|
Serer History (medieval Era To Present)
The medieval history of the Serer people of Senegambia is partly characterised by resisting Islamization from perhaps the 11th century during the Almoravid movement (which would later result in the Serers of Takrur migration to the south), to the 19th century Marabout movement of Senegambia and continuation of the old Serer paternal dynasties. Resistance to Islam, 11th century According to Galvan (2004), "The oral historical record, written accounts by early Arab and European explorers, and physical anthropological evidence suggest that the various Serer peoples migrated south from the Fuuta Tooro region (Senegal River valley) beginning around the eleventh century, when Islam first came across the Sahara."Galvan, Dennis Charles, ''The State Must Be Our Master of Fire: How Peasants Craft Culturally Sustainable Development in Senegal'' Berkeley, University of California Press, 2004 p.51 Over generations these people, possibly Pulaar speaking herders originally, migrated through Wol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levtzion, Nehemia
Nehemia Levtzion ( he, נחמיה לבציון; November 24, 1935 — August 15, 2003) was an Israeli scholar of African history, Near East, Islamic, and African studies, and the President of the Open University of Israel from 1987 to 1992 and the Executive Director of the Van Leer Jerusalem Institute from 1994 to 1997. Early and personal life Levtzion was born in the moshav A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 an ... of Be'er Tuvia. His parents were Pnina (née Perlow) and Aron Lubetski, who later changed their surname to Levtzion, and he had an older sister named Hanna. He was Jewish, and had four children."Nehemia Levt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babacar Sédikh Diouf
Babacar Sedikh Diouf or Babacar Sédikh Diouf ( Serer: Babakar Sidiix Juuf, b. 1928Babacar Sedikh Diouf's body of works: Diouf, Babacar Sedikh, ''O maad a sinig : Kumba Ndoofeen fa Maak JUUF (Buka-Cilaas)'', 1853–1871 (PAPF, 1987) n Consortium of Academic and Research Libraries in Illinois (CARLI) nCARLI I-Shar(retrieved 8 February 2020)) is a Senegalese historian, author, researcher, campaigner against " Wolofization", a Pan-Africanist, and former teacher. He has written extensively about the history and culture of Senegal, Africa, and that of the Serer ethnic group to which he belong. He usually writes by the pen name ''Babacar Sedikh Diouf''. Academia In 1951, Diouf met Léopold Sédar Senghor – the future President of Senegal, when Senghor visited a village in Casamance were Diouf was working at the time as a teacher. Senghor, who was then a member of parliament was visiting the area as a surprise and had to sleep overnight in a hut—away from the comforts he was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially. The different types of cultural assimilation include full assimilation and forced assimilation; full assimilation being the most prevalent of the two, as it occurs spontaneously. During cultural assimilation, minority groups are expected to adapt to the everyday practices of the dominant culture through language and appearance as well as via more significant socioeconomic factors such as absorption into the local cultural and employment community. Some types of cultural assimilation resemble acculturation in which a minority group or culture completely assimilates into the dominant culture in which defining characteristics of the minority culture are less obverse or outright disappear; while in other types of cultural assimilation such as cultural integration mostly fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maad A Sinig Maysa Wali Jaxateh Manneh
Maad a Sinig Maysa Wali Jaxateh Manneh ( Serer proper : Maysa Waali Maane, many variations : Maysa Waaly Dione, Gravrand, Henry, "La Civilisation Sereer – ''Pangool''", vol.2, Les Nouvelles Editions Africaines du Senegal, (1990), P 344, Maïssa Wali Dione, Sarr, Alioune, " Histoire du Sine-Saloum", (Sénégal), Introduction, bibliographie et notes par Charles Becker. Version légèrement remaniée par rapport à celle qui est parue en 1986-87. p 19 Maysa Wali Jon, Maissa Waly Mané,Diouf, Niokhobaye, "Chronique du royaume du Sine", suivie de Notes sur les traditions orales et les sources écrites concernant le royaume du Sine. p 3-4 (p 703-5) etc.) was a king described in the oral tradition of the Serer pre-colonial Kingdom of Sine and the first of the Guelowar maternal dynasty to rule in Serer country. He reigned as Maad a Sinig (''king of Sine'') from to 1370. History In Serer oral tradition, Maysa Wali was a member of the Guelowar family who had escaped Kaabu wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joof Family
Joof ( English spelling in the Gambia) or Diouf (French spelling in Senegal and Mauritania) is a surname that is typically Serer. This surname is also spelt Juuf or Juf (in the Serer language). They are the same people. The differences in spelling is because Senegal was colonized by France, while the Gambia was colonized by the United Kingdom. Although spelt differently, they are pronounced the same way. The totem and symbol of the Joof family is the antelope, the symbol of grace, royalty, wisdom, hard work and protection in Serer mythology. The name of their clan is ''"Njoofene"'' variations: ''"Njuufeen"'' or ''"Njufeen"'' (in Serer). Members of this family had ruled over many of the pre-colonial kingdoms of Senegambia, including the Kingdom of Sine, the Kingdom of Saloum and the Kingdom of Baol. The royal princesses ( Lingeers) from the Joof family were also given in marriage to the pre-colonial kings and princes of Senegambia. Some of these included the kings of Jolof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faye (surname)
Faye is a typical Serer surname - an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia and Mauritania. This Serer surname is unrelated to the similar given name in the Western world. They are also pronounced differently. People with the surname Faye include: * Abdala Faye (born 1971), Senegalese mixed media artist * Abdoulaye Faye (born 1978), Senegalese footballer * Alice Faye, stage name of American actress and singer Alice Jeanne Leppert (1915–1998) * Amdy Faye (born 1977), Senegalese footballer * Andreas Faye (1802–1869), Norwegian priest, folklorist, and historian * Fary Faye (born 1974), Senegalese retired footballer * Fatou Lamin Faye (born 1954), Gambian politician * Frances Faye (1912–1991), American singer and pianist * Gaël Faye (born 1982), Rwandan-French singer and writer * Gaynor Faye (born 1971), English actress and writer * Guillaume Faye (1949–2019), French journalist and writer * Hervé Faye (1814–1902) French astronomer * H. P. Faye (1859–1928), Norwegia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mbissel
* Mbissel is a village in the west of Sénégal. It is situated in the region of Fatick. The population is overrun by the Serer people. History Mbissel was the capital of the first Guelowar king of Sine - Maad a Sinig Maysa Wali Jaxateh Manneh commonly known as Maysa Wali Jon. Maysa Wali made it his capital in the 14th century. The area just like the whole of Sine and Saloum has many historical monuments. The traditional site of the tomb of Maysa Wali is located in Mbissel.Jean-Marc Gastellu. L'égalitarisme économique des Serer du Sénégal. p303. IRD Editions, 1981 See also *Kingdom of Sine * Kingdom of Saloum *Serer people The Serer people are a West African ethnoreligious group. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebou People
The Lebu (Lebou, ''Lébou'') are an ethnic group of Senegal, West Africa, living on the peninsula of Cap-Vert. The Lebu are primarily a fishing community, but they have a substantial business in construction supplies and real estate.Keese, Alexander, "Ethnicity and the Colonial State: Finding and Representing Group Identifications in a Coastal West African and Global Perspective (1850–1960)", BRILL (2015), p. 94/ref> They speak Lebu Wolof, which is closely related to Wolof proper but is not intelligible with it. Their political and spiritual capital is at Layene, situated in the Yoff neighborhood of northern Dakar. They have a religious sect and theocracy, the Layene, headquartered there. The traditional date of the founding of Yoff is 1430. Although they were conquered by the Kingdoms of Jolof (Diolof) and Cayor, and later the French in the 19th century, and were incorporated into modern Senegal, since 1815 they have had a special legal autonomy as a special kind of "theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Jolof
The Kingdom of Jolof ( ar, جولوف), also known as Wolof and Wollof, was a West African rump state located in what is today the nation of Senegal. For nearly two hundred years, the Wolof rulers of the Jolof Empire collected tribute from vassal kings states who voluntarily agreed to the confederacy. At the Battle of Danki, the Buurba Jolof was defeated by the lord of Kayor resulting in the rapid disintegration of the empire. Jolof survived as a meager state, unable to prosper from the Atlantic trade between its former vassal territories and the Portuguese. Mauretanian promise In 1670, wandering Muslim clerics from Mauretania stirred up a rebellion against the Wolof rulers by a ruse. They promised to show the Wolof people how to produce millet without the labor of planting. During the ensuing rebellion, the Mauretanians invaded, killed the rulers of Waalo and Kayor and defeated the ''burba Jolof''. However, when the Mauretanians could not deliver on their promise, the Wolof resto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
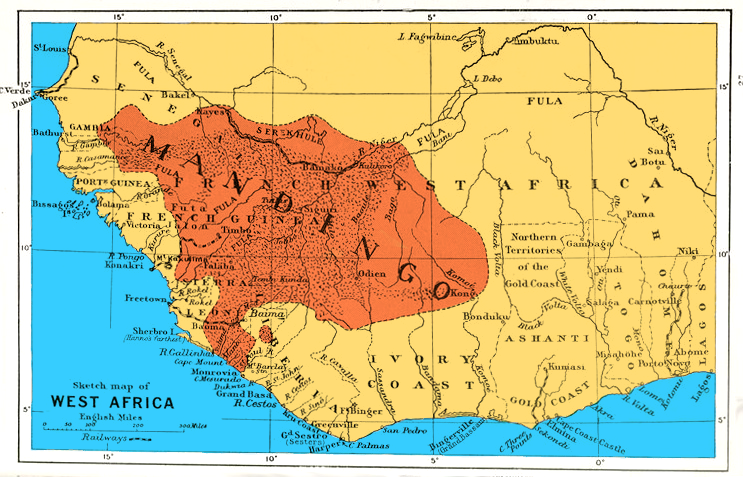
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a '' lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Sene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to: Religion * Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible * The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan Historical events * Exodus of 1879 (The Kansas Exodus), in which black Americans known as Exodusters fled the Southern United States for Kansas * The Exodus (1940), in Belgium and France * 1948 Palestinian exodus * 1948 Palestinian exodus from Lydda and Ramle * 1949–1956 Palestinian exodus * 1967 Palestinian exodus * 2021 Kabul airlift * Cuban exodus * Exodus of Kashmiri Hindus wherein ethnic Kashmiri Hindus were expelled from the Kashmir Valley, threatened with rape, death and conversion to Islam if they chose otherwise. * Exodus of Slav-Macedonians from Greece, the exodus of ethnic Macedonians following the Greek Civil War * Istrian-Dalmatian exodus, the exodus of Italians from Istria, Fiume and Dalmatia after World War II * Jewish exodus from Muslim cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
._19th_Century._Jung-Jung_From_The_Kingdom_of_Sine_(in_modern_day_Senegal).jpg)