|
Seller Concentration
In economics, market concentration is a function of the number of firms and their respective shares of the total production (alternatively, total capacity or total reserves) in a market. In any industry, a handful of firms that hold a significant portion of the market share and likely engage in the practice of consolidation will indicate higher market concentration within that industry. The market concentration ratio measures the concentration of the top firms in the market, this can be through various metrics such as sales, employment numbers, active users or other relevant indicators. In theory and in practice, market concentration is closely associated with market competitiveness, and therefore is important to various antitrust agencies when considering proposed mergers and other regulatory issues. Market concentration is important in determining firm market power in setting prices and quantities. Market concentration is affected through various forces, including barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Organization
In economics, industrial organization is a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure of (and, therefore, the boundaries between) firms and market (economics), markets. Industrial organization adds real-world complications to the perfect competition, perfectly competitive model, complications such as transaction costs, limited information economics, information, and barriers to entry of new firms that may be associated with imperfect competition. It analyzes determinants of firm and market organization and behavior on a continuum between Competition (economics), competition and monopoly, including from government actions. There are different approaches to the subject. One approach is descriptive in providing an overview of industrial organization, such as measures of competition and the size-concentration ratio, concentration of firms in an industry. A second approach uses microeconomic models to explain internal firm organization and market strategy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranking
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than" or "ranked equal to" the second. In mathematics, this is known as a weak order or total preorder of objects. It is not necessarily a total order of objects because two different objects can have the same ranking. The rankings themselves are totally ordered. For example, materials are totally preordered by hardness, while degrees of hardness are totally ordered. If two items are the same in rank it is considered a tie. By reducing detailed measures to a sequence of ordinal numbers, rankings make it possible to evaluate complex information according to certain criteria. Thus, for example, an Internet search engine may rank the pages it finds according to an estimation of their relevance, making it possible for the user quickly to select the pages they are likely to want to see. Analysis of data obtained by ranking commonly requires non-par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no :wikt:order, order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual random events are, by definition, unpredictable, but if the probability distribution is known, the frequency of different outcomes over repeated events (or "trials") is predictable.Strictly speaking, the frequency of an outcome will converge almost surely to a predictable value as the number of trials becomes arbitrarily large. Non-convergence or convergence to a different value is possible, but has probability zero. For example, when throwing two dice, the outcome of any particular roll is unpredictable, but a sum of 7 will tend to occur twice as often as 4. In this view, randomness is not haphazardness; it is a measure of uncertainty of an outcome. Randomness applies to concepts of chance, probability, and information entropy. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small But Significant And Non-transitory Increase In Price
In competition law, before deciding whether companies have significant market power which would justify government intervention, the test of small but significant and non-transitory increase in price (SSNIP) is used to define the relevant market in a consistent way. It is an alternative to ad hoc determination of the relevant market by arguments about product similarity. The SSNIP test is crucial in competition law cases accusing abuse of dominance and in approving or blocking mergers. Competition regulating authorities and other actuators of antitrust law intend to prevent market failure caused by cartel, oligopoly, monopoly, or other forms of market dominance. History In 1982 the U.S. Department of Justice Merger Guidelines introduced the SSNIP test as a new method for defining markets and for measuring market power directly. In the EU it was used for the first time in the ''Nestlé/Perrier'' case in 1992 and has been officially recognized by the European Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relevant Market
In competition law, a relevant market is a market in which a particular product or service is sold. It is the intersection of a relevant product market and a relevant geographic market. The European Commission defines a relevant market and its product and geographic components as follows: #A relevant product market comprises all those products and/or services which are regarded as interchangeable or substitutable by the consumer by reason of the products' characteristics, their prices and their intended use; #A relevant geographic market comprises the area in which the firms concerned are involved in the supply of products or services and in which the conditions of competition are sufficiently homogeneous. Definition and use The notion of relevant market is used in order to identify the products and undertakings which are directly competing in a business. Therefore, the relevant market is the market where the competition takes place. The enforcement of the provisions of competition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
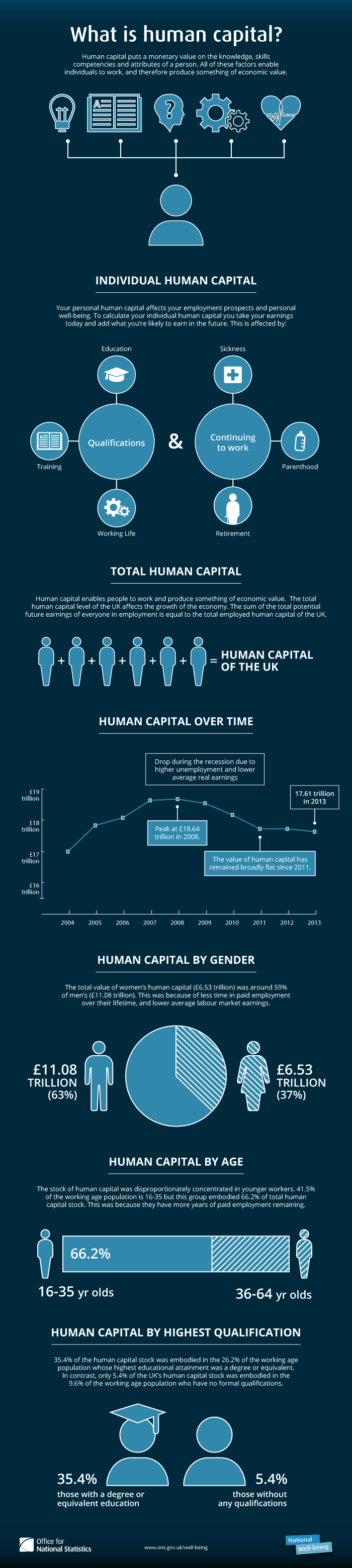
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Differentiation
In economics and marketing, product differentiation (or simply differentiation) is the process of distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market. This involves differentiating it from competitors' products as well as from a firm's other products. The concept was proposed by Edward Chamberlin in his 1933 book, '' The Theory of Monopolistic Competition''. Rationale Firms have different resource endowments that enable them to construct specific competitive advantages over competitors. Resource endowments allow firms to be different, which reduces competition and makes it possible to reach new segments of the market. Thus, differentiation is the process of distinguishing the differences of a product or offering from others, to make it more attractive to a particular target market. Although research in a niche market may result in changing a product in order to improve differentiation, the changes themselves are not diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brand Loyalty
In marketing, brand loyalty describes a consumer's positive feelings towards a brand, and their dedication to purchasing the brand's products and/or services repeatedly, regardless of deficiencies, a competitor's actions, or changes in the environment. It can also be demonstrated with other behaviors such as positive word-of-mouth advocacy. Corporate brand loyalty is where an individual buys products from the same manufacturer repeatedly and without wavering, rather than from other suppliers. Loyalty implies dedication and should not be confused with habit with its less-than-emotional engagement and commitment. Businesses whose financial and ethical values (for example, ESG responsibilities) rest in large part on their brand loyalty are said to use the loyalty business model. Marketing Brand loyalty, in marketing, consists of a consumer's commitment to repurchase or continue to use the brand. Consumers can demonstrate brand loyalty by repeatedly buying a product, service, or by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept. Economies of scale apply to a variety of the organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranking
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than" or "ranked equal to" the second. In mathematics, this is known as a weak order or total preorder of objects. It is not necessarily a total order of objects because two different objects can have the same ranking. The rankings themselves are totally ordered. For example, materials are totally preordered by hardness, while degrees of hardness are totally ordered. If two items are the same in rank it is considered a tie. By reducing detailed measures to a sequence of ordinal numbers, rankings make it possible to evaluate complex information according to certain criteria. Thus, for example, an Internet search engine may rank the pages it finds according to an estimation of their relevance, making it possible for the user quickly to select the pages they are likely to want to see. Analysis of data obtained by ranking commonly requires non-par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |