|
Set Operations (SQL)
Set operations allow the results of multiple queries to be combined into a single result set. Set operators include UNION, INTERSECT, and EXCEPT. UNION operator In SQL the UNION clause combines the results of two SQL queries into a single table of all matching rows. The two queries must result in the same number of columns and compatible data types in order to unite. Any duplicate records are automatically removed unless UNION ALL is used. UNION can be useful in data warehouse applications where tables are not perfectly normalized. A simple example would be a database having tables sales2005 and sales2006 that have identical structures but are separated because of performance considerations. A UNION query could combine results from both tables. Note that UNION ALL does not guarantee the order of rows. Rows from the second operand may appear before, after, or mixed with rows from the first operand. In situations where a specific order is desired, ORDER BY must be used. Note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Result Set
An SQL result set is a set of rows from a database, as well as metadata about the query such as the column names, and the types and sizes of each column. Depending on the database system, the number of rows in the result set may or may not be known. Usually, this number is not known up front because the result set is built on-the-fly. A result set is effectively a table Table may refer to: * Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs * Table (landform), a flat area of land * Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns * Table (database), how the table data .... The ORDER BY clause can be used in a query to impose a certain sort condition on the rows. Without that clause, there is no guarantee whatsoever on the order in which the rows are returned. Databases {{database-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table (database)
A table is a collection of related data held in a table format within a database. It consists of columns and rows. In relational databases, and flat file databases, a ''table'' is a set of data elements (values) using a model of vertical columns (identifiable by name) and horizontal rows, the cell being the unit where a row and column intersect. A table has a specified number of columns, but can have any number of rows. Each row is identified by one or more values appearing in a particular column subset. A specific choice of columns which uniquely identify rows is called the primary key. "Table" is another term for "relation"; although there is the difference in that a table is usually a multiset (bag) of rows where a relation is a set and does not allow duplicates. Besides the actual data rows, tables generally have associated with them some metadata, such as constraints on the table or on the values within particular columns. The data in a table does not have to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Row (database)
In the context of a relational database, a row—also called a tuple—represents a single, implicitly structured data item in a table. In simple terms, a database table can be thought of as consisting of ''rows'' and columns. Cory Janssen, Techopedia, retrieved 27 June 2014 Each row in a table represents a set of related data, and every row in the table has the same structure. For example, in a table that represents companies, each row would represent a single company. Columns might represent things like company name, company street address, whether the company is publicly held, its , etc. In a table that represents ''the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column (database)
In a relational database, a column is a set of data values of a particular type, one value for each row of the database.The term "column" also has equivalent applications in other, more generic contexts. See e.g., Flat file database, Table (information). A column may contain text values, numbers, or even pointers to files in the operating system. Columns typically contain simple types, though some relational database systems allow columns to contain more complex data types, such as whole documents, images, or even video clips. A column can also be called an attribute. Each row would provide a data value for each column and would then be understood as a single structured data value. For example, a database that represents company contact information might have the following columns: ID, Company Name, Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, and Postal Code. More formally, a row is a tuple containing a specific value for each column, for example: (1234, 'Big Company Inc.', '123 East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Type
In computer science and computer programming, a data type (or simply type) is a set of possible values and a set of allowed operations on it. A data type tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers (of varying sizes), floating-point numbers (which approximate real numbers), characters and Booleans. A data type constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function, might take. This data type defines the operations that can be done on the data, the meaning of the data, and the way values of that type can be stored. Concept A data type is a collection or grouping of data values. Such a grouping may be defined for many reasons: similarity, convenience, or to focus the attention. It is frequently a matter of good organization that aids the understanding of complex definitions. Almost all programming languages explicitly include the notion of da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
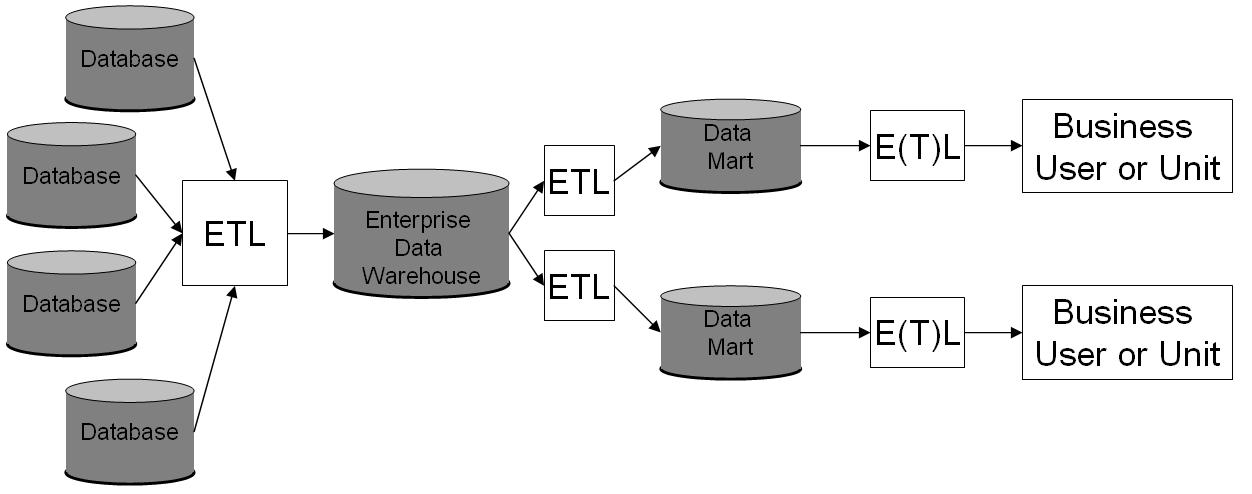
Data Warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Normalization
Database normalization or database normalisation (see spelling differences) is the process of structuring a relational database in accordance with a series of so-called normal forms in order to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. It was first proposed by British computer scientist Edgar F. Codd as part of his relational model. Normalization entails organizing the columns (attributes) and tables (relations) of a database to ensure that their dependencies are properly enforced by database integrity constraints. It is accomplished by applying some formal rules either by a process of ''synthesis'' (creating a new database design) or ''decomposition'' (improving an existing database design). Objectives A basic objective of the first normal form defined by Codd in 1970 was to permit data to be queried and manipulated using a "universal data sub-language" grounded in first-order logic. An example of such a language is SQL, though it is one that Codd regarded as se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join (SQL)
A join clause in SQL – corresponding to a join operation in relational algebra – combines columns from one or more tables into a new table. Informally, a join stitches two tables and puts on the same row records with matching fields : INNER, LEFT OUTER, RIGHT OUTER, FULL OUTER and CROSS. Example tables To explain join types, the rest of this article uses the following tables: Department.DepartmentID is the primary key of the Department table, whereas Employee.DepartmentID is a foreign key. Note that in Employee, "Williams" has not yet been assigned to a department. Also, no employees have been assigned to the "Marketing" department. This is the SQL statement to create the above tables: CREATE TABLE department( DepartmentID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, DepartmentName VARCHAR(20) ); CREATE TABLE employee ( LastName VARCHAR(20), DepartmentID INT REFERENCES department(DepartmentID) ); INSERT INTO department VALUES (31, 'Sales'), (33, 'Engineering'), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null (SQL)
In SQL, null or NULL is a special marker used to indicate that a data value does not exist in the database. Introduced by the creator of the relational database model, E. F. Codd, SQL null serves to fulfil the requirement that all ''true relational database management systems (RDBMS)'' support a representation of "missing information and inapplicable information". Codd also introduced the use of the lowercase Greek omega (ω) symbol to represent null in database theory. In SQL, NULL is a reserved word used to identify this marker. A null should not be confused with a value of 0. A null value indicates a lack of a value, which is not the same thing as a value of zero. For example, consider the question "How many books does Adam own?" The answer may be "zero" (we ''know'' that he owns ''none'') or "null" (we ''do not know'' how many he owns). In a database table, the column reporting this answer would start out with no value (marked by Null), and it would not be updated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003
File:2003 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The crew of STS-107 perished when the Space Shuttle Columbia Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, disintegrated during reentry into Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere; SARS became an 2002–2004 SARS outbreak, epidemic in China, and was a precursor to SARS-CoV-2; A destroyed building in Bam, Iran after the 2003 Bam earthquake killed 30,000 people; A U.S. Army M1 Abrams tank patrols the streets of Baghdad after the city Battle of Baghdad (2003), fell to U.S.-led forces; Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse, Abuse and torture of Iraq, Iraqi prisoners at Abu Ghraib prison by U.S. personnel; Protests against the Iraq War, Protests in London against the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Invasion of Iraq; "Mission Accomplished" became an ironic symbol of the protractedness of the Iraq War after President George W. Bush's infamous Mission Accomplished speech, speech; a statue of Saddam Hussein is toppled in Baghdad after he was deposed during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (set Theory)
In set theory, the union (denoted by ∪) of a collection of sets is the set of all elements in the collection. It is one of the fundamental operations through which sets can be combined and related to each other. A refers to a union of zero (0) sets and it is by definition equal to the empty set. For explanation of the symbols used in this article, refer to the table of mathematical symbols. Union of two sets The union of two sets ''A'' and ''B'' is the set of elements which are in ''A'', in ''B'', or in both ''A'' and ''B''. In set-builder notation, :A \cup B = \. For example, if ''A'' = and ''B'' = then ''A'' ∪ ''B'' = . A more elaborate example (involving two infinite sets) is: : ''A'' = : ''B'' = : A \cup B = \ As another example, the number 9 is ''not'' contained in the union of the set of prime numbers and the set of even numbers , because 9 is neither prime nor even. Sets cannot have duplicate elements, so the union of the sets and is . Multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Select (SQL)
The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records, from one or more tables. A SELECT statement retrieves zero or more rows from one or more database tables or database views. In most applications, SELECT is the most commonly used data manipulation language (DML) command. As SQL is a declarative programming language, SELECT queries specify a result set, but do not specify how to calculate it. The database translates the query into a " query plan" which may vary between executions, database versions and database software. This functionality is called the "query optimizer" as it is responsible for finding the best possible execution plan for the query, within applicable constraints. The SELECT statement has many optional clauses: * SELECT clause is the list of columns or SQL expressions that must be returned by the query. This is approximately the relational algebra projection operation. * AS optionally provides an alias for each column or expression in the SELECT c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)