|
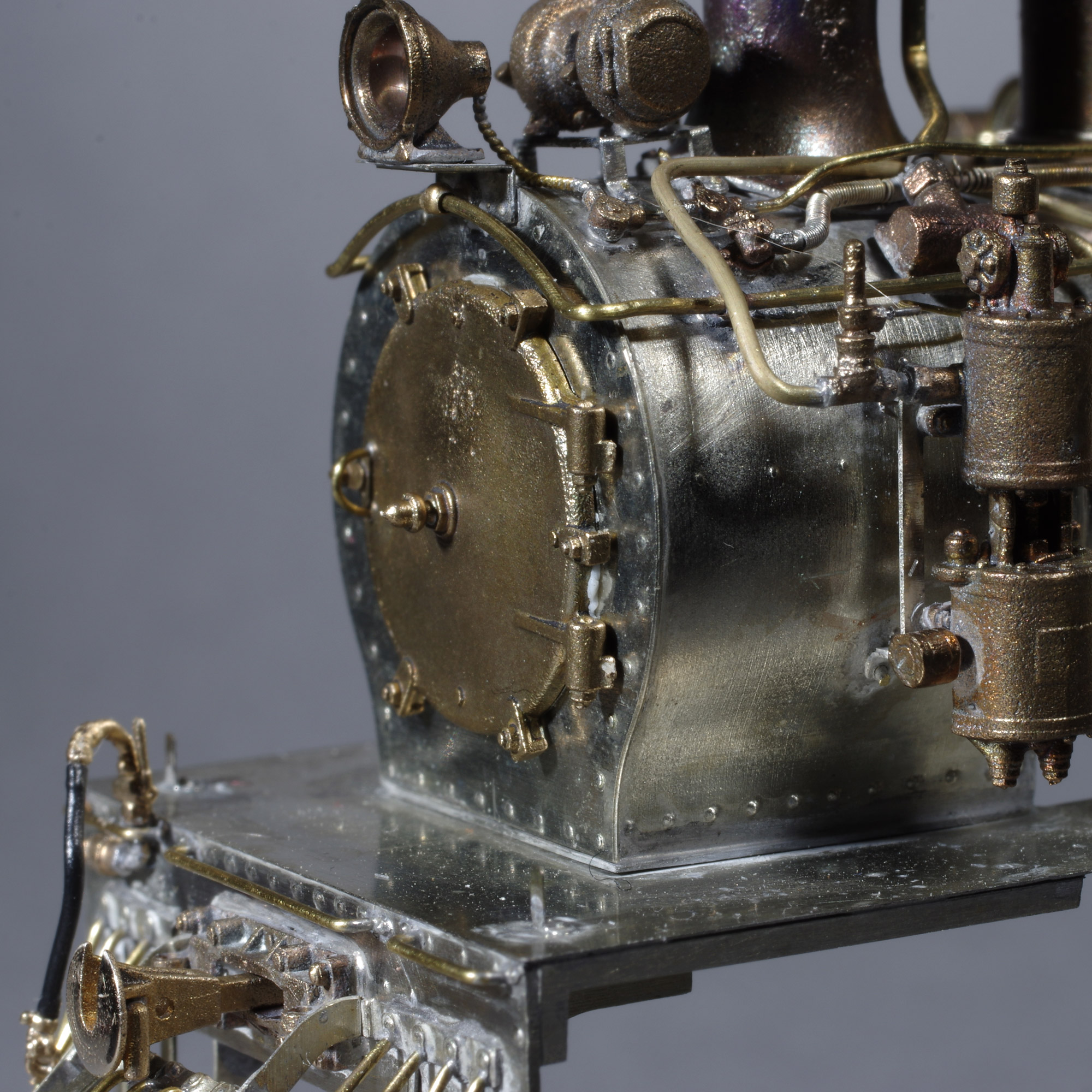
S Scale
S scale (or S gauge) is a model railroad scale modeled at 1:64 scale, S scale track gauge (space between the rails) is 22,48 (22,5) mm, 0.885 in. S gauge trains are manufactured in both DC and AC powered varieties. S gauge is not to be confused with '' toy train standard gauge'', a large-scale standard for toy trains in the early part of the 20th century. History S scale is one of the oldest model railroading scales. The earliest known 1:64 scale train was constructed from card stock in 1896. The first working models appeared in England in the early 20th century. Modeling in S scale increased in the 1930s and 1940s when CD Models marketed 3/16" model trains. American Flyer was a manufacturer of standard gauge and O gauge "tinplate" trains, based in Chicago, Illinois. It never produced S scale trains as an independent company. Chicago Flyer was purchased by A.C. Gilbert Co. in the late 1930s. Gilbert began manufacturing S scale trains around 1939 that ran on three rail "O" gauge tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Railroad
Railway modelling (UK, Australia, New Zealand, and Ireland) or model railroading (US and Canada) is a hobby in which rail transport systems are modelled at a reduced scale. The scale models include locomotives, rolling stock, streetcars, tracks, signalling, cranes, and landscapes including: countryside, roads, bridges, buildings, vehicles, harbors, urban landscape, model figures, lights, and features such as rivers, hills, tunnels, and canyons. The earliest model railways were the 'carpet railways' in the 1840s. The first documented model railway was the Railway of the Prince Imperial (French: Chemin de fer du Prince impérial) built in 1859 by emperor Napoleon III for his then 3-year-old son, also Napoleon, in the grounds of the Château de Saint-Cloud in Paris. It was powered by clockwork and ran in a figure-of-eight. Electric trains appeared around the start of the 20th century, but these were crude likenesses. Model trains today are more realistic, in addition to bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64 Scale
64 or sixty-four or ''variation'', may refer to: * 64 (number) Dates * one of the years 64 BC, AD 64, 1864, 1964, 2064, etc. * June 4th (6/4) ** the date of the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests and massacre * April 6th (6/4) * April 6 AD (6/4) * June 4 AD (6/4) Places * Highway 64, see list of highways numbered 64 ** Interstate 64, a national route in the United States * +64, country code dialing code of New Zealand; see Telephone numbers in New Zealand * 64 Angelina (asteroid 64), a main-belt asteroid Other uses * Nintendo 64, the third home console by Nintendo, released in 1996 * Commodore 64 * 64-bit computing * "64" (song), a 2011 song by hip hop band Odd Future * '' Sixty Four'' (album), a 2004 album recorded in 1964 by Donovan * Sixty-four (ship), a type of sailing warship * A /64 Classless Inter-Domain Routing Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR ) is a method for allocating IP addresses and for IP routing. The Internet Engineering Task Force introduced CIDR in 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge (toy Trains)
Standard Gauge, also known as wide gauge, was an early model railway and toy train rail gauge, introduced in the United States in 1906 by Lionel Corporation. As it was a toy standard, rather than a scale modeling standard, the actual scale of Standard Gauge locomotives and rolling stock varied. It ran on third rail (model railroading), three-rail track whose running rails were apart. Origins Lionel dubbed its new standard "Standard Gauge" and trademarked the name. Lionel's Standard Gauge is distinct from the standard gauge of real railroads, and the later 1:64 scale S gauge popularized by American Flyer after World War II. Due to the trademark, Lionel's competitors mostly called their similar offerings "wide gauge". Historians offer two alternative explanations for the creation of Standard Gauge. One is that Lionel misread the specifications for Märklin's European Gauge 2, measuring the distance between the inside portion of the rails rather than between the centers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Card Stock
Card stock, also called cover stock and pasteboard, is paper that is thicker and more durable than normal writing and printing paper, but thinner and more flexible than other forms of paperboard. Card stock is often used for business cards, postcards, playing cards, catalogue covers, scrapbooking, and other applications requiring more durability than regular paper gives. The surface usually is smooth; it may be textured, metallic, or glossy. When card stock is labeled cover stock, it often has a glossy coating on one or both sides (''C1S'' or ''C2S'', for "coated: one side" or "coated: two sides"); this is used especially in business cards and book covers. Measurements Most nations describe paper in terms of grammage—the weight in grams of one sheet of the paper measuring one square meter. Other people, especially in the United States, describe paper in terms of pound weight—the weight in pounds per ream (500 sheets) of the paper with a given area (based on historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Flyer
American Flyer is a brand of toy train and model railroad manufactured in the United States. The Chicago era, 1907–1938 Although best remembered for the S gauge trains of the 1950s that it made as a division of the A. C. Gilbert Company, American Flyer was initially an independent company whose origins date back nearly a half century earlier. Chicago, Illinois-based toymaker William Frederick Hafner developed a clockwork motor for toy cars in 1901 while working for a company called Toy Auto Company. According to the recollections of William Hafner's son, John, he had developed a clockwork train running on O gauge track by 1905. Hafner's friend, William Ogden Coleman, gained control of the Edmonds-Metzel Hardware Company, a struggling hardware manufacturer in Chicago, in 1906 or 1907. Hafner and Coleman began producing toy trains using Edmonds-Metzel's excess manufacturing capability after Hafner was able to secure $15,000 worth of orders. By 1907, two American retaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMRA
The National Model Railroad Association (NMRA) is a non-profit organization for those involved in the hobby or business of model railroading. It was founded in the United States in 1935, and is also active in Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. It was previously headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana, and was based in Chattanooga, Tennessee next to the Tennessee Valley Railroad Museum (TVRM) from 1982 to 2013 and has since relocated to Soddy Daisy. General The classifications listed below are from the A.A.R. Individual roads may use other designations. Illustrations show a typical member of the class detailed underneath the following a class description indicates a rare or obsolete type. Industry involvement The best-known activity of the NMRA is the defining of standards, and advisory documents known as Recommended Practices (RP), for model railroad equipment. Many standards defined by the NMRA are widely followed by the industry and modellers, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Gauge
1 gauge, gauge 1 or gauge one is a model railway and toy train standard that was popular in the early 20th century, particularly with European manufacturers. Its track measures , making it larger than 0 gauge but slightly smaller than wide gauge, which came to be the dominant U.S. standard during the 1920s. Gauge one was standardised, according to ''Model Railways and Locomotive'' magazine of August 1909, at . An exact 1:32 scale would yield for standard gauge prototype. The distance between the wheel tyres was set at and between the centre of the track 48 mm (no inch equivalent suggesting it was metric users' requirement only). The wheel width was set at . Definitions using gauge, rather than scale, were more common in the early days with the four gauges for which standards were adopted being No. 0 (commonly called O gauge currently), No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3. Popularity Initially as popular in the United States as in the UK, 1 gauge lost popularity in the U.S. due to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lionel Corporation
Lionel Corporation was an American toy manufacturer and holding company of retailers that had been in business for over 120 years. It was founded as an electrical novelties company. Lionel specialized in various products throughout its existence. Toy trains and model railroads were its main claim to fame. David Lander "Lionel" ''American Heritage'', Nov./Dec. 2006. Lionel trains have been produced since 1900, and their trains drew admiration from model railroaders around the world for the solidity of their construction and the authenticity of their detail. During its peak years in the 1950s, the company sold $25 million worth of trains per year.Osterhoff, Robert J. "When the Lights Went out at Lionel, ''Classic Toy Trains'', May 1999. Page 76. In 2006, Lio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sn3½
In rail transport modelling, Sn3½ is a scale/gauge combination derived from S scale to represent narrow gauge track by using gauge track (the same as HO gauge). The scale is 1:64. Sn3½ is popular in South Africa, Australia (particularly Western Australia, Queensland and Tasmania where narrow gauge systems exist) and New Zealand. Sn3½ is very rarely or never used for modelling in other countries with 3 foot 6 (1067mm) gauge railways such as Japan, Taiwan, Indonesia etc. Track As track scales down to 16.5mm at 1:64, modelers use HO gauge track (which represents Standard gauge at 1:87 scale) on Sn3½ layouts. New Zealand Sn3½ is the primary scale for modeling New Zealand's narrow gauge 3 ft 6 in railways. The majority of rolling stock available, are white-metal kits, making them considerably more expensive and heavier than other scales and countries. Many of these kits are highly detailed. Buildings are generally hand-made and track (HO gauge track) can either be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HO Gauge
HO or H0 is a rail transport modelling scale using a 1:87 scale (3.5 mm to 1 foot). It is the most popular scale of model railway in the world. The rails are spaced apart for modelling standard gauge tracks and trains in HO.NMRA"Modeling Scales: Scale and Gauge. ''NMRA.org''. December 2000. Retrieved 4 March 2010. The name H0 comes from 1:87 scale being ''half'' that of 0 scale, which was originally the smallest of the series of older and larger 0, 1, 2 and 3 gauges introduced by Märklin around 1900. Rather than referring to the scale as "half-zero" or "H-zero", English-speakers have consistently pronounced it and have generally written it with the letters HO. In other languages it also remains written with the letter H and number 0 (zero); in German it is thus pronounced as . History After the First World War there were several attempts to introduce a model railway about half the size of 0 scale that would be more suitable for smaller home layouts and cheape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen
german: Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen (french: Normes Européennes de Modélisme ferroviaires, literally European Standards for Model Railways, known in the UK as Normal European Modelling Standards (NEM Standards)) are standards for model railroads, issued by the MOROP. Standards The NEM standards are defined and maintained by the Technical Commission of the MOROP in collaboration with model railroad manufacturers. The NEM standards define the model railroad scales and guide :Model railroad manufacturers, manufacturers in creating compatible products and assist modellers in constructing model railroad layouts that operate reliably. The standards cover areas like suggested grade (slope), grades, railroad switch, turnout radii, wheel profiles, coupling designs and Digital Command Control (DCC) and are mostly scale specific. A fundamental principle in NEM standards are compromises in the exact scale reduction ratio in order to favour operational reliability of model railroad syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sn2 Gauge
Rail transport modelling uses a variety of scales (ratio between the real world and the model) to ensure scale models look correct when placed next to each other. Model railway scales are standardized worldwide by many organizations and hobbyist groups. Some of the scales are recognized globally, while others are less widespread and, in many cases, virtually unknown outside their circle of origin. Scales may be expressed as a numeric ratio (e.g. 1/87 or 1:87) or as letters defined in rail transport modelling standards (e.g. HO, OO, N, O, G, TT and Z.) The majority of commercial model railway equipment manufacturers base their offerings on ''Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen'' (NEM) or National Model Railroad Association (NMRA) standards in most popular scales. Terminology Although '' scale'' and ''gauge'' are often confused, ''scale'' means the ratio between a unit of measurement on a model compared with a unit of measurement in corresponding full size prototype, while ''g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |