|
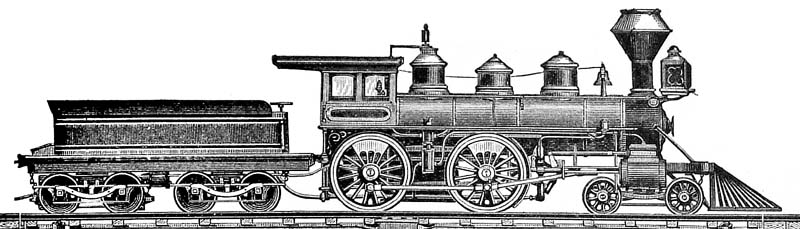
SER A Class
The SER A class was a class of 4-4-0 locomotives on the South Eastern Railway. History For many years the South Eastern Railway (SER) had relied upon locomotives of the 2-4-0 wheel arrangements for their semi-fast passenger services. James Stirling had been appointed to the post of locomotive superintendent of the SER on 28 March 1878. He came from the Glasgow and South Western Railway where, since 1873, he had used 4-4-0 locomotives for express passenger services as being more capable than the 2-4-0s hitherto favoured. Accordingly, his first new class of locomotive for the SER was a 4-4-0, and 12 were built at Ashford Works Ashford railway works was in the town of Ashford in the county of Kent in England. History South Eastern Railway Ashford locomotive works was built by the South Eastern Railway on a new site in 1847, replacing an earlier locomotive repair fa ... between 1879 and 1881. The boiler was interchangeable with that of the O class 0-6-0 (introduced 1878 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Stirling (engineer, Born 1835)
James Stirling (1835–1917) was a Scottish mechanical engineer. He was Locomotive Superintendent of the Glasgow and South Western Railway and later the South Eastern Railway. Stirling was born on 2 October 1835, a son of Robert Stirling, rector of Galston, East Ayrshire. Career Glasgow and South Western Railway After working for a village millwright he joined the Glasgow and South Western Railway (GSWR) where he was apprenticed to his brother Patrick, who had been Locomotive Superintendent of that railway since 1853. On completion of his apprenticeship, he spent a year as a fitter at Sharp Stewart in Manchester, before returning to the GSWR drawing office at Kilmarnock; he later became works manager. On 1 March 1866, his brother Patrick left the GSWR for the Great Northern Railway (GNR), where he became Works Manager at Doncaster, and James was appointed Locomotive Superintendent of the GSWR in his place. Patrick became the Locomotive Superintendent of the GNR from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashford Works
Ashford railway works was in the town of Ashford in the county of Kent in England. History South Eastern Railway Ashford locomotive works was built by the South Eastern Railway on a new site in 1847, replacing an earlier locomotive repair facility at New Cross in London. By 1850 over 130 houses had been built for staff (called Alfred Town by the railway but New Town by everybody else). The works employed about 600 people in 1851 increasing to about 950 by 1861, and around 1,300 by 1882. A carriage and wagon works was opened on an adjacent site in 1850. The works led Ashford to be the largest industrial town in east Kent. South Eastern and Chatham Railway On 1 January 1899, the railway entered into a working union with the London Chatham and Dover Railway, forming the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR). Each antecedent company had its own locomotive works, but Ashford was larger than Longhedge works and so became the principal locomotive works for the new organisation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Railway (UK)
The South Eastern Railway (SER) was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent. The SER absorbed or leased other railways, some older than itself, including the London and Greenwich Railway and the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway. Most of the company's routes were in Kent, eastern Sussex and the London suburbs, with a long cross-country route from in Surrey to Reading, Berkshire. Much of the company's early history saw attempts at expansion and feuding with its neighbours; the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) in the west and the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) to the north-east. However, in 1899 the SER agreed with the LCDR to share operation of the two railways, work them as a single system (marketed as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway) and pool receipts: but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern And Chatham Railway
The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee (SE&CRCJMC),Awdry (1990), page 199 known as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR), was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Eastern Railway (UK), South Eastern Railway (SER) and London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LC&DR), which operated between London and south-east England. Between 1899 and 1923, the SE&CR had a monopoly of railway services in Kent and to the main English Channel, Channel ports for ferries to France and Belgium. The companies had competed extensively, with some of the bitterest conflicts between British railway companies. Competing routes to the same destinations were built, so several towns in Kent had been served with a similar frequency service by both companies. In places, unfettered competition allowed two stations and services to multiple London termini. It would be a constituent of the Southern Railway (UK), Southern Railway as part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels. The notation 2-4-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, on which its water and fuel is carried on board the engine itself, rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-4-0 configuration was developed in the United Kingdom in the late 1830s or early 1840s as an enlargement of the 2-2-0 and 2-2-2 types, with the additional pair of coupled wheels giving better adhesion. The type was initially designed for freight haulage. One of the earliest examples was the broad-gauge GWR Leo Class, designed by Daniel Gooch and built during 1841 and 1842 by R. & W. Hawthorn, Leslie and Company; Fenton, Murray and Jackson; and Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell. Because of its popularity for a period with English railways, noted railway author C. Hamilton Ellis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive Superintendent
Chief mechanical engineer and locomotive superintendent are titles applied by British, Australian, and New Zealand railway companies to the person ultimately responsible to the board of the company for the building and maintaining of the locomotives and rolling stock. In Britain, the post of ''locomotive superintendent'' was introduced in the late 1830s, and ''chief mechanical engineer'' in 1886. Emerging professional roles In the early Victorian era, projected canal or railway schemes were prepared by groups of promoters who hired specialists such as civil engineers, surveyors, architects or contractors to survey a route; and this resulted in the issue of a prospectus setting out their proposals. Provided that adequate capital could be raised from potential investors, agreements obtained from the landowners along the proposed route and, in Britain, an Act of Parliament obtained (different terminology is used in other countries), then construction might begin either by a new compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow And South Western Railway
The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) was a railway company in Scotland. It served a triangular area of south-west Scotland between Glasgow, Stranraer and Carlisle. It was formed on 28 October 1850 by the merger of two earlier railways, the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway and the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway. Already established in Ayrshire, it consolidated its position there and extended southwards, eventually reaching Stranraer. Its main business was mineral traffic, especially coal, and passengers, but its more southerly territory was very thinly populated and local traffic, passenger and goods, was limited, while operationally parts of its network were difficult. It later formed an alliance with the English Midland Railway and ran express passenger trains from Glasgow to London with that company, in competition with the Caledonian Railway and its English partner, the London and North Western Railway, who had an easier route. In 1923 the G&S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SER O Class
The South Eastern Railway (SER) O Class (some of which were later rebuilt, becoming the O1 Class) was a class of 0-6-0 steam locomotive designed for freight work, and were the main freight engines of the SER, and later the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR) for a number of years. However, they were displaced by the more powerful C class locomotives following the amalgamation of the South Eastern Railway and London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) in 1899. This relegated the class to working on the numerous branch lines in Kent, on both passenger and freight work. They worked most notably on the Kent & East Sussex Railway and East Kent Railway, operating coal trains from the Kent coal fields to London, as well as shunting work at such locations as Shepherds Well, Hoo Junction and Ashford. The majority were withdrawn before the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939, and those that remained were slowly withdrawn from nationalisation onwards. The death knell for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SER Q Class
The SER Q class was a class of 0-4-4T steam locomotives of the South Eastern Railway. The class was designed by James Stirling and introduced in 1881. Construction Prior to the appointment of James Stirling as Locomotive Superintendent of the South Eastern Railway (SER) in 1878, that railway possessed only a small number of tank locomotives suitable for the London suburban passenger services. There were twelve 0-4-2WT of the 205 class (later G class) dating from 1863–64; seven 0-4-4WT of the 235 class (later J class) dating from 1866; six 0-4-2WT of the 73 class (later H class) dating from 1867–69; and nine 0-4-4T of the 58 class (later M class) dating from 1877–78. The SER had opened a connection to the London, Chatham and Dover Railway in June1878 giving access to Blackfriars station, the Widened Lines and thus the Great Northern Railway. Tender locomotives were not suitable for working this route, and nor were many of the existing tank engines which were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Wainwright
Harry Smith Wainwright (16 November 1864 – 19 September 1925) was an English railway engineer, and was the Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Superintendent of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway from 1899 to 1913. He is best known for a series of simple but competent locomotives produced under his direction at the company's Ashford railway works in the early years of the twentieth century. Many of these survived in service until the end of steam traction in Britain in 1968, and are regarded as some of the most elegant designs of the period. Biography Wainwright was born at Worcester on 16 November 1864, the third son of William Wainwright. In 1896, he was appointed Carriage & Wagon Superintendent of the South Eastern Railway (SER), in succession to his father. On 1 January 1899, the SER entered into a working union with the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR); their respective Locomotive Superintendents, James Stirling and William Kirtley, both retired, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Correspondence And Travel Society
The Railway Correspondence and Travel Society (RCTS) is a national society founded in Cheltenham, England in 1928 to bring together those interested in rail transport and locomotives. Since 1929 the Society has published a regular journal ''The Railway Observer'' which records the current railway scene. It also has regional branches which organise meetings and trips to places of interest and an archive & library. It has published definitive multi-volume locomotive histories of the Great Western, Southern and London & North Eastern Railways, and has in progress similar works on the London, Midland & Scottish Railway and British Railways standard steam locomotives. It also has published many other historical railway books since the mid-1950s. On 2 November 2016, the RCTS become a Charitable Incorporated Organisation (CIO), registered number 1169995. Its new Archive and Library (located within the former station-master's house at Leatherhead station) was opened on 6 October 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |