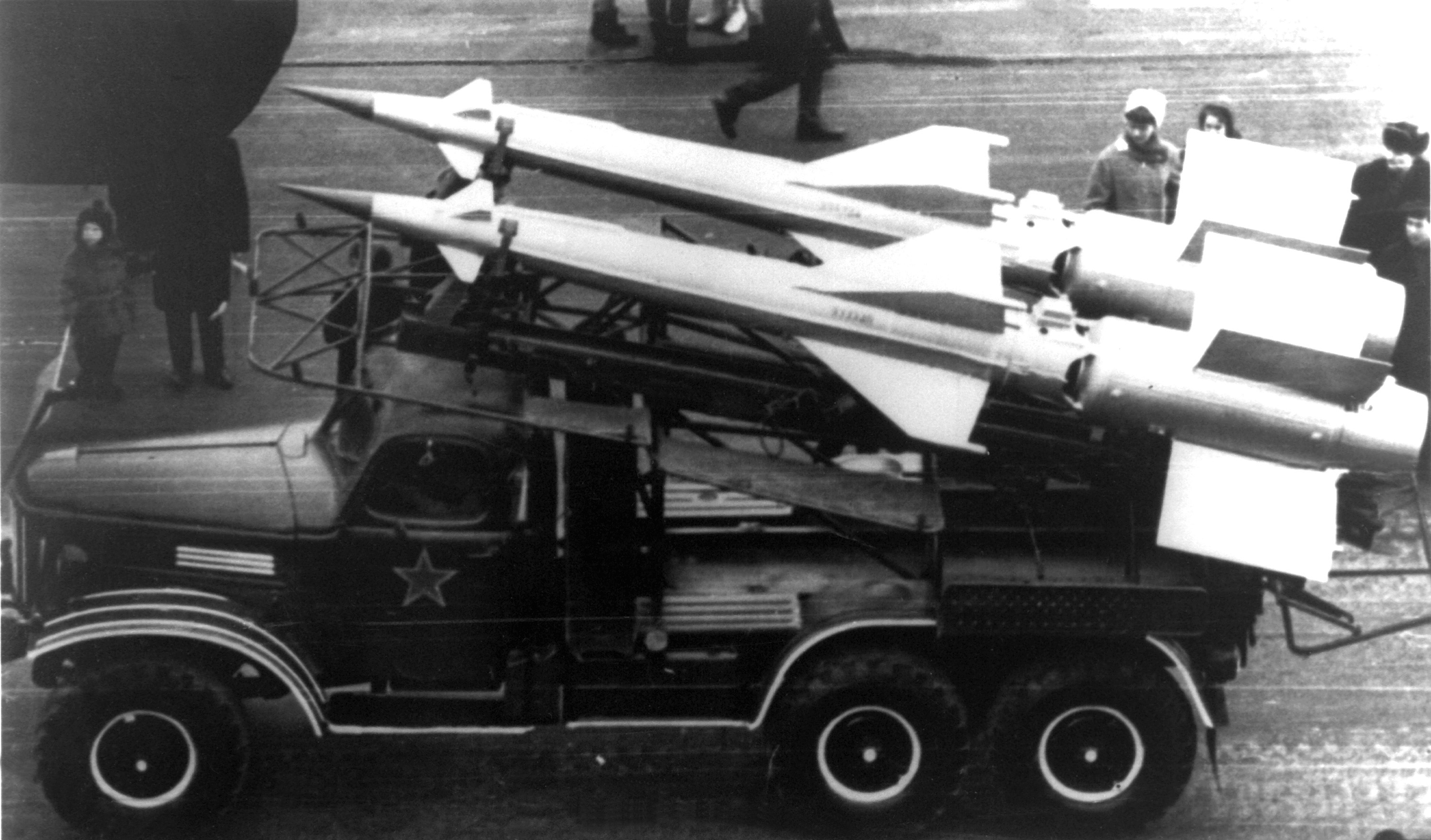
S-125 Neva/Pechora
The S-125 ''Neva/Pechora'' (russian: С-125 "Нева"/"Печора", NATO reporting name SA-3 ''Goa'') is a Soviet surface-to-air missile system that was designed by Aleksei Isaev to complement the S-25 and S-75. It has a shorter effective range and lower engagement altitude than either of its predecessors and also flies slower, but due to its two-stage design it is more effective against more maneuverable targets. It is also able to engage lower flying targets than the previous systems, and being more modern it is much more resistant to ECM than the S-75. The 5V24 (V-600) missiles reach around Mach 3 to 3.5 in flight, both stages powered by solid fuel rocket motors. The S-125, like the S-75, uses radio command guidance. The naval version of this system has the NATO reporting name SA-N-1 Goa and original designation M-1 Volna (Russian Волна – ''wave''). Operational history Soviet Union The S-125 was first deployed between 1961 and 1964 around Moscow, augmenting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalamcheh (missile)
Shalamcheh ( fa, شلمچه) is an Iranian surface-to-air missile claimed to be capable of destroying several sorts of modern fighter jets and drones. This missile is launched from the Mersad domestic air defense system. Shalamcheh is considered as a medium-range missile which can also be utilized as a short-range missile. It travels at the speed of Mach 3, is resistant to enemy electronic warfare Electronic warfare (EW) is any action involving the use of the electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum) or directed energy to control the spectrum, attack an enemy, or impede enemy assaults. The purpose of electronic warfare is to deny the opponen ..., and its average range is 40 kilometres. Military tests On 5 May 2014, the army of Iran successfully test-fired Shalamcheh missile, where it shot down the Iranian domestic drone Karrar. In November 2018, air defense drills were held in the central, northern and western parts of Iran. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabas (air Defense System)
The Tabas ( fa, طبس) missile-system is an Iranian medium range road-mobile aerial defense system that was first revealed on 11 May 2014. It is believed to be another version of the Ra'ad air defense system along with Sevom Khordad. The name of the air defense system refers to Operation Eagle Claw which took place at Tabas and hence the name of the missile system. Characteristics The missile system resembles the Buk-M1 missile system due to its lets sophisticated radar system. The speed of its TELAR is estimated to be 65 km/h, each vehicle can carry 3 missiles. It is also likely that the system can intercept ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, anti-radiation missiles, smart bombs and UAVs. Each Tabas battery consists of one TELAR and two TELs hence each battery carries 9 missiles. Each battalion consists of four batteries and hence can engage multiple targets simultaneously. Each battalion is also equipped with a Bashir S-band 3-D Phased array radar Radar is a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taer-2
The Taer 2 ( fa, طائر, meaning "bird") is an Iranian mid-range radar guided solid fueled surface-to-air missile designed to defend against aerial threats at altitudes of up to 25–27 km (75000 ft) and distances of up to 50 km away. It is meant for use as part of the Ra'ad air defense system, and was revealed during a military parade in Tehran on 21 September 2012. It shows similarities to the 9M317 missile just as the Raad air defense system does to the Buk missile system. History During Velayat 91 maneuvers in December 2012 the Iranian Navy , ''Daryādelān''"Seahearts" , patron = , motto = fa, راه ما، راه حسین است, ''Rāh-e ma, rāh-e hoseyn ast''"''Our Path, Is Hussain's Path''" , colors = , ... successfully tested the Raad Air Defense System but it is not clear if the Raad missile tested in Iranian Navy is the same one as the Taer-2 missile of Raad system des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyad-1
Sayyad ( fa, صیاد, Hunter) is a serie of solid fuel surface-to-air missiles (SAM) manufactured by Iran. Sayyad-1 Sayyad-1 is the Iranian upgraded version of the Chinese HQ-2 SAM, however it differs from the Chinese versions in guidance and control subsystems. Sayyad-1 is equipped with an about 200-kilogram warhead and has a speed of about 1,200 meters per second. The said missile is very different from the rest of Sayyad family of missiles (Sayyad-2 and the successor missiles are based on US designed RIM-66 Standard missiles). Sayyad-2 The Sayyad-2 is a canister-launched, reverse engineered version of the RIM-66 Standard Missile (SM-1) naval surface-to-air missile that Iran obtained from the United States before the 1979 revolution. It is an upgraded version of the Sayyad-1 system with higher precision, range and defensive power. The range of the Sayyad-2 missile is not known. Different sources claim various numbers, from 60 km to 120 km. After the unveil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Ballistics
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or in the vacuum of space, but most certainly flying under the influence of a gravitational field. Gun-launched projectiles may be unpowered, deriving all their velocity from the propellant's ignition until the projectile exits the gun barrel. However, exterior ballistics analysis also deals with the trajectories of rocket-assisted gun-launched projectiles and gun-launched rockets; and rockets that acquire all their trajectory velocity from the interior ballistics of their on-board propulsion system, either a rocket motor or air-breathing engine, both during their boost phase and after motor burnout. External ballistics is also concerned with the free-flight of other projectiles, such as balls, arrows etc. Forces acting on the projectile W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)