|
SCSI Log Pages
SCSI target Target may refer to: Physical items * Shooting target, used in marksmanship training and various shooting sports ** Bullseye (target), the goal one for which one aims in many of these sports ** Aiming point, in field artillery, fi ... devices provide a number of SCSI log pages. These can be interrogated by a Log Sense command and in some cases can be set by a Log Select command. The Log Sense and Log Select commands include a 6-bit address field, allowing for 64 possible log pages. There is a standard map of log page addresses below. Note that any given SCSI device type will only support a subset of these log pages. *00h - supported log pages *01h - buffer over-run/under-run *02h - error counter (write) *03h - error counter (read) *04h - error counter (read reverse) *05h - error counter (verify) *06h - non-medium error *07h - last n error events *08h-2Fh - reserved *30h-3Eh - vendor-specific *3Fh - reserved SCSI {{Compu-hardware-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
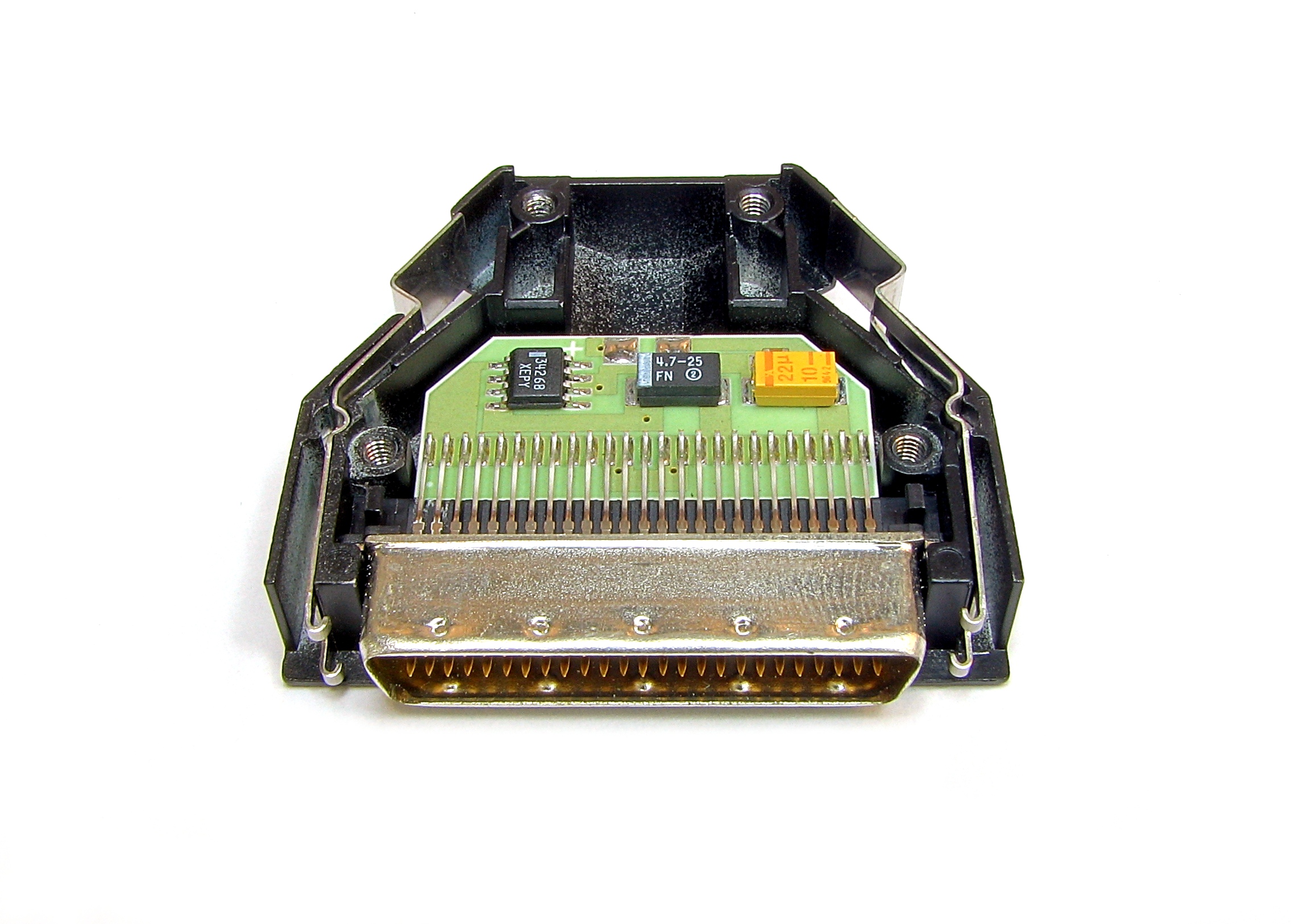
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI Target
In computer data storage, a SCSI initiator is the endpoint that initiates a SCSI session, that is, sends a SCSI command. The initiator usually does not provide any Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs). On the other hand, a SCSI target is the endpoint that does ''not'' initiate sessions, but instead waits for initiators' commands and provides required input/output data transfers. The target usually provides to the initiators one or more LUNs, because otherwise no read or write command would be possible. Detailed information Typically, a computer is an initiator and a data storage device is a target. As in a client–server architecture, an initiator is analogous to the client, and a target is analogous to the server. Each SCSI address (each identifier on a SCSI bus) displays behavior of initiator, target, or (rarely) both at the same time. There is nothing in the SCSI protocol that prevents an initiator from acting as a target or vice versa. SCSI initiators are sometimes wrongly calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI Log Sense Command
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI Log Select Command
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |