|
Seasonal Tendencies
A calendar effect (or calendar anomaly) is any market anomaly, different behaviour of stock markets, or economic effect which appears to be related to the calendar, such as the day of the week, time of the month, time of the year, time within the U.S. presidential cycle, decade within the century, etc... Some people believe that if they do exist, it is possible to use market timing. Seasonal patterns are not confined to prices; many other systems can exhibit the same kind of calendar effect. However, the term is most often used in an economic context. Causes Market prices are often subject to seasonal tendencies because the availability and demand for an item is not constant throughout the year. For example, natural gas prices often rise in the winter because that commodity is in demand as a heating fuel. In the summer, when the demand for heat is lower, prices typically fall. Examples Notable calendar effects include: * Sell in May principle (or Halloween indicator) * January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Anomaly
A market anomaly in a financial market is predictability that seems to be inconsistent with (typically risk-based) theories of asset prices. Standard theories include the capital asset pricing model and the Fama–French three-factor model, Fama-French Three Factor Model, but a lack of agreement among academics about the proper theory leads many to refer to anomalies without a reference to a benchmark theory (Daniel and Hirschleifer 2015 and Barberis 2018, for example). Indeed, many academics simply refer to anomalies as "return predictors", avoiding the problem of defining a benchmark theory. Academics have documented more than 150 return predictors (see ''Market anomaly#List of Anomalies Documented in Academic Journals, List of Anomalies Documented in Academic Journals).'' These "anomalies", however, come with many caveats. Almost all documented anomalies focus on illiquid, small stocks. Moreover, the studies do not account for trading costs. As a result, many anomalies do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Presidential Election Cycle
The four-year United States presidential election cycle is a theory that stock markets are weakest in the year following the election of a new U.S. president. It suggests that the presidential election has a predictable impact on America's economic policies and market sentiment irrespective of the specific policies of the President. It goes on to suggest the levels of stocks for each of the four-years of the presidential term as part of an stock market cycles. Theory The four-year U.S. presidential cycle is attributed to politics and its impact on America's economic policies. Either or both of these factors could be the cause for the stock market's statistically improved performance during most of the third and fourth years of a president's four-year term. The month-end seasonality cycle is attributed to the automatic purchases associated with retirement accounts. The secular stock market cycles that last about 30 years move in lockstep with corresponding secular economic, soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar Effect
A calendar effect (or calendar anomaly) is any market anomaly, different behaviour of stock markets, or economic effect which appears to be related to the calendar, such as the day of the week, time of the month, time of the year, time within the U.S. presidential cycle, decade within the century, etc... Some people believe that if they do exist, it is possible to use market timing. Seasonal patterns are not confined to prices; many other systems can exhibit the same kind of calendar effect. However, the term is most often used in an economic context. Causes Market prices are often subject to seasonal tendencies because the availability and demand for an item is not constant throughout the year. For example, natural gas prices often rise in the winter because that commodity is in demand as a heating fuel. In the summer, when the demand for heat is lower, prices typically fall. Examples Notable calendar effects include: * Sell in May principle (or Halloween indicator) * Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
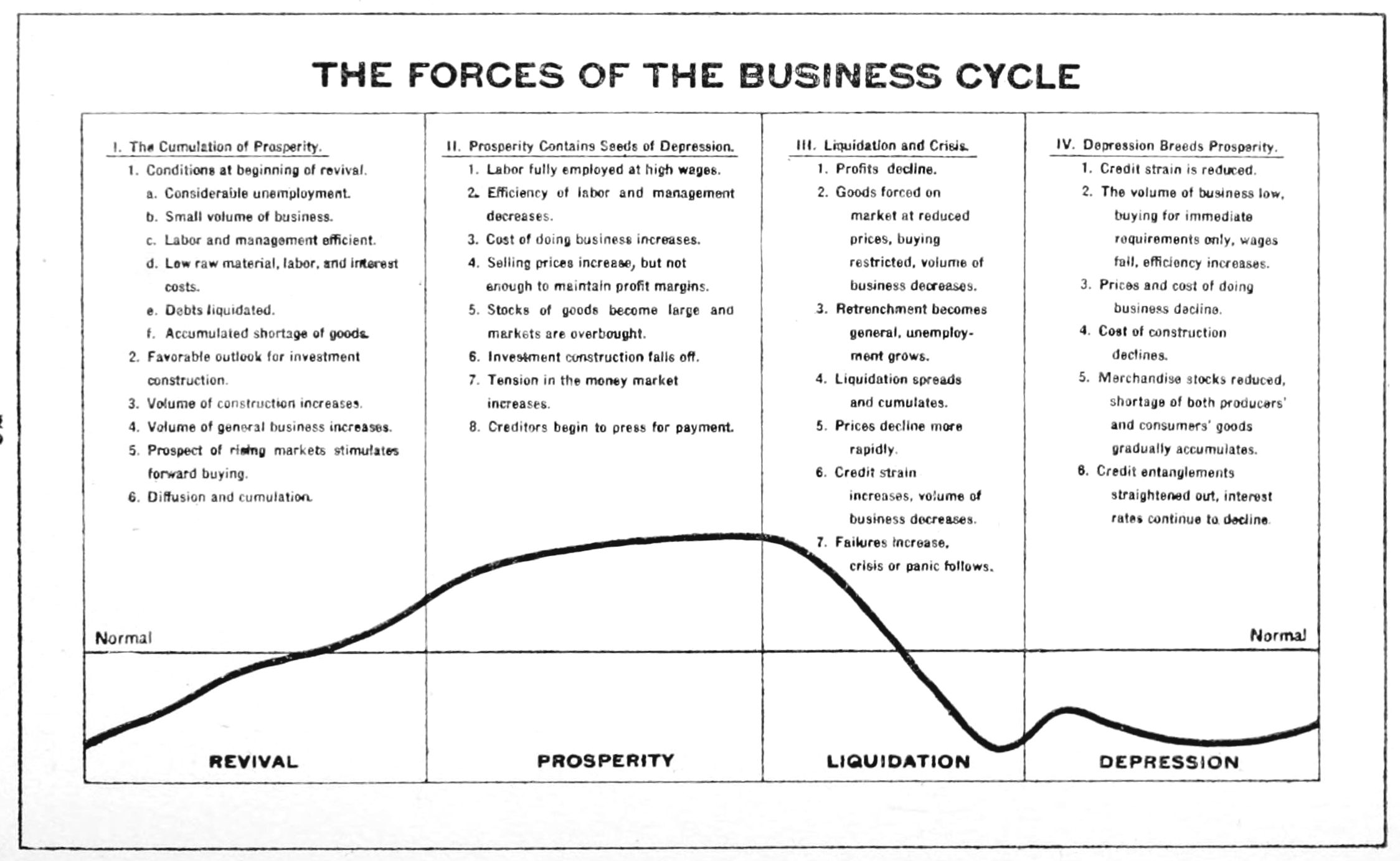
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of Economic expansion, expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in [Harvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics''], such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient-market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory refers to a set of guidelines that help understand economic and social behaviour. The theory originated in the eighteenth century and can be traced back to political economist and philosopher, Adam Smith. The theory postulates that an individual will perform a cost-benefit analysis to determine whether an option is right for them.Gary Browning, Abigail Halcli, Frank Webster (2000). ''Understanding Contemporary Society: Theories of the Present'', London: SAGE Publications. It also suggests that an individual's self-driven rational actions will help better the overall economy. Rational choice theory looks at three concepts: rational actors, self interest and the invisible hand. Rationality can be used as an assumption for the behaviour of individuals in a wide range of contexts outside of economics. It is also used in political science, sociology, and philosophy. Overview The basic premise of rational choice theory is that the decisions made by individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics studies the effects of psychological, cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the decisions of individuals or institutions, such as how those decisions vary from those implied by classical economic theory. Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. The study of behavioral economics includes how market decisions are made and the mechanisms that drive public opinion. The concepts used in behavioral economics today can be traced back to 18th-century economists, such as Adam Smith, who deliberated how the economic behavior of individuals could be influenced by their desires. The status of behavioral economics as a subfield of economics is a fairly recent development; the breakthroughs that laid the foundation for it were published through the last three decades of the 20th century. Behavio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Econometrics
The ''Journal of Econometrics'' is a scholarly journal in econometrics. It was first published in 1973. Its current managing editors are Serena Ng and Elie Tamer, Torben Andersen and Xiaohong Chen serve as editors. The journal publishes work dealing with estimation and other methodological aspects of the application of statistical inference to economic data, as well as papers dealing with the application of econometric techniques to economics. The journal also publishes a supplement to the Journal of Econometrics which is called "Annals of Econometrics". Each issue of the Annals includes a collection of papers on a single topic selected by the editor of the issue. See also * ''Econometrics Journal'' References External links Homepage Econometrics, Journal of Econometrics journals Econometrics Econometrics is the application of Statistics, statistical methods to economic data in order to give Empirical evidence, empirical content to economic relationships.M. Hashem P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Dredging
Data dredging (also known as data snooping or ''p''-hacking) is the misuse of data analysis to find patterns in data that can be presented as statistically significant, thus dramatically increasing and understating the risk of false positives. This is done by performing many statistical tests on the data and only reporting those that come back with significant results. The process of data dredging involves testing multiple hypotheses using a single data set by exhaustively searching—perhaps for combinations of variables that might show a correlation, and perhaps for groups of cases or observations that show differences in their mean or in their breakdown by some other variable. Conventional tests of statistical significance are based on the probability that a particular result would arise if chance alone were at work, and necessarily accept some risk of mistaken conclusions of a certain type (mistaken rejections of the null hypothesis). This level of risk is called the ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange, as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies which are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. Investment is usually made with an investment strategy in mind. Size of the market The total market capitalization of all publicly traded securities worldwide rose from US$2.5 trillion in 1980 to US$93.7 trillion at the end of 2020. , there are 60 stock exchanges in the world. Of these, there are 16 exchanges with a market capitalization of $1 trillion or more, and they account for 87% of global market capitalization. Apart from the Australian Securities Exchange, these 16 exchanges are all in North America, Europe, or Asia. By country, the largest stock markets as of January 2022 are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
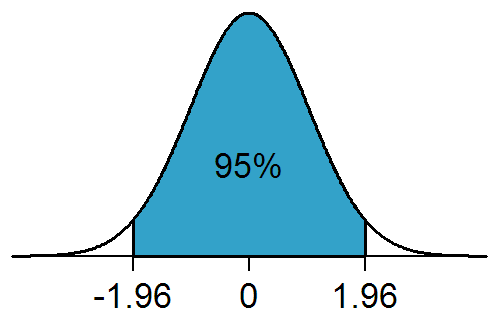
Statistically Significant
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the p-value, ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or Observational study, observation that involves drawing a Sampling (statistics), sample from a Statistical population, population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Effect
The lunar effect is a purported unproven correlation between specific stages of the roughly 29.5-day lunar cycle and behavior and physiological changes in living beings on Earth, including humans. In some cases the purported effect may depend on external cues, such as the amount of moonlight. In other cases, such as the approximately monthly cycle of menstruation in humans (but not other mammals), the coincidence in timing reflects no known lunar influence. A considerable number of studies have examined the effect on humans. By the late 1980s, there were at least 40 published studies on the purported lunar-lunacy connection, and at least 20 published studies on the purported lunar-birthrate connection. This has allowed several extensive literature reviews and metanalyses to be produced, which have found no correlation between the lunar cycle and human biology or behavior. The widespread and persistent beliefs about the influence of the moon may depend on illusory correlation †... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |