|
Saihriem Language
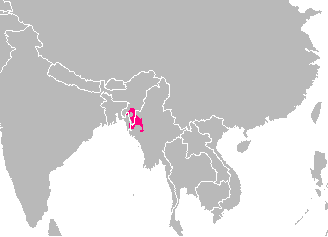
The Saihriem (Faihriem, Syriem) language is spoken by a mixture of the Saihriem/ Faihriem people- a sub tribe of Hmar group of tribes of the Chin-Kuki-Mizo and other ethnically closely related people such as the Aimol, Kuki, Vaiphei, in four neighbouring villages (Noxatilla, Bagbahar, Balisor, Nagathol & Saihriemkhuo villages) around Dwarbond in Bojalenga Block of Cachar District, Assam. It is critically endangered, with the people who still speak the language numbering a few hundreds only. It was recorded wrongly as Sairang in the ''Census of India, 1901'' and there were mere 71 speakers of the language at that time. It belongs to the Kuki-Chin branch of the Tibeto-Burman The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ... family of languages. Basic vocabulary Numbers Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cachar
Cachar district is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. After independence the undivided Cachar district was split into four districts in Assam: Dima Hasao district (formerly North Cachar Hills), Cachar district alongside Hailakandi and Karimganj. Etymology The Kacharis (Kachari kingdom) have given their name to the modern district Cachar. The Kacharis call themselves Barman in Barak valley and Dimasa in the Dima Hasao district. They were known to the Ahoms as Timisa, a corruption of the word "Dimasa". The Kacharis are allied to the Boro, Koches, Chutias, Lalungs (aka Tiwa) and Morans of the Brahmaputra valley and to the Garos and Tripuras of the southern hills. The Kacharis were perhaps the earliest inhabitants of the Brahmaputra valley and Barak valley. They are identical with the people called ‘Mech’ in Goalpara and North Bengal. History Pre-independence period It was a part of Kachari kingdom.At Dimapur, Dimasa Kachari Princes Elder Drikpati & y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Boro are the official languages of Assam, while Bengali is an additional official language in the Barak Valley. Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Assam is home to the one-horned Indian rhinoceros, along with the wild water buffalo, pygmy hog, tiger and various species of Asiatic birds, and provides one of the last wild habitats for the Asian elephant. The Assamese economy is aided by wildlife tourism to Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faihriem People
The Faihriem, or Saihriem, are one of the clans of Hmar Hmar may refer to: *Hmars or Hmar people *Hmar language Hmar language, also known by its endonym Khawsak Ṭawng, belongs to the Kukish branch of the Sino-Tibetan family of languages. The speakers of the language are also known as Hmar. Acc ... tribe. References Bibliography B.C.Allen, B.A., ICS, Superintendent of Census Operations in Assam. ''Census of India, 1901. Volume IV. Assam. Part I. Report.'' Printed at the Assam Secretariat Printing Office, 1902. 1999, Robin D. Tribhuwan, Preeti R. Tribhuwan. ''Tribal Dances of India (Encyclopaedic profile of Indian tribes, volume 1).'' Page 117. Gazette of India Extraordinary No.40, New Delhi. Wednesday, 6 September 1950. S.R.O. 510. {{Hill tribes of Northeast India Hmar Ethnic groups in Northeast India Mizo clans Kuki tribes Ethnic groups in South Asia Social groups of Assam People from Mizoram Scheduled Tribes of India Social groups of Manipur Sched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed parallels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuki-Chin Languages
The Kuki-Chin languages (also called Kuki-Chin-Mizo, Kukish or South-Central Tibeto-Burman languages) are a branch of 50 or so Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most speakers of these languages are known as Mizo in Mizoram and Manipur. Also, as Kukī in Assamese and Bengali and as Chin in Burmese; some also identify as Zomi. Mizo is the most widely spoken of the Kuki-Chin languages. Kuki-Chin is sometimes placed under Kuki-Chin–Naga, a geographical rather than linguistic grouping. Most Kuki-Chin languages are spoken in and around Chin State, Myanmar, with some languages spoken in Sagaing Division, Magway Region and Rakhine State as well. In Northeast India, many Northern Kuki-Chin languages are also spoken in Mizoram State and Manipur State of India, especially in Churachandpur District, Pherzawl District, Kangpokpi District, Senapati District. Northwestern Kuki-Chin languages are spoken mostly in Chandel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Kuki-Chin Languages
Central Kuki-Chin is a branch of the Kuki-Chin languages. Central Kuki-Chin languages are spoken primarily in Mizoram and other parts of North East India and also in Hakha Township and Falam Township of Chin State, Myanmar. Official use Mizo is the official language of Mizoram State, India. Classification VanBik (2009:23) classifies the Central Kuki-Chin languages as follows. ;Central Kuki-Chin * Pangkhua? * Laamtuk Thet (Tawr): Laamtuk, Ruavaan dialects * Lai languages **Hakha cluster: Halkha, Farrawn, Thantlang, Mi-E, Zokhua **Falam cluster: Bawm, Bualkhaw, Laizo, Lente, Khualsim, Khuangli, Sim, Tlaisun, Zanniat * Mizo languages ** Mizo cluster: Fanai, Hualngo, Lusei, Khiangte, Renthlei **Hmar cluster: Hmar, Biete , Hrangkhol , Sakachep ,Zote ,Thiek , Saihriem(Faihriem) ,etc VanBik (2009) is unsure about the classification of Pangkhua, and tentatively places it within Central Kuki-Chin. Sound changes VanBik (2009) lists the following sound changes from Proto-Kuki-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hmar Languages
The Hmar languages(Hmar Ṭawng) are a subbranch of the Kukish branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family which comprises Hmar proper (Khawsak) , Biete , Hrangkhol , Sakachep ,Zote ,Thiek, Saihriem(Faihriem),etc,. The Hmar languages are often treated as dialects of a single language, since differences between them are reportedly minor.Baruah, Dutta P.N. & V.L.Y. Bapui. 1996. ''Hmar Grammar.'' Mysore: Central Institute of Indian Languages, p. 3: "Different sub-tribes and clans speak different varieties ..The differences among them, however, are marginal". The speakers of the language are also known as Hmar. In Manipur, Hmar exhibits partial mutual intelligibility with the other Kukish dialects of the area including Thadou, Paite, Vaiphei, Simte, Kom and Gangte Gangte is an ethnic group mainly living in the Indian state of Manipur. They belong to the Zo people and are parts of the Kuki or under Mizo tribe and are recognised a tribe of Manipur, India. They are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aimol
The Aimol people are an ethnic group living mainly in Manipur and in parts of Mizoram, Tripura,Nagaland Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ... and Assam in India. They speak Aimol language which is a Tibeto-Burman, Kuki-Chin language. Aimol people are one of the Chin-Kuki-Mizo people. They practice slash-and-burn agriculture and are primarily Christian. Aimol identity is contentious as they are influenced by Kuki-Chin-Mizo groups. Their language is classified as Kuki-Chin-Mizo languages.Burling, Robbins. 2003. The Tibeto-Burman languages of northeastern India. In Graham Thurgood and Randy J. LaPolla (eds.), The Sino-Tibetan languages, 169-191. London & New York: Routledge. References Sources * http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=aim {{authorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuki People
The Kuki people are an ethnic group native to the Mizo Hills (formerly Lushai), a mountainous region in the southeastern part of Mizoram and Manipur in India. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. Some fifty tribes of Kuki peoples in India are recognised as scheduled tribes, based on the dialect spoken by that particular Kuki community as well as their region of origin. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people. History Early history The early history of the Kukis is obscure. The origin of the word "Kuki" is uncertain; it is an exonym: it was not originally as a self-designation by the tribes that are now called Kukis. According to the colonial British writer Adam Scott Reid, the earliest reference to the word Kuki can be dated to 1777 CE, when it first appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaiphei People
The Vaiphei people is an ethnic group who live in North-East Indian state of Manipur and its neighbouring country of Myanmar (Burma). Lt. Colonel J. Shakespeare (1887–1905), the first superintendent of the then Lushai Hills, referred to them as one of the ''Kuki'' clans of Manipur and recognized as part of the '' Chin-Kuki-Mizo'' tribe by the state government of Manipur. The group is originally from the Siyin valley located in the northern part of Chin State. The group speak the Vaiphei language. Each clan has a chief called ‘Upa’. The Vaiphei people follows primogeniture system where the eldest son inherits his father's property. Considered to be the first among the Chin-Kuki-Mizo groups to settle in Manipur Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ... and hence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cachar District
Cachar district is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. After independence the undivided Cachar district was split into four districts in Assam: Dima Hasao district (formerly North Cachar Hills), Cachar district alongside Hailakandi and Karimganj. Etymology The Kacharis (Kachari kingdom) have given their name to the modern district Cachar. The Kacharis call themselves Barman in Barak valley and Dimasa in the Dima Hasao district. They were known to the Ahoms as Timisa, a corruption of the word "Dimasa". The Kacharis are allied to the Boro, Koches, Chutias, Lalungs (aka Tiwa) and Morans of the Brahmaputra valley and to the Garos and Tripuras of the southern hills. The Kacharis were perhaps the earliest inhabitants of the Brahmaputra valley and Barak valley. They are identical with the people called ‘Mech’ in Goalpara and North Bengal. History Pre-independence period It was a part of Kachari kingdom.At Dimapur, Dimasa Kachari Princes Elder Drikpati & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |