|
Saint-Chély-d'Aubrac Domerie
Saint-Chély-d'Aubrac (; Languedocien dialect, Languedocien: ''Sanch Èli d'Aubrac'' or ''Sench Eli d'Aubrac'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Aveyron Departments of France, department in southern France about 7 kilometres from Aubrac. Population Location The town is in a large and beautiful green valley on the GR 65, the Way of Saint James pilgrim route. When travelling on the long distance footpath, Saint Chély d'Aubrac is the next town after Aubrac. Going down a wild, wooded valley, the walker discovers this little town in a large clearing and comes into the town by the old bridge with its pilgrim's cross, like the pilgrims of the past. The town of Saint-Chély-d'Aubrac is recognized by UNESCO as part of the Routes of Santiago de Compostela in France. The Bridge of the Pilgrims is specifically named as part of this designation. Landscape The town has been a member of the Natura 2000 network since August 2006. It hosts an annual chess festival. Sights * Jardin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
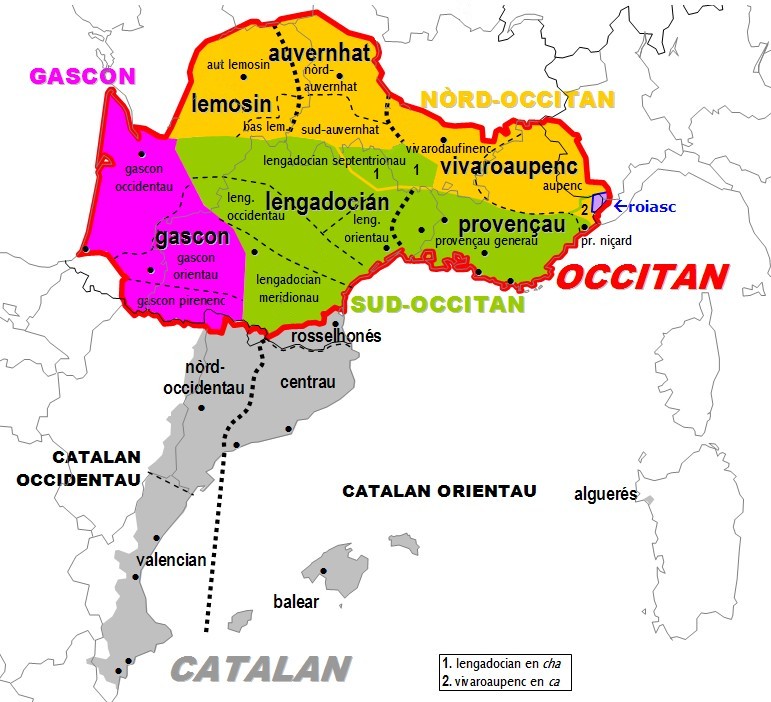
Languedocien Dialect
Languedocien (French name, ), Languedocian or Lengadocian (), is an Occitan dialect spoken in rural parts of southern France such as Languedoc, Rouergue, Quercy, Agenais and Southern Périgord. It is sometimes also called Languedocien-Guyennais. Due to its central position among the dialects of Occitan, it is often used as a basis for a Standard Occitan. About 10% of the population of Languedoc are fluent in the language (about 300,000), and another 20% (600,000) "have some understanding" of the language. All speak French as their first or second language. Geographic distribution Languedocien is spoken in certain parts of three French regions. * Occitanie: Aveyron, Lot, Tarn, Tarn-et-Garonne except Lomagne, Ariège (except a western part), Haute-Garonne (except the districts of Saint-Gaudens and Muret), Aude, Hérault, Lozère, western and northern parts of Gard and Fenouillèdes. * Nouvelle-Aquitaine: south of the Dordogne, east of the Gironde, north-eastern two-thirds of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aveyron
Aveyron (; oc, Avairon; ) is a department in the region of Occitania, Southern France. It was named after the river Aveyron. Its inhabitants are known as ''Aveyronnais'' (masculine) or ''Aveyronnaises'' (feminine) in French. The inhabitants of Aveyron's prefecture, Rodez, are called ''Ruthénois'', based upon the first Celtic settlers in the area, the Ruteni. With an area of and a population of 279,595, Aveyron is a largely rural department with a population density of 32 per square kilometer (83/sq mi). History Aveyron is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. The first known historical inhabitants of the region were the Rutenii tribe, but the area was inhabited previously to this, boasting many prehistoric ruins including over 1,000 dolmens, more than any other department in France. During the medieval and early modern periods, and until the 1790s, the territory covered by Aveyron was a province known as Rouergue. In 179 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrac
Aubrac is a small village in the southern Massif Central of France. The name is also applied to the surrounding countryside, which is properly called L'Aubrac in French. The Aubrac region has been a member of the Natura 2000 network since August 2006. It straddles three ''départements'' (Cantal, Aveyron and Lozère) and three ''régions'' (Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées and Languedoc-Roussillon). Geography, geology Aubrac is a volcanic and granitic plateau that extends over an area of 1,500 km2. The volcanic eruptions occurred between 6 and 9 million year ago and were of Hawaiian type with fluid lavas. There are therefore no individual volcanic cones. The volcanic zone occupies the west side while the other part of the plateau is formed of granite. The average altitude is about 1,200 meters with the highest point at 1,469 meters (Signal de Mailhebiau) in the south. All the region has been eroded by glaciers during three glacial periods. The Aubrac includes four glacial lakes: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim Bridge - Saint-Chély-d’Aubrac
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of a particular religious belief system. In the spiritual literature of Christianity, the concept of pilgrim and pilgrimage may refer to the experience of life in the world In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ... (considered as a period of exile) or to the inner path of the spiritual aspirant from a state of wretchedness to a state of beatitude. History Pilgrims and the making of pilgrimages are common in many religions, including the faiths of ancient Egypt, Persia in the Mithraism, Mithraic period, India, China, and Japan. The an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GR 65
The GR 65 is a long-distance walking route of the Grande Randonnée network that extends from the French Prealps, across south central France, through the Pyrenees. The French name for this GR route is the ''Chemin de Saint-Jacques'' and the Spanish name is the ''Camino de Santiago francés'', because the GR 65 is an important variant route of the old Christian pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela, one of several variants of the Way of St. James. In English it is the French Way, sometimes called ''The Le Puy Route'' or by its Latin name ''Via Podiensis'', including its subtrails GR651 and GR652. The GR 65 is part of the system of European long-distance paths known as E3 European long distance path. The route starts in Geneva, Switzerland, and continues through France to La Côte-Saint-André ( Isère), Le Puy-en-Velay (Haute-Loire), Nasbinals (Lozère), Conques (Aveyron), Figeac ( Lot), Cahors ( Lot) Moissac (Tarn-et-Garonne), and Aire-sur-l'Adour ( Landes), to Ronceval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Way Of Saint James
The Camino de Santiago ( la, Peregrinatio Compostellana, "Pilgrimage of Compostela"; gl, O Camiño de Santiago), known in English as the Way of St James, is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle Saint James the Great in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tradition holds that the remains of the apostle are buried. As Pope Benedict XVI said, "It is a way sown with so many demonstrations of fervour, repentance, hospitality, art and culture which speak to us eloquently of the spiritual roots of the Old Continent." Many follow its routes as a form of spiritual path or retreat for their spiritual growth. It is also popular with hiking and cycling enthusiasts and organized tour groups. Created and established after the discovery of the relics of Saint James the Great at the beginning of the 9th century, the Way of St James became a major pilgrimage route of medieval Christianity from the 10th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on Pilgrimage, a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of a particular religious belief system. In the spiritual literature of Christianity, the concept of pilgrim and pilgrimage may refer to the experience of life in World (theology), the world (considered as a period of exile) or to the inner path of the spiritual aspirant from a state of wretchedness to a state of beatitude. History Pilgrims and the making of pilgrimages are common in many religions, including the faiths of ancient Egypt, Persia in the Mithraism, Mithraic period, India, China, and Japan. The ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman customs of consulting the Deity, gods at local oracles, such as those at Dodona or Delphi, both in Greece, are widely known. In Greece, pilgrimages could either be personal or state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natura 2000
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively. The network includes both terrestrial and Marine Protected Areas. History In May 1992, the governments of the European Communities adopted legislation designed to protect the most seriously threatened habitats and species across Europe. The Habitats Directive complements the Birds Directive adopted earlier in 1979 and together they make up the Natura 2000 network of protected areas. The Birds Directive requires the establishment of Special Protection Areas for birds. The Habitats Directive similarly requires Sites of Community Importance which upon the agreement of the European Commission become Special Areas of Conservation to be designated for species other than birds, and for habitat types (e.g. particular types of forest, grassland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

