|
SAVIAC
The Shock and Vibration Information Analysis Center (SAVIAC) is a U.S. Government organization established by the U.S. Navy Office of Naval Research on 20 December 1946. SAVIAC's purpose is to promulgate information on the transient and vibratory response of structures and materials. This broad field includes such technical areas as the testing, analysis and design of structural or mechanical systems subjected to dynamic conditions and loading such as vibration, blast, impact, and shock for various agencies in the U. S. Government including NASA, the Department of Energy (DOE), and the Department of Defense (DOD). The organization sponsored the professional journal ''Shock and Vibration Journal'' and currently sponsors and publishes the professional journal ''Journal of Critical Technology in Shock and Vibration.'' SAVIAC also sponsored and published a series of monograms addressing different aspects of shock and vibration. In 2012 SAVIAC became inactive as a result of new Depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic function, periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road. Vibration can be desirable: for example, the motion of a tuning fork, the Reed (music), reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, a mobile phone, or the cone of a loudspeaker. In many cases, however, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating unwanted sound. For example, the vibrational motions of engines, electric motors, or any Machine, mechanical device in operation are typically unwanted. Such vibrations could be caused by Engine balance, imbalances in the rotating parts, uneven friction, or the meshing of gear teeth. Careful designs usually minimize unwanted vibrations. The studies of sound and vibration are closely related. Sound, or pressure waves, are ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Government Of The United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a federal district (the city of Washington in the District of Columbia, where most of the federal government is based), five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government, sometimes simply referred to as Washington, is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court. Naming The full name of the republic is "United States of America". No other name appears in the Constitution, and this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Engineering Organizations
{{disambiguation ...
Civil may refer to: *Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit * Civil affairs *Civil and political rights *Civil disobedience *Civil engineering *Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces *Civil law (other), multiple meanings *Civil liberties *Civil religion *Civil service *Civil society *Civil war *Civil (surname) Civil is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Alan Civil (1929–1989), British horn player *François Civil (born 1989), French actor * Gabrielle Civil, American performance artist *Karen Civil (born 1984), American social media an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
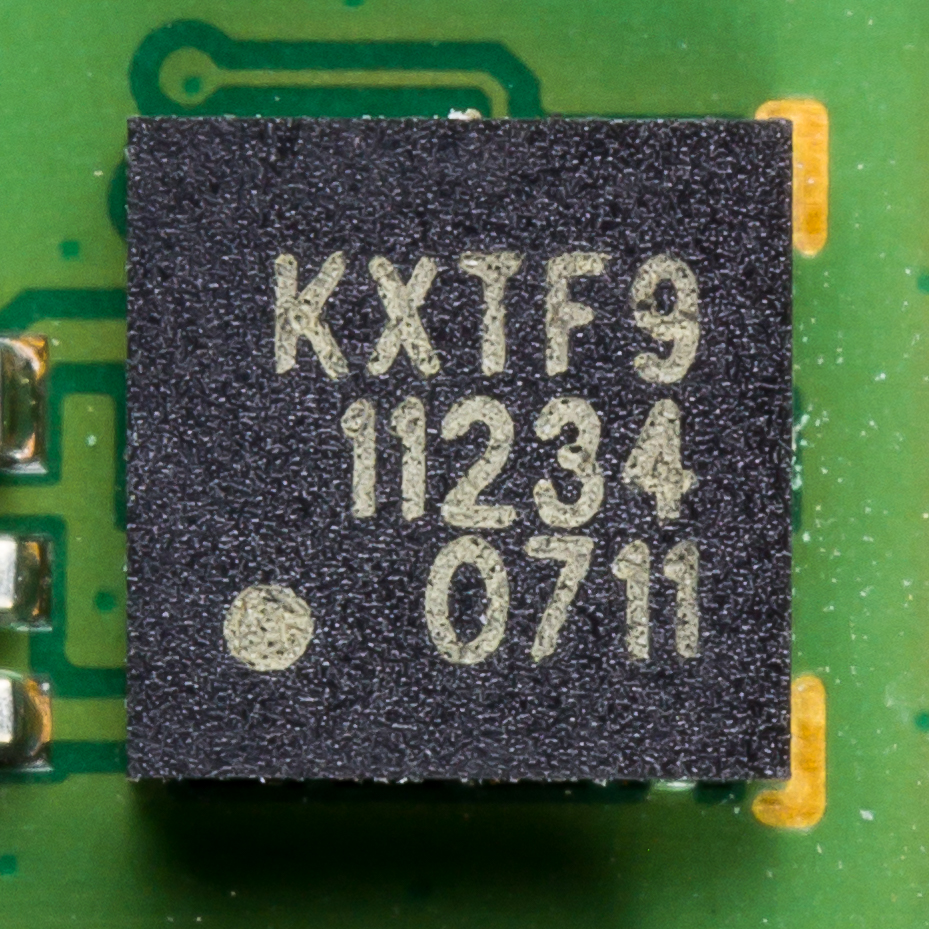
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Dynamics
Structural dynamics is a type of structural analysis which covers the behavior of a structure subjected to dynamic (actions having high acceleration) loading. Dynamic loads include people, wind, waves, traffic, earthquakes, and blasts. Any structure can be subjected to dynamic loading. Dynamic analysis can be used to find dynamic displacements, time history, and modal analysis. Structural analysis is mainly concerned with finding out the behavior of a physical structure when subjected to force. This action can be in the form of load due to the weight of things such as people, furniture, wind, snow, etc. or some other kind of excitation such as an earthquake, shaking of the ground due to a blast nearby, etc. In essence all these loads are dynamic, including the self-weight of the structure because at some point in time these loads were not there. The distinction is made between the dynamic and the static analysis on the basis of whether the applied action has enough acceleration in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Engineering
Earthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake (or seismic) engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. Earthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, applied physics, etc. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penetration (weapons)
Strictly speaking, penetration occurs when a projectile enters a target without passing through it and perforation occurs when the projectile completely passes through the target, but the word ''penetration'' is commonly used to refer to either. Penetration into a ''semi-infinite'' or ''massive'' target is penetration (in the strict sense of the word) of targets so thick that the level of penetration is not affected by the target's thickness. There is a ''transition region'' between semi-infinite penetration and perforation, in which the target is not perforated but the projectile, as it nears the back face of the target, meets reduced resistance and is capable of penetrating a greater distance than it would in a semi-infinite target. This effect is variously named the back or rear surface, plate, or face effect and is also present when perforation occurs. A penetrating projectile may cause the target to break into multiple pieces, spewing from both the front and back of the targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Blast
Atmospheric focusing is a type of wave interaction causing shock waves to affect areas at a greater distance than otherwise expected. Variations in the atmosphere create distortions in the wavefront by refracting a segment, allowing it to converge at certain points and constructively interfere. In the case of destructive shock waves, this may result in areas of damage far beyond the theoretical extent of its blast effect. Examples of this are seen during supersonic booms, large extraterrestrial impacts from objects like meteors, and nuclear explosions. Density variations in the atmosphere (e.g. due to temperature variations), or airspeed variations cause refraction along the shock wave, allowing the uniform wavefront to separate and eventually interfere, dispersing the wave at some points and focusing it at others. A similar effect occurs in water when a wave travels through a patch of different density fluid, causing it to diverge over a large distance. For powerful shock wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Contractor
A government contractor is a company (privately owned, publicly traded or a state-owned enterprise)either for profit or non-profitthat produces goods or services under contract for the government. Some communities are largely sustained by government contracting activity; for instance, much of the economy of Northern Virginia consists of government contractors employed directly or indirectly by the federal government of the United States. United Kingdom Section 12(2) and (3) of the Official Secrets Act 1989 define the expression "Government Contractor" for the purposes of that Act. from the National Archives See also *< ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Clearance
A security clearance is a status granted to individuals allowing them access to classified information (state or organizational secrets) or to restricted areas, after completion of a thorough background check. The term "security clearance" is also sometimes used in private organizations that have a formal process to vet employees for access to sensitive information. A clearance by itself is normally not sufficient to gain access; the organization must also determine that the cleared individual needs to know specific information. No individual is supposed to be granted automatic access to classified information solely because of rank, position, or a security clearance. Canada Background Government classified information is governed by the Treasury Board Standard on Security Screening, the ''Security of Information Act'' and '' Privacy Act''. Only those that are deemed to be loyal and reliable, and have been cleared are allowed to access sensitive information. The policy w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known as detonations and travel through shock waves. Subsonic explosions are created by low explosives through a slower combustion process known as deflagration. Causes Explosions can occur in nature due to a large influx of energy. Most natural explosions arise from volcanic or stellar processes of various sorts. Explosive volcanic eruptions occur when magma rises from below, it has very dissolved gas in it. The reduction of pressure as the magma rises and causes the gas to bubble out of solution, resulting in a rapid increase in volume. Explosions also occur as a result of impact events and in phenomena such as hydrothermal explosions (also due to volcanic processes). Explosions can also occur outside of Earth in the universe in events s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classified Information
Classified information is material that a government body deems to be sensitive information that must be protected. Access is restricted by law or regulation to particular groups of people with the necessary security clearance and need to know, and mishandling of the material can incur criminal penalties. A formal security clearance is required to view or handle classified material. The clearance process requires a satisfactory background investigation. Documents and other information must be properly marked "by the author" with one of several (hierarchical) levels of sensitivity—e.g. restricted, confidential, secret, and top secret. The choice of level is based on an impact assessment; governments have their own criteria, including how to determine the classification of an information asset and rules on how to protect information classified at each level. This process often includes security clearances for personnel handling the information. Some corporations and non-governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |