|
SNPedia
SNPedia (pronounced "snipedia") is a wiki-based bioinformatics web site that serves as a database of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Each article on a SNP provides a short description, links to scientific articles and personal genomics web sites, as well as microarray information about that SNP. Thus SNPedia may support the interpretation of results of personal genotyping from, e.g., 23andMe and similar companies. SNPedia is a semantic wiki, powered by MediaWiki and the Semantic MediaWiki extension. SNPedia was created, and is run by, geneticist Greg Lennon and programmer Mike Cariaso, who at the time of the site's founding were both located in Bethesda, Maryland. , the website has 537 medical conditions and 109,729 SNPs in its database. The number of SNPs in SNPedia has doubled roughly once every 14 months since August 2007. On 7 September 2019, MyHeritage announced that they acquired both SNPedia and Promethease. All non-European raw genetic data files previously uploa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNPedia
SNPedia (pronounced "snipedia") is a wiki-based bioinformatics web site that serves as a database of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Each article on a SNP provides a short description, links to scientific articles and personal genomics web sites, as well as microarray information about that SNP. Thus SNPedia may support the interpretation of results of personal genotyping from, e.g., 23andMe and similar companies. SNPedia is a semantic wiki, powered by MediaWiki and the Semantic MediaWiki extension. SNPedia was created, and is run by, geneticist Greg Lennon and programmer Mike Cariaso, who at the time of the site's founding were both located in Bethesda, Maryland. , the website has 537 medical conditions and 109,729 SNPs in its database. The number of SNPs in SNPedia has doubled roughly once every 14 months since August 2007. On 7 September 2019, MyHeritage announced that they acquired both SNPedia and Promethease. All non-European raw genetic data files previously uploa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
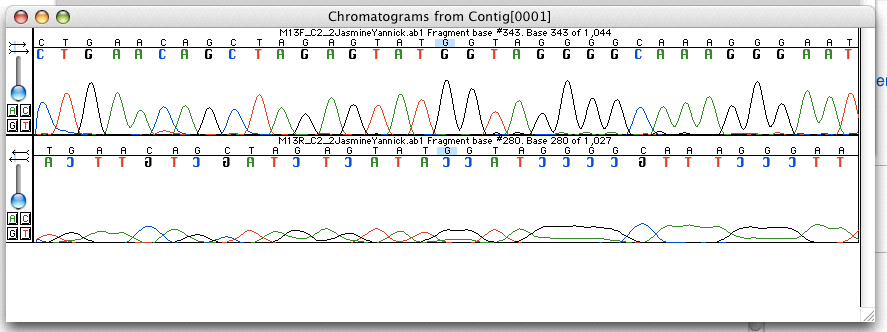
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MyHeritage
MyHeritage is an online genealogy platform with web, mobile, and software products and services, introduced by the Israeli company MyHeritage in 2003. Users of the platform can obtain their family trees, upload and browse through photos, and search through over 14 billion historical records, among other features. As of 2020, the service supports 42 languages and has more than 50 million users worldwide who have built around 52 million family trees. In 2016, it launched a genetic testing service called MyHeritage DNA. The company is headquartered in Or Yehuda, Israel, with additional offices in Tel Aviv, Israel, Lehi, Utah, Kyiv, Ukraine, and Burbank, California. History 2003–2007: Foundation and early years MyHeritage was founded in 2003 by Israeli entrepreneur Gilad Japhet (who continues to serve as the company's CEO). Japhet started the company from his living room in Bnei Atarot, Israel. For a long time, the company's headquarters were located in a family farmhouse in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MediaWiki
MediaWiki is a free and open-source wiki software. It is used on Wikipedia and almost all other Wikimedia websites, including Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons and Wikidata; these sites define a large part of the requirement set for MediaWiki. It was developed for use on Wikipedia in 2002, and given the name "MediaWiki" in 2003. MediaWiki was originally developed by Magnus Manske and improved by Lee Daniel Crocker. Magnus Manske's announcement of "PHP Wikipedia", wikipedia-l, August 24, 2001 Its development has since then been coordinated by the Wikimedia Foundation. MediaWiki is written in the PHP programming language and stores all text content into a database. The software is optimized to efficiently handle large projects, which can have terabytes of content and hundreds of thousands of views per second. Because Wikipedia is one of the world's largest websites, achieving scalability through multiple layers of caching and database replication has been a major concern for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MediaWiki Websites
MediaWiki is a free and open-source wiki software. It is used on Wikipedia and almost all other Wikimedia websites, including Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons and Wikidata; these sites define a large part of the requirement set for MediaWiki. It was developed for use on Wikipedia in 2002, and given the name "MediaWiki" in 2003. MediaWiki was originally developed by Magnus Manske and improved by Lee Daniel Crocker. Magnus Manske's announcement of "PHP Wikipedia", wikipedia-l, August 24, 2001 Its development has since then been coordinated by the Wikimedia Foundation. MediaWiki is written in the PHP programming language and stores all text content into a database. The software is optimized to efficiently handle large projects, which can have terabytes of content and hundreds of thousands of views per second. Because Wikipedia is one of the world's largest websites, achieving scalability through multiple layers of caching and database replication has been a major concern for dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DbSNP
The Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database (dbSNP) is a free public archive for genetic variation within and across different species developed and hosted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) in collaboration with the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). Although the name of the database implies a collection of one class of polymorphisms only (i.e., single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)), it in fact contains a range of molecular variation: (1) SNPs, (2) short deletion and insertion polymorphisms (indels/DIPs), (3) microsatellite markers or short tandem repeats (STRs), (4) multinucleotide polymorphisms (MNPs), (5) heterozygous sequences, and (6) named variants. The dbSNP accepts apparently neutral polymorphisms, polymorphisms corresponding to known phenotypes, and regions of no variation. It was created in September 1998 to supplement GenBank, NCBI’s collection of publicly available nucleic acid and protein sequences. In 2017, NCBI stopped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic MediaWiki
Semantic MediaWiki (SMW) is an extension to MediaWiki that allows for annotating semantic data within wiki pages, thus turning a wiki that incorporates the extension into a semantic wiki. Data that has been encoded can be used in semantic searches, used for aggregation of pages, displayed in formats like maps, calendars and graphs, and exported to the outside world via formats like RDF and CSV. Authors Semantic MediaWiki was initially created by Markus Krötzsch, Denny Vrandečić and Max Völkel, and was first released in 2005. Its development was initially funded by the EU-funded FP6 project SEKT (CORDIS site), and was later supported in part by Institute AIFB of the University of Karlsruhe (later renamed the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology). Currently James Hong Kong is the lead developer , while the other core developer is Jeroen De Dauw. Basic syntax Every semantic annotation within SMW is a "property" connecting the page on which it resides to some other piece of dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Wiki
A semantic wiki is a wiki that has an underlying model of the knowledge described in its pages. Regular, or syntactic, wikis have structured text and untyped hyperlinks. Semantic wikis, on the other hand, provide the ability to capture or identify information about the data within pages, and the relationships between pages, in ways that can be queried or exported like a database through semantic queries. Semantic wikis were first proposed in the early 2000s, and began to be implemented seriously around 2005. As of 2021, well-known semantic wiki engines are Semantic MediaWiki and Wikibase. Key characteristics Formal notation The knowledge model found in a semantic wiki is typically available in a formal language, so that machines can process it into an entity-relationship model or relational database. The formal notation may be included in the pages themselves by users, as in Semantic MediaWiki, or it may be derived from the pages or the page names or the means of linking. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Mendelian Inheritance In Man
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes. Versions and history OMIM is the online continuation of Dr. Victor A. McKusick's ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man'' (MIM), which was published in 12 editions between 1966 and 1998.McKusick, V. A. ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Phenotypes.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1st ed, 1996; 2nd ed, 1969; 3rd ed, 1971; 4th ed, 1975; 5th ed, 1978; 6th ed, 1983; 7th ed, 1986; 8th ed, 1988; 9th ed, 1990; 10th ed, 1992. Nearly all of the 1,486 entries in the first edition of MIM discussed phenotypes. MIM/OMIM is produced and curated at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profilin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |