|
Russula Cupreola
''Russula cupreola'' is an agaricoid fungal species first typed in 1990. It shows a white stem and a purple/ochre coloured cap, with a maximum diameter of 30 mm. The gills will be white in younger fruiting bodies, but as the gills age they will become ochraceous. This species is currently found in Scandinavia. Merging of species ''Russula cupreola'' and '' R. purpureofusca'' were merged under one name, ''Russula cupreola'', in 2016. The typing of ''R. purpureofusca'' was done with a juvenile specimen of ''R. cupreola,'' leading mycologists to believe it was a separate species. After noticing similar features between the two species, researchers performed ITS1 Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. I ... sequencing and verified that the two species were conspecific. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricoid
An agaric () is a type of fungus fruiting body characterized by the presence of a pileus (cap) that is clearly differentiated from the stipe (stalk), with lamellae (gills) on the underside of the pileus. In the UK, agarics are called "mushrooms" or "toadstools". In North America they are typically called "gilled mushrooms". "Agaric" can also refer to a basidiomycete species characterized by an agaric-type fruiting body. Archaically, agaric meant 'tree-fungus' (after Latin ''agaricum''); however, that changed with the Linnaean interpretation in 1753 when Linnaeus used the generic name ''Agaricus'' for gilled mushrooms. Most species of agaricus belong to the order Agaricales in the subphylum Agaricomycotina. The exceptions, where agarics have evolved independently, feature largely in the orders Russulales, Boletales, Hymenochaetales, and several other groups of basidiomycetes. Old systems of classification placed all agarics in the Agaricales and some (mostly older) sources use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochraceous
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. * Yellow ochre, , is a hydrated iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre. * Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite, which is an anhydrous iron oxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russula Purpureofusca
''Russula cupreola'' is an agaricoid fungal species first typed in 1990. It shows a white stem and a purple/ochre coloured cap, with a maximum diameter of 30 mm. The gills will be white in younger fruiting bodies, but as the gills age they will become ochraceous. This species is currently found in Scandinavia. Merging of species ''Russula cupreola'' and '' R. purpureofusca'' were merged under one name, ''Russula cupreola'', in 2016. The typing of ''R. purpureofusca'' was done with a juvenile specimen of ''R. cupreola,'' leading mycologists to believe it was a separate species. After noticing similar features between the two species, researchers performed ITS1 Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. I ... sequencing and verified that the two species were conspecific. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
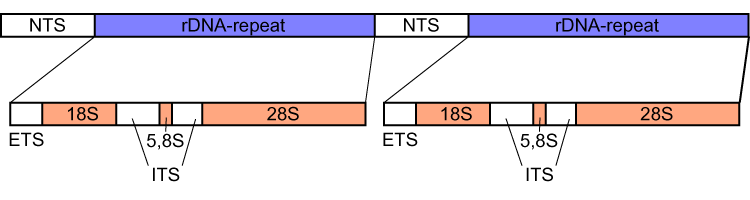
ITS1
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRNA ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Specificity
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organisms or constituents of living organisms of being special or doing something special. Each animal or plant species is special. It differs in some way from all other species...biological specificity is the major problem about understanding life." Biological specificity within ''Homo sapiens'' ''Homo sapiens'' has many characteristics that show the biological specificity in the form of behavior and morphological traits. Morphologically, humans have an enlarged cranial capacity and more gracile features in comparison to other hominins. The reduction of dentition is a feature that allows for the advantage of adaptability in diet and survival. As a species, humans are culture dependent and much of human survival relies on the culture and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russula
''Russula'' is a very large genus composed of around 750 worldwide species of ectomycorrhizal mushrooms. They are typically common, fairly large, and brightly colored – making them one of the most recognizable genera among mycologists and mushroom collectors. Their distinguishing characteristics include usually brightly coloured caps, a white to dark yellow spore print, brittle, attached gill (mushroom), gills, an absence of latex, and absence of partial veil or universal veil, volva tissue on the stem. Microscopically, the genus is characterised by the amyloid ornamented spores and flesh (trama) composed of spherocysts. Members of the related genus ''Lactarius (fungus), Lactarius'' have similar characteristics but emit a milky latex when their gills are broken. The genus was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1796. Taxonomy Christian Hendrik Persoon first circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed the genus ''Russula'' in his 1796 work ''Observationes Mycologicae'', and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |