|
Setting Circles
Setting circles are used on telescopes equipped with an equatorial mount to find astronomical objects in the sky by their equatorial coordinates often used in star charts or ephemerides. Description Setting circles consist of two graduated disks attached to the axes – right ascension (RA) and declination (DEC) – of an equatorial mount. The RA disk is graduated into hours, minutes, and seconds. The DEC disk is graduated into degrees, arcminutes, and arcseconds. Since the RA coordinates are fixed onto the celestial sphere, the RA disk is usually driven by a clock mechanism in sync with sidereal time. Locating an object on the celestial sphere using setting circles is similar to finding a location on a terrestrial map using latitude and longitude. Sometimes the RA setting circle has two scales on it: one for the Northern Hemisphere and one for the Southern. Application Research telescopes Historically setting circles have rivaled the telescopes optics as far as difficulty in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setting Circles Equatorial Mount
Setting may refer to: * A location (geography) where something is set * Set construction in theatrical scenery * Setting (narrative), the place and time in a work of narrative, especially fiction * Setting up to fail a manipulative technique to engineer failure * Stonesetting, in jewelry, when a diamond or gem is set into a frame or bed * Campaign setting in role playing play * In computers and electronics, the computer configuration or options of the software or device ** Settings (Windows) * Typesetting * Set and setting, the context for psychedelic drug experiences * Setting (knot), the tightening of a knot * Musical setting, the composition of music for an existing text, usually in choral music Education * Ability grouping, small groups formed within a single classroom * Tracking (education), also called streaming, separating pupils by academic ability into groups for all subjects within a school * The location where the education takes place, for example the classroom A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
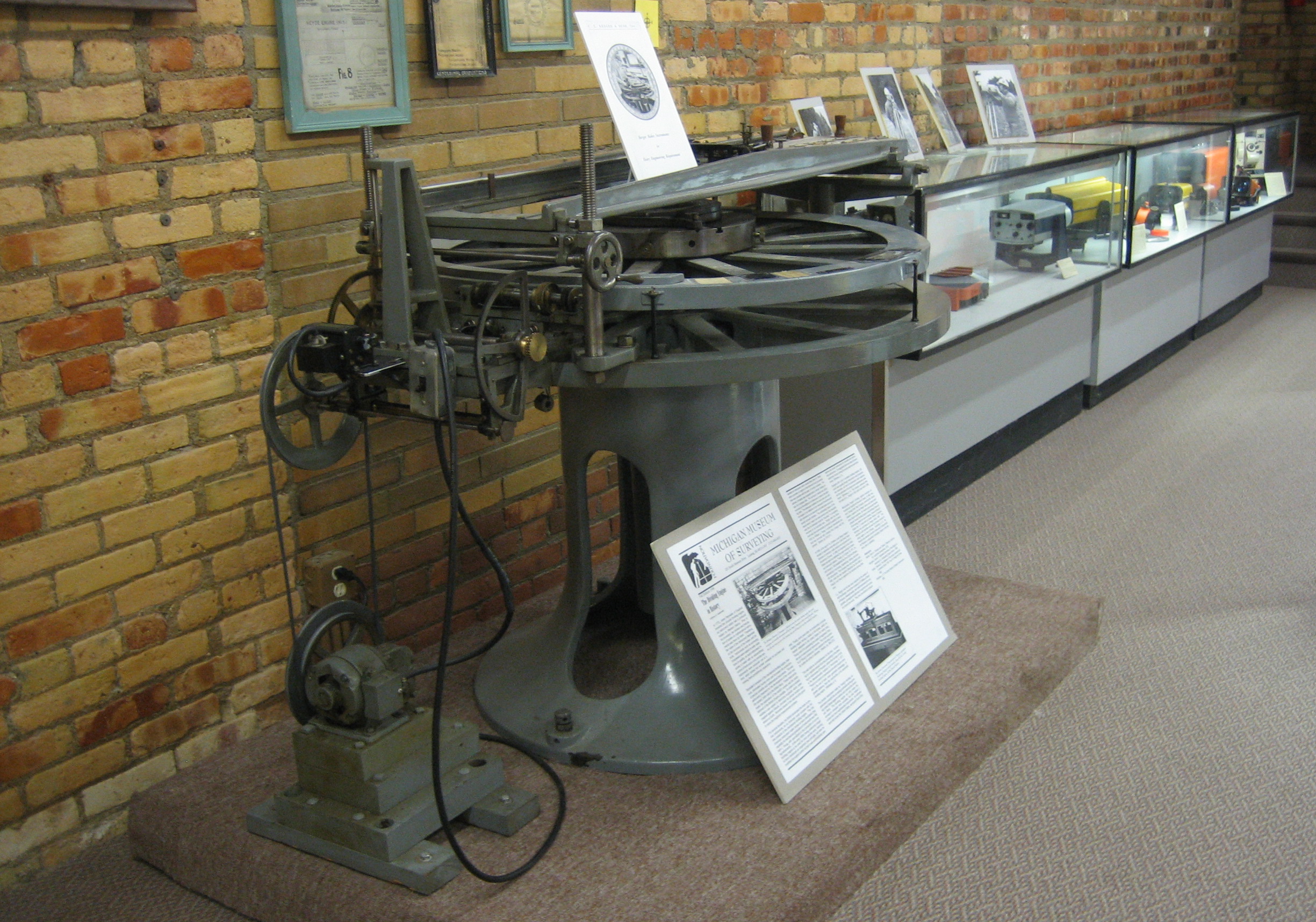
Dividing Engine
A dividing engine is a device employed to mark graduations on measuring instruments to allow for reading smaller measurements than can be allowed by directly engraving them. The well-known vernier scale and micrometer screw-gauge are classic examples that make use of such graduations. History There has always been a need for accurate measuring instruments. Whether it is a linear device such as a ruler or vernier or a circular device such as a protractor, astrolabe, sextant, theodolite, or setting circles for astronomical telescopes, the desire for ever greater precision has always existed. For every improvement in the measuring instruments, such as better alidades or the introduction of telescopic sights, the need for more exact graduations immediately followed. In early instruments, graduations were typically etched or scribed lines in wood, ivory or brass. Instrument makers devised various devices to perform such tasks. Early Islamic instrument makers must have had technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive (though indeed present-day mainframes such as the IBM System z machines use one or more custom microprocessors as their CPUs). Many microcomputers (when equipped with a keyboard and screen for input and output) are also personal computers (in the generic sense). An early use of the term ''personal computer'' in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. ''(See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below)''. A ''microcomputer'' used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Hopping
{{unreferenced, date=February 2015 Star hopping is a technique that amateur astronomers often use to locate astronomical objects in the night sky. It can be used instead of or in addition to setting circles or go-to/push-to systems. The problem Many celestial objects of interest are too faint to be visible to the unaided eye. Telescopes or binoculars collect much more light, making faint objects visible, but have a smaller field of view, thus complicating orientation on the sky. The field of view of binoculars is rarely more than eight degrees, while that of typical amateur telescopes may be substantially less than one degree, depending on the magnification used. Many objects are best observed using higher magnifications, which inevitably go along with narrow fields of view. The technique Star hopping uses bright stars as a guide to finding fainter objects. A knowledge of the relative positions of bright stars and target objects is essential. After planning the star hop with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the ( hour circle of the) point in question above the earth. When paired with declination, these astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system. An old term, ''right ascension'' ( la, ascensio recta), "''Ascensio recta'' Solis, stellæ, aut alterius cujusdam signi, est gradus æquatorus cum quo simul exoritur in sphæra recta"; roughly translated, "''Right ascension'' of the Sun, stars, or any other sign, is the degree of the equator that rises together in a right sphere" refers to the ''ascension'', or the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from Earth's equator, where the celestial equator intersects the horizon at a right angle. It contrasts with ''oblique ascension'', the point on the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
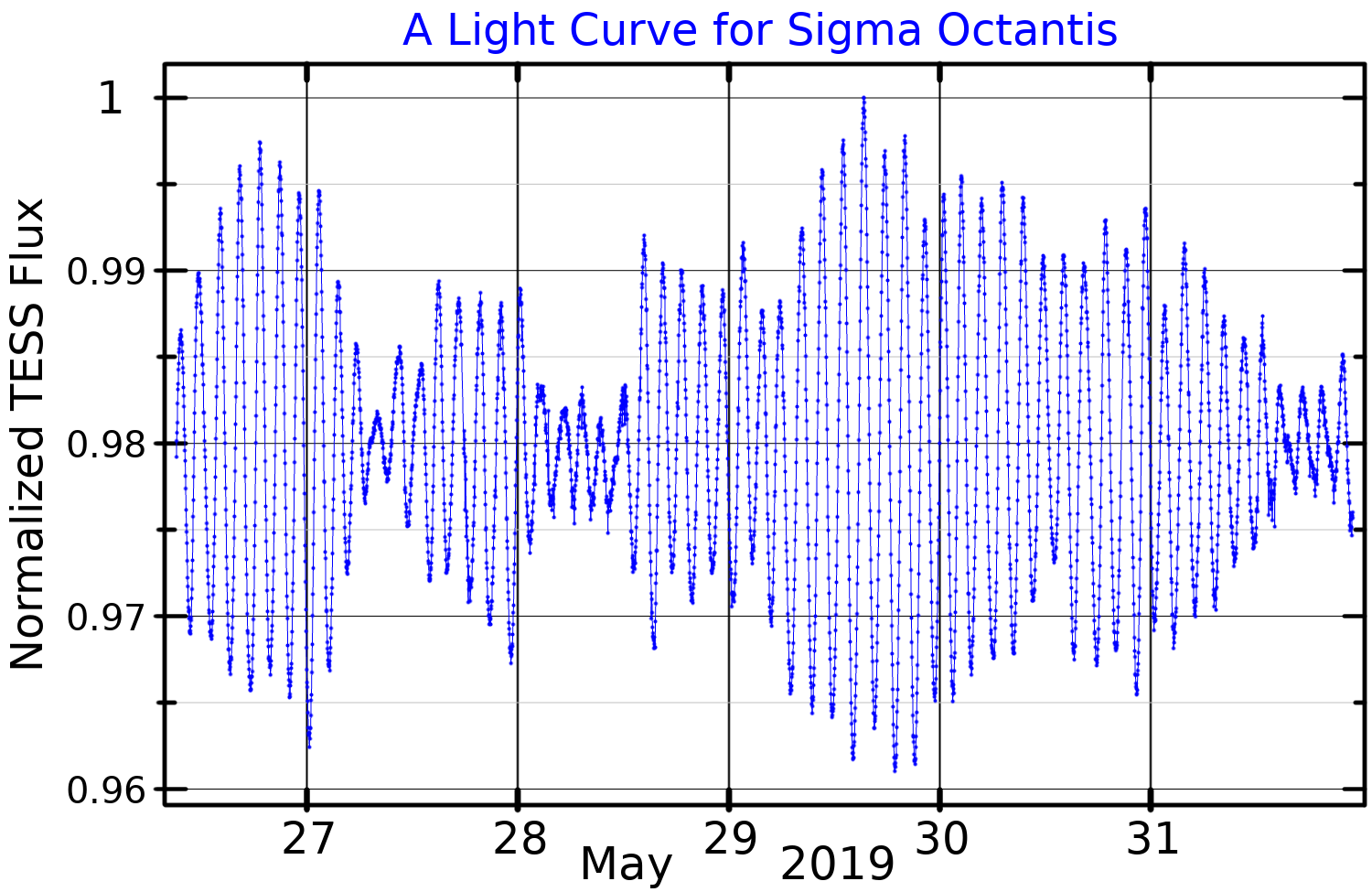
Sigma Octantis
Sigma Octantis is a solitary star in the Octans constellation that forms the pole star of the Southern Hemisphere. Its name is also written as σ Octantis, abbreviated as Sigma Oct or σ Oct, and it is officially named Polaris Australis (). The star is positioned one degree away from the southern celestial pole of the Southern Hemisphere, lying nearly opposite to the North Star. Located approximately from Earth, it is classified as a subgiant with a spectral type of F0 III. Sigma Octantis has an apparent magnitude of 5.5, but is slightly variable and is classified as a Delta Scuti variable. Nomenclature ''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation. As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Polaris Australis'' for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that fluctuates around 1.98, it is the brightest star in the constellation and is readily visible to the naked eye at night. The position of the star lies less than 1° away from the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star. The stable position of the star in the Northern Sky makes it useful for navigation. As the closest Cepheid variable its distance is used as part of the cosmic distance ladder. The revised ''Hipparcos'' stellar parallax gives a distance to Polaris of about , while the successor mission ''Gaia'' gives a distance of about . Calculations by other methods vary widely. Although appearing to the naked eye as a single point of light, Polaris is a triple star system, composed of the primary, a yellow super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
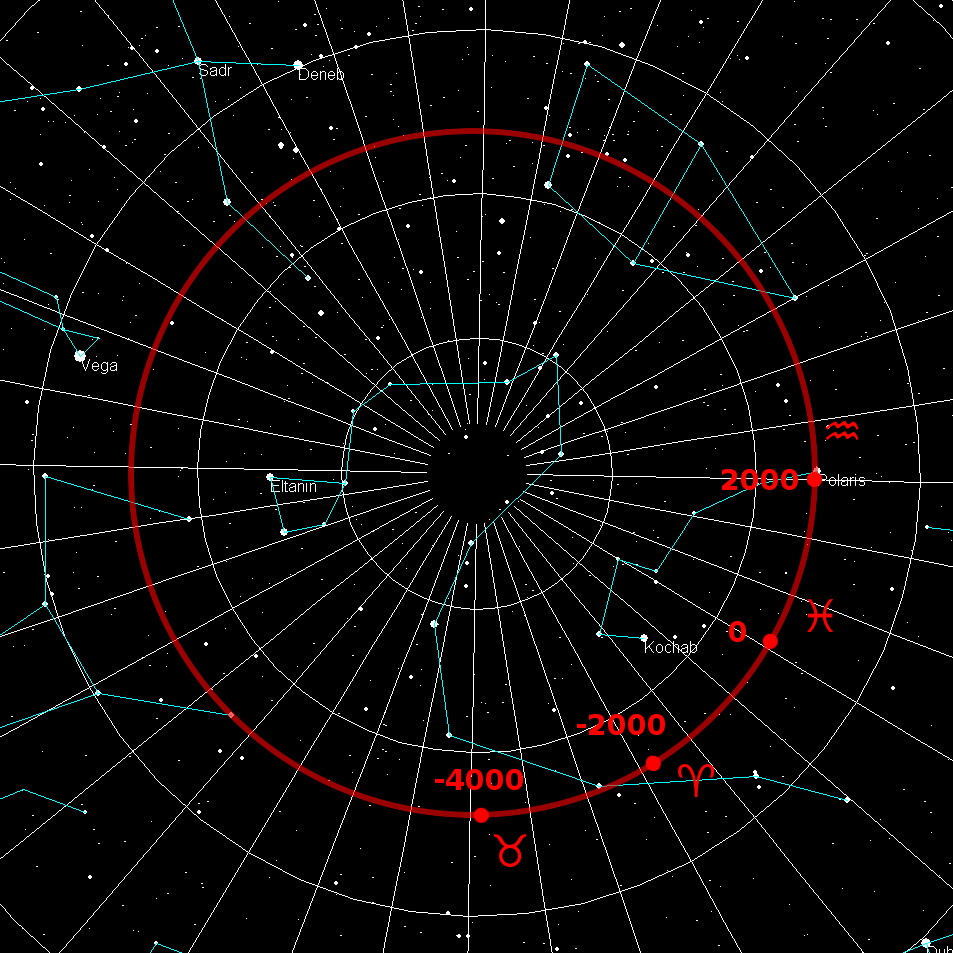
Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Alignment
Polar alignment is the act of aligning the rotational axis of a telescope's equatorial mount or a sundial's gnomon with a celestial pole to parallel Earth's axis. Alignment methods The method to use differs depending on whether the alignment is taking place in daylight or in night. Furthermore, the method differs if the alignment is done in the Northern Hemisphere or Southern Hemisphere. The purpose of the alignment also must be considered; for example, the value of accuracy is much more significant in astrophotography than in casual stargazing. Aiming at the pole stars In the Northern hemisphere, sighting Polaris the North Star is the usual procedure for aligning a telescope mount's polar axis parallel to the Earth's axis. Polaris is approximately three quarters of a degree from the North Celestial Pole, and is easily seen by the naked eye. σ Octantis, sometimes known as the South Star, can be sighted in the Southern hemisphere to perform polar alignment. At magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Astronomy
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers make contributions in doing citizen science, such as by monitoring variable stars, double stars, sunspots, or occultations of stars by the Moon or asteroids, or by discovering transient astronomical events, such as comets, galactic novae or supernovae in other galaxies. Amateur astronomers do not use the field of astronomy as their primary source of income or support, and usually have no professional degree in astrophysics or advanced academic training in the subject. Most amateurs are hobbyists, while others have a high degree of experience in astronomy and may often assist and work alongside professional astronomers. Many astronomers have studied the sky throughout history in an amateur framework; however, since the beginning o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Encoder
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to analog or digital output signals. There are two main types of rotary encoder: absolute and incremental. The output of an absolute encoder indicates the current shaft position, making it an angle transducer. The output of an incremental encoder provides information about the ''motion'' of the shaft, which typically is processed elsewhere into information such as position, speed and distance. Rotary encoders are used in a wide range of applications that require monitoring or control, or both, of mechanical systems, including industrial controls, robotics, photographic lenses, computer input devices such as optomechanical mice and trackballs, controlled stress rheometers, and rotating radar platforms. Technologies * Mechanical: Also known as conductive encoders. A series of circumferential copper tracks etched onto a PCB is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Minute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |