|
Sandy Island, Anguilla
Sandy Island is an island in Anguilla, a British Overseas Territory, and is part of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Sandy Island is a small island on which a local restaurant is located. From Sandy Ground, Anguilla can be reached in 15 minutes, and the owner of the restaurant takes care of the free boat crossing. The island is small (ca. 250x75 meters), consisting of round white sands with in the middle a little vegetation with shrubs and palm trees. The island is popular with tourists for the richness of its seabed, the beach of fine sand and coral for the presence of a business (bar / restaurant) famous in the area. In 1995, the island was submerged by Hurricane Luis Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, an ... for some days while the facilities were severely da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilles
The Antilles (; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy; es, Antillas; french: Antilles; nl, Antillen; ht, Antiy; pap, Antias; Jamaican Patois: ''Antiliiz'') is an archipelago bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the south and west, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east. The Antillean islands are divided into two smaller groupings: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. The Greater Antilles includes the larger islands of the Cayman Islands, Cuba, Hispaniola (subdivided into the nations of the Dominican Republic and Haiti), Jamaica, and Puerto Rico. The Lesser Antilles contains the northerly Leeward Islands and the southeasterly Windward Islands as well as the Leeward Antilles just north of Venezuela. The Lucayan Archipelago (consisting of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), though a part of the West Indies, is generally not included among the Antillean islands. Geographically, the Antillean islands are generally consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former British Empire and do not form part of the United Kingdom itself. The permanently inhabited territories are internally Self-governance, self-governing, with the United Kingdom retaining responsibility for Defence (military), defence and foreign relations. Three of the territories are inhabited only by a transitory population of military or scientific personnel. All but one of the rest are listed by the Special Committee on Decolonization, UN Special Committee on Decolonization as United Nations list of non-self-governing territories, non-self-governing territories. All fourteen have the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch as head of state. three territories (the Falkland Islands, Gibraltar and the Akrotiri an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territory consists of the main island of Anguilla, approximately long by wide at its widest point, together with a number of much smaller islands and cays with no permanent population. The territory's capital is The Valley. The total land area of the territory is , with a population of approximately (). Etymology The native Arawak name for the island was ''Malliouhana''. In reference to the island's shape, the Italian ', meaning "eel" (in turn, from the Latin diminutive of ''anguis'', "snake") was used as its name. History Anguilla was first settled by Indigenous Amerindian peoples who migrated from South America. The earliest Native American artefacts found on Anguilla have been dated to around 1300 BC; remains of settlements da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Time Zone
The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America and some Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to result in UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In Canada, the provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island are in this zone, though legally they calculate time specifically as an offset of four hours from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT–4) rather than from UTC. Small portions of Quebec (eastern Côte-Nord and the Magdalen Islands) also observe Atlantic Time. Officially, the entirety of Newfoundland and Labrador observes Newfoundland Stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguilla Islands
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territory consists of the main island of Anguilla, approximately long by wide at its widest point, together with a number of much smaller islands and cays with no permanent population. The territory's capital is The Valley. The total land area of the territory is , with a population of approximately (). Etymology The native Arawak name for the island was ''Malliouhana''. In reference to the island's shape, the Italian ', meaning "eel" (in turn, from the Latin diminutive of ''anguis'', "snake") was used as its name. History Anguilla was first settled by Indigenous Amerindian peoples who migrated from South America. The earliest Native American artefacts found on Anguilla have been dated to around 1300 BC; remains of settlements dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the northern coast of South America. The Gulf of Mexico lies to the northwest. The entire area of the Caribbean Sea, the numerous islands of the West Indies, and adjacent coasts are collectively known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, Gulf of Venezuela, Gulf of Darién, Golfo de los Mosquitos, Gulf of Paria and Gulf of Honduras. The Caribbean Sea has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
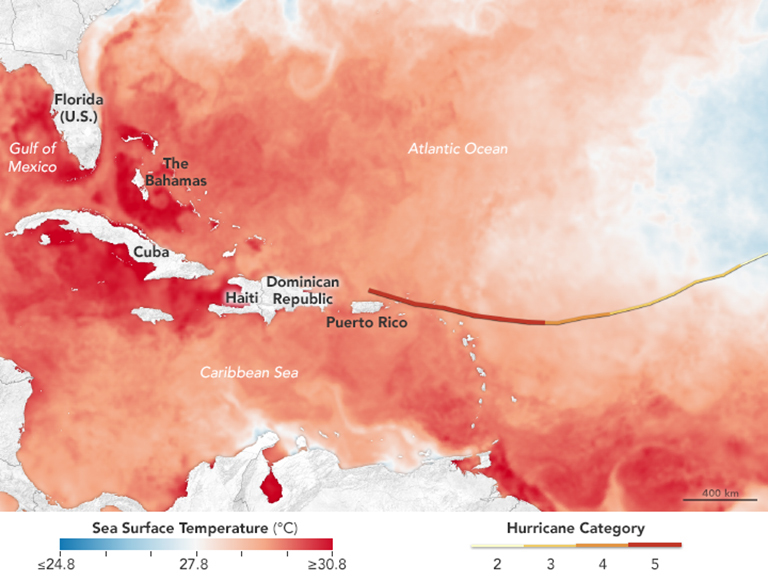
Hurricane Luis
Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, and Karen, was one of four simultaneous tropical systems in the Atlantic basin. Luis caused very extensive damage to Antigua, St. Barthelemy, the island of St. Martin and Anguilla as it affected Bermuda. The storm accounted for 19 confirmed deaths, left nearly 20,000 homeless (mostly in Anguilla, Barbuda, and St. Martin), and affected more than 70,000 people. Total damage was estimated at $3.3 billion (1995 USD) across the affected areas. Earlier Category 4 storms that impacted the Leeward Islands in the 20th century include Hurricane Dog in 1950, Hurricane Donna in 1960, Hurricane David in 1979, and Hurricane Hugo in 1989. Luis was the second of three tropical cyclones to affect Guadeloupe in a short period; Hurricane Iris had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two weeks later. At the time, it was considered as the most powerful hurricane on record in the open Atlantic region, outside of the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico until it was surpassed by Hurricane Dorian two years later. It was also the third strongest Atlantic hurricane at landfall ever recorded, just behind the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane and Dorian. The ninth named storm, fourth hurricane, second major hurricane, and first Category 5 hurricane of the 2017 season, Irma caused widespread and catastrophic damage throughout its long lifetime, particularly in the northeastern Caribbean and the Florida Keys. It was also the most intense hurricane to strike the continental United States since Katrina in 2005, the first major hurrican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)