|
Russian Cruiser Pamiat Azova
''Pamiat Azova'' (russian: Память Азовa) was a unique armoured cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the late 1880s. She was decommissioned from front line service in 1909, converted into a depot ship and sunk by British torpedo boats during the Baltic Naval War, part of the Russian Civil War. Name The name of the ship commemorated the Russian ship of the line , the flagship of the Russian squadron in the Battle of Navarino. The name of that ship, in its turn, referred to the Azov campaigns of Peter the Great. After the battle Nicholas I of Russia decreed that after the retirement of ''Azov'' the Imperial Navy must perpetually have a ship named ''Pamyat Azova'' (English: ''The Memory of Azov''). The cruiser commissioned in 1890 was the third ship carrying this name. Design The ship was designed as a commerce raider and rigged with sails to extend her range. She was built by Baltic Works in Saint Petersburg and launched on 1 July 1888. Her machinery was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
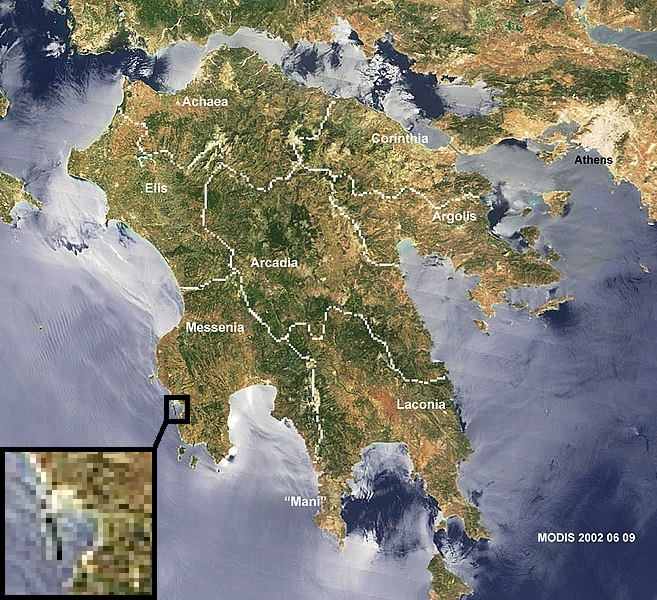
Battle Of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied forces from Britain, France, and Russia decisively defeated Ottoman and Egyptian forces which were trying to suppress the Greeks, thereby making Greek independence much more likely. An Ottoman armada which, in addition to Imperial warships, included squadrons from the ''eyalets'' (provinces) of Egypt and Tunis, was destroyed by an Allied force of British, French and Russian warships. It was the last major naval battle in history to be fought entirely with sailing ships, although most ships fought at anchor. The Allies' victory was achieved through superior firepower and gunnery. The context of the three Great Powers' intervention in the Greek conflict was the Russian Empire's long-running expansion at the expense of the decaying Ottoman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Of Azov (Fabergé Egg)
The Memory of Azov (or the Azova Egg) is a jewelled Easter egg made under the supervision of the Russian jeweller Peter Carl Fabergé in 1891 for Tsar Alexander III of Russia. It was presented by Alexander III as an Easter gift to his wife, the Tsarina Maria Feodorovna. It is currently held in the Kremlin Armoury Museum in Moscow. Design Carved from a solid piece of heliotrope jasper, also known as bloodstone, the Memory of Azov Egg is decorated in the Louis XV style with a superimposed gold pattern of Rococo scrolls with brilliant diamonds and chased gold flowers. The broad flute gold bezel is set with a drop ruby and two diamonds that complete the clasp. The egg's interior is lined with green velvet. Surprise The surprise contained within is a miniature replica of the Imperial Russian Navy cruiser '' Pamiat Azova'' (Memory of Azov), executed in red and yellow gold and platinum with small diamonds for windows, set on a piece of aquamarine representing the water. The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabergé Egg
A Fabergé egg (russian: link=no, яйцо Фаберже́, translit=yaytso Faberzhe) is a jewelled egg created by the jewellery firm House of Fabergé, in Saint Petersburg, Russia. As many as 69 were created, of which 57 survive today. Virtually all were manufactured under the supervision of Peter Carl Fabergé between 1885 and 1917. The most famous are his 52 "Imperial" eggs, 46 of which survive, made for the Russian Tsars Alexander III and Nicholas II as Easter gifts for their wives and mothers. Fabergé eggs are worth millions of dollars and have become symbols of opulence. History The House of Fabergé was founded by Gustav Fabergé in 1842 in St. Petersburg, Russia. The Fabergé egg was a later addition to the product line by his son, Peter Carl Fabergé. Prior to 1885, Tsar Alexander III gave his wife Empress Maria Feodorovna jeweled Easter eggs. For Easter in 1883, before his coronation, Alexander III and Maria Feodorovna were given eggs, one of which contained a sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
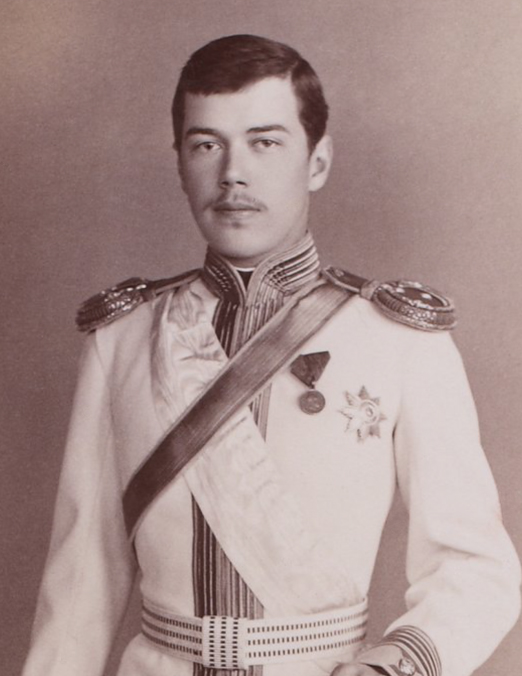
Czar Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prime ministers, Sergei Witte and Pyotr Stolypin. He advocated modernization based on foreign loans and close ties with France, but resisted giving the new parliament (the Duma) major roles. Ultimately, progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, strong aristocratic opposition and defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 304-year rule of Russia (1613� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Journey Of Nicholas II
The Eastern journey of Nicholas II in 1890–91 was a journey made by Nicholas Alexandrovich–then Tsesarevich of Russia–around the greater part of the Eurasian continent. The total length of the journey exceeded 51,000 kilometres, including 15,000 km of railway and 22,000 km of sea routes. During his visit to the Empire of Japan, Nicholas was the target of a failed assassination attempt. Background After the Grand Embassy of Peter the Great, a long trip for educational purposes became an important part of training for the state activity of the members of the Russian Imperial house. In 1890 Emperor Alexander III of Russia decided to establish the Trans-Siberian Railway and his heir Tsesarevich Nicholas took part in the opening ceremony. Voyage On 23 October, after a church service in Gatchina, the Tsesarevich went by train via Vienna to Trieste where he boarded the cruiser '' Pamiat Azova'' (''Memory of Azov''). This route was selected because of probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg , image_size = 150 , caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign , dates = 18 May 1703 – present , country = , allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present) , branch = Russian navy , type = , role =Naval warfare; Amphibious warfare;Combat patrols in the Baltic;Naval presence/diplomacy missions in the Atlantic and elsewhere , size = c. 42 Surface warships (surface combatants, major amphibious units, mine warfare) plus support ships and auxiliaries 1 Submarine , command_structure = Russian Armed Forces , garrison = Kaliningrad (HQ)BaltiyskKronstadt , garrison_label = , nickname = , patron = , motto = , colors = , colors_label = , march = , mascot = , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = Great Northern War * Battle of Stäket *Battle of Gangut Seven Years' War Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790) Russo-Turkish WarsCrimean War Russo-Japanese WarWorld War IRussian Civil War W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Of Azov Egg
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory processor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellville Boilers
Bellville may refer to: ;Argentina * Bell Ville, Córdoba ;South Africa * Bellville, Western Cape ** Bellville railway station ;United States * Bellville, Georgia * Bellville, Missouri * Bellville, Ohio * Bellville, Texas See also *Belleville (other) *Belville (other) Belville can refer to: Places *Belville (Belgrade), an urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. *Bell Ville, Córdoba Province, Argentina ** the Belville meteorite of 1937, which fell in Córdoba, Argentina (see Meteorite falls) * Bel ... {{geodis nl:Belleville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
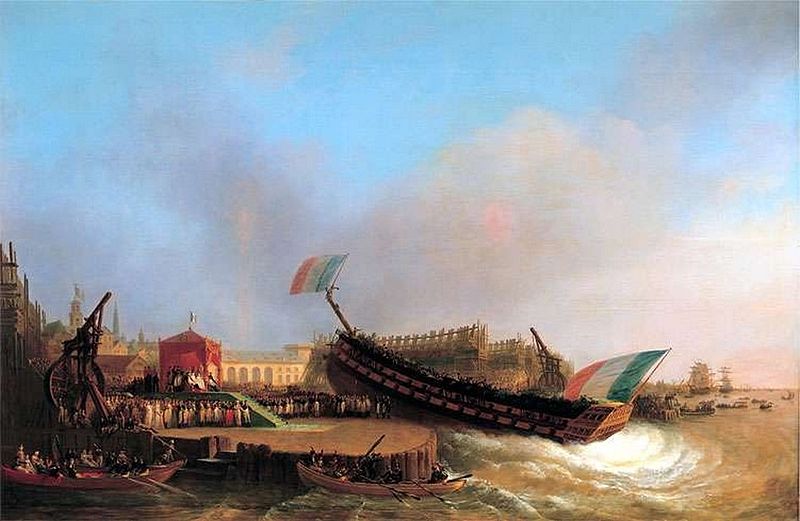
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commerce Raider
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than engaging its combatants or enforcing a blockade against them. Privateering The first sort of commerce raiding was for nations to commission privateers. Early instances of this type of warfare were by the English and Dutch against the Spanish treasure fleets of the 16th century, which resulted in financial gain for both captain and crew upon capture of enemy vessels ("prizes"). 17th and 18th centuries Privateers formed a large part of the total military force at sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. In the First Anglo-Dutch War, English privateers attacked the trade on which the United Provinces entirely depended, capturing over 1,000 Dutch merchant ships. During the subsequent war with Spain, Spanish and Flemish privateers in the service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |