|
Scheuermann's Disease
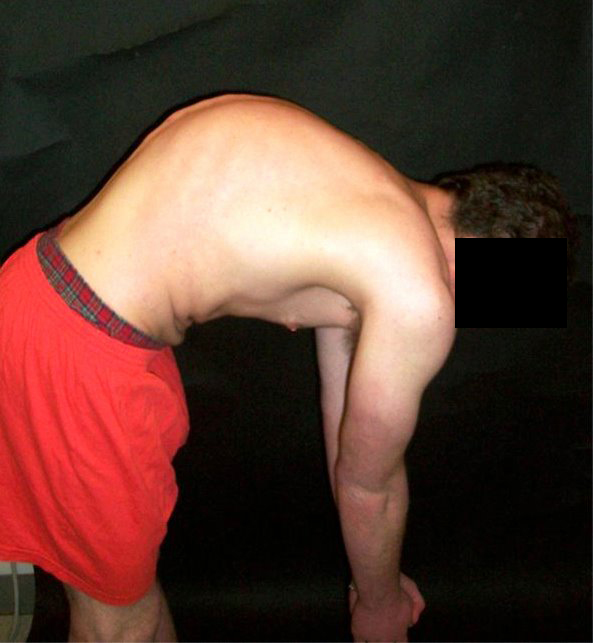
Scheuermann's disease is a skeletal disorder. It describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the signature "wedging" shape of the vertebrae, causing kyphosis. It is named after Danish surgeon Holger Scheuermann. Signs and symptoms Scheuermann's disease is considered to be a form of osteochondrosis of the spine. It typically develops during adolescence and presents a significantly worse deformity than postural kyphosis. Patients with Scheuermann’s kyphosis cannot consciously correct their posture. The apex of their curve, located in the thoracic vertebrae, is quite rigid. Scheuermann's disease is notorious for causing lower and mid-level back and neck pain, which can be severe and disabling. The individual may feel pain at the apex of the curve, which is aggravated by physical activity and by periods of standing or sitting; this can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopaedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually became the cornerstone of orthopedic pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Vital Capacity
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of Public health surveillance, health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Testing Spirometer The spirometry test is performed using a device called a spirometer, which comes in several different varieties. Most spirometers display the following graphs, called spirograms: * a ''volume-time curve'', showing volume (litres) along the Y-axis and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrel Chest
Barrel chest generally refers to a wikt:broad, broad, deep chest found on a patient (or other person). A barrel chested person will usually have a naturally large ribcage, very round (i.e., vertically cylindrical) torso, large lung capacity, and can potentially have great upper body strength. It can sometimes be found alongside acromegaly (an enlargement of the extremities resulting from excess levels of human growth hormone (HGH) in the body). Barrel chest, as a medical condition, is most commonly related to osteoarthritis as individuals age. Arthritis can stiffen the chest causing the ribs to become fixed in their most expanded position, giving the appearance of a barrel chest. Barrel chest refers to an increase in the anteroposterior diameter of the chest wall resembling the shape of a barrel, most often associated with emphysema. There are two main causes of the barrel chest phenomenon in emphysema: # Increased lung compliance, compliance of the lungs leads to the accumulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Capacities
Lung volumes and lung capacities are measures of the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle. The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air. Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathing; the tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such breath. The average human respiratory rate is 30–60 breaths per minute at birth, decreasing to 12–20 breaths per minute in adults. Factors affecting volumes Several factors affect lung volumes; some can be controlled, and some cannot be controlled. Lung volumes vary with different people as follows: A person who is born and lives at sea level will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high altitude. This is because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude which, as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream. In response to higher altitude, the body's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordosis
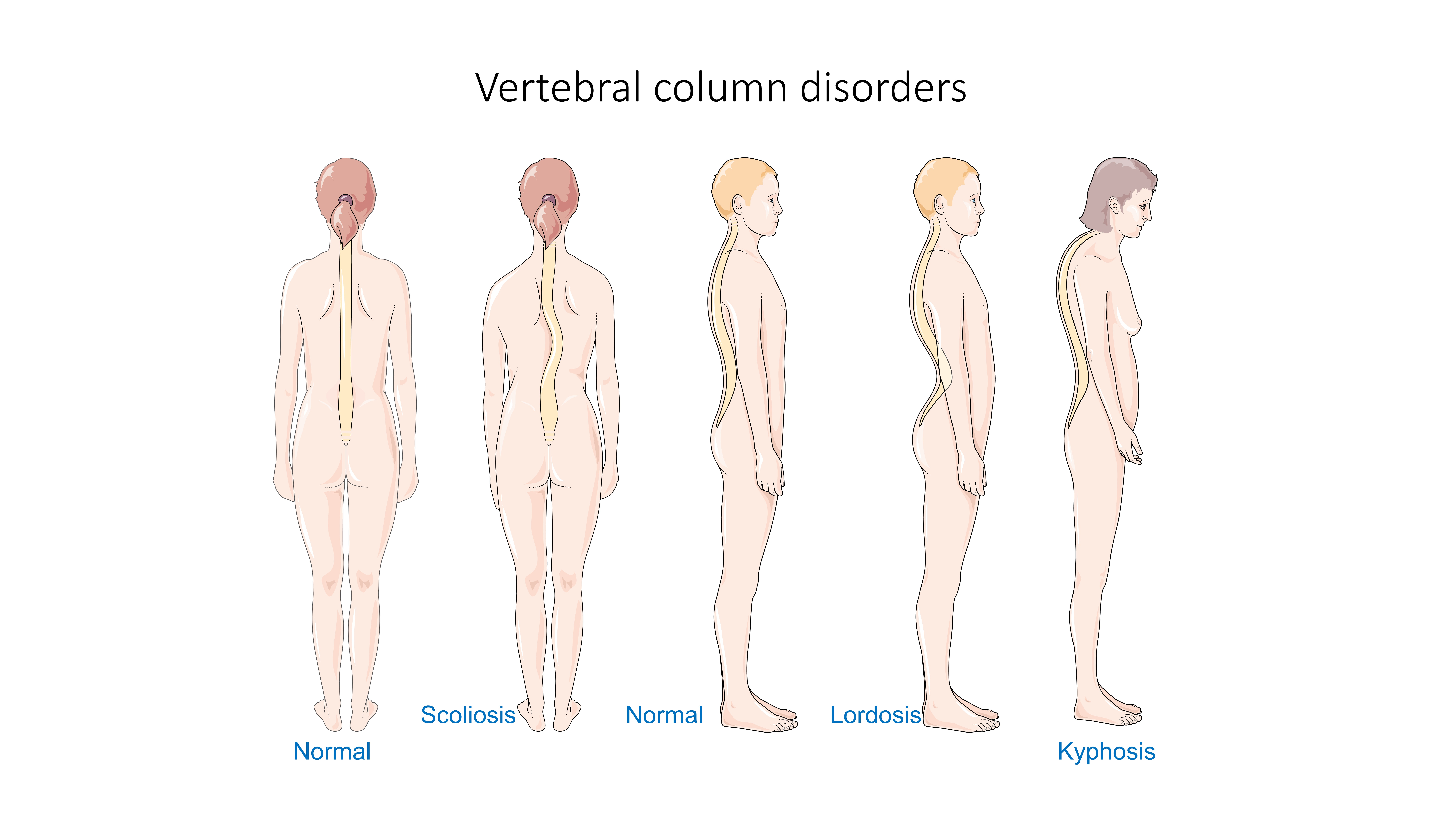
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, cervical regions of the human vertebral column, spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to ''abnormal'' convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacrum, sacral regions is also termed ''kyphosis'' or ''kyphotic''. The term comes . Lordosis in the human vertebral column, human spine makes it easier for humans to bring the bulk of their mass over the pelvis. This allows for a much more efficient walking Gait (human), gait than that of other primates, whose inflexible spines cause them to resort to an inefficient forward-leaning "bent-knee, bent-waist" gait. As such, lordosis in the human spine is considered one of the primary physiological adaptations of the human skeleton that allows for human gait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of a bone, in particular to the epiphysis, followed by localized bony necrosis, and later, regrowth of the bone. This disorder is defined as a focal disturbance of endochondral ossification and is regarded as having a multifactorial cause, so no one thing accounts for all aspects of this disease. Osteochondrosis is a developmental disease. It usually occurs in an early stage of life. It has personified features as focal chondronecrosis and confinement of growth cartilage due to a failing of endochondral ossification. Fissures can develop from lesions over the top articular cartilage and form a cartilage flap and an osteochondral fragment. It is diagnosed as osteochondritis dissecans. In animals In dogs osteochondrosis is seen in elbow, sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holger Scheuermann
Holger Werfel Scheuermann (12 February 1877 – 3 March 1960) was a Danish surgeon after whom Scheuermann's disease is named. Biography Scheuermann was born into a medical family in Hørsholm, a small town between Copenhagen and Øresund. He began his studies in 1895 and graduated in medicine at the University of Copenhagen in 1902. He then spent his hospital service in Copenhagen at the Frederiks Hospital, at Sankt Johannesstiftelsen, as well as Rigshospitalet. At Rigshospitalet he was assistant at the departments of roentgenology and massage. Scheuermann trained in orthopaedic surgery and radiology, becoming a specialist in orthopaedics and radiology in 1918. From 1910 to 1919 he was 1st assistant surgeon at the Copenhagen Home for the Crippled and then became director of radiology at the military and Sundby Hospitals, and head physician to the navy. He undertook several study travels to Germany, Austria and Sweden, and was chairman of the Danske Røntgenologers Foreni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyphosis
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the Spinal column, spine as it occurs in the Thoracic spine, thoracic and sacrum, sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the Cervical spine, cervical and Lumbar spine, lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |