|
Schistosoma Bovis
''Schistosoma bovis'' is a two-host blood fluke, that causes intestinal schistosomiasis in ruminants in North Africa, Mediterranean Europe and the Middle East. ''S. bovis'' is mostly transmitted by ''Bulinus'' freshwater snail species. It is one of nine haematobium group species and exists in the same geographical areas as ''Schistosoma haematobium'', with which it can hybridise. ''S. bovis-haematobium'' hybrids can infect humans, and have been reported in Senegal since 2009, and a 2013 outbreak in Corsica. Taxonomy and identification ''Schistosoma bovis'' is a digenetic, two-host blood fluke. It was discovered by Italian parasitologist Prospero Sonsino at Zagazig meat market in Egypt in 1876 from a bull. It is generally similar to other schistosomes, but Sonsino knew that it was larger and its eggs were different from those of the human species (first and only known schistosome at the time), ''Schistosoma haematobium'', discovered by a German physician Theodor Bilharz in 1852, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect bivalves and bony fishes.https://www.biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.3918.3.2 Digenea — which comprise the majority of trematodes — ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planorbarius Metidjensis
''Planorbarius metidjensis'' is a freshwater lung snail. MolluscaBase eds. (2022). MolluscaBase. Planorbarius metidjensis (Forbes, 1838). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1062886 on 2022-06-16 Experiments confirmed it to be a host of the ''Schistosoma'' parasites, while the ''Bulinus truncatus'' freshwater snail has been known much longer as a carrier of schistosomiasis. Description The snail measures 8 mm x 16 to 18 mm. The shell is light yellowish, while the periostracum is brown, reddish or greenish. The body is nearly black with a grey foot and tentacles. Schistosomiasis transmission While ''P. metidjensis'' has been successfully infected with ''Schistosoma haematobium'' in the laboratory, in Morocco, no free-living infected snails have been found during a survey. Likewise, in the laboratory, snail specimens from Portugal and Salamanca were found to be very susceptible to infections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulinus Truncatus
''Bulinus truncatus'' is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the subfamily Bulininae of the family Bulinidae, the ram's horn snails and the like. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Bulinus truncatus (Audouin, 1827). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=716338 on 2022-01-14 ;Subspecies: * ''Bulinus truncatus contortus'' (Michaud, 1829) (synonym: ''Physa contorta'' Michaud, 1829 ) * ''Bulinus truncatus rivularis'' (Philippi, 1836) * ''Bulinus truncatus truncatus'' (Audouin, 1827) Distribution Distribution of ''Bulinus truncatus'' include: *Africa: Egypt, Morocco Northern Sahara, D.R. Congo, Malawi and Ethiopia. * in Ferlo Valley, Western Africa: Senegal Sarr A., Kinzelbach R. & Diouf M. (2011, in press). "Diversité spécifique et écologie des mollusques continenatux de la basse vallée du Ferlo (Sénégal). pecific dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulinus Nyassanus
''Bulinus nyassanus'' is a species of small air-breathing freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies. This species is endemic to Lake Malawi in Africa, where found both in shallow and relatively deep water. Its shell generally reached a size of up to around . This detritus-feeder typically burrows slightly into the sediment, no more than , unlike some of its relatives like '' B. globosus'', which usually live on rocks or aquatic vegetation. Although only a minority of these snails are infected (generally 2% or less in ''B. nyassanus''), they do play an important role in the spread of bilharzia Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody ... (schistosomiasis), a parasite that ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulinus Forskalii
''Bulinus forskalii'' is a species of tropical freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Bulinidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies.MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Bulinus forskalii (Ehrenberg, 1831). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1058686 on 2020-06-27 Distribution ''Bulinus forskalii'' is an afrotropical species which occurs in number of countries in Africa: * Northern Africa: only in Egypt and Sudan. * Western Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Senegal Sarr A., Kinzelbach R. & Diouf M. (2011, in press). "Diversité spécifique et écologie des mollusques continenatux de la basse vallée du Ferlo (Sénégal). pecific diversity and ecology of continental molluscs from the Lower Ferlo Valley (Senegal). ''MalaCo'' 7: 8 ppPDF. and Togo. * Eastern Africa: Burundi, Ethiopia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulinus Globosus
''Bulinus globosus'' is a species of a tropical freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies. Parasites ''Bulinus globosus'' is an intermediary host of ''Schistosoma haematobium'', along with ''Bulinus truncatus ''Bulinus truncatus'' is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the subfamily Bulininae of the family Bulinidae, the ram's horn snails and the like. MolluscaBase eds. (2 ...''. References Further reading * External links Bulinus Gastropods described in 1866 {{Planorbidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miracidia
Trematodes are parasitic flatworms of the class ''Trematoda'', specifically parasitic flukes with two suckers: one ventral and the other oral. Trematodes are covered by a tegument, that protects the organism from the environment by providing secretory and absorptive functions. The life cycle of a typical trematode begins with an egg. Some trematode eggs hatch directly in the environment (water), while others are eaten and hatched within a host, typically a mollusc. The hatchling is called a ''miracidium,'' a free-swimming, ciliated larva. Miracidia will then grow and develop within the intermediate host into a sac-like structure known as a sporocyst or into rediae, either of which may give rise to free-swimming, motile cercariae larvae. The cercariae then could either infect a vertebrate host or a second intermediate host. Adult metacercariae or mesocercariae, depending on the individual trematode's life cycle, will then infect the vertebrate host or be rejected and excreted th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows. *The interior of the gastrointestinal tract *The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures: *thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, or microtubule Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occurring through lumina, including: *Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
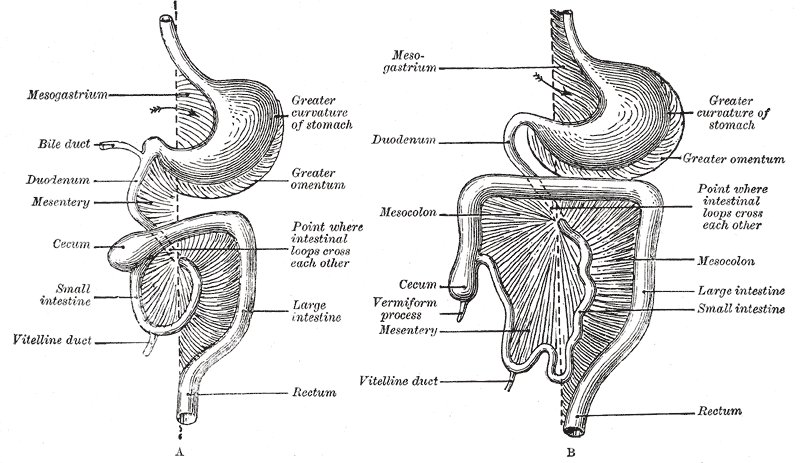
Mesenteric
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematoda
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate internal Parasitism, parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host_(biology), hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect Bivalvia, bivalves and Osteichthyes, bony fishes.https://www.bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)