|
Rudolf Heidenhain
Rudolf Peter Heinrich Heidenhain (; 29 January 1834 – 13 October 1897) was a German physiologist born in Marienwerder, East Prussia (now Kwidzyn, Poland). His son, Martin Heidenhain, was a highly regarded anatomist. Academic career He studied medicine at the Universities of University of Halle-Wittenberg, Halle and University of Berlin, Berlin. After receiving his doctorate, he remained in Berlin as an assistant to Emil du Bois-Reymond (1818-1896). In 1856 he returned to Halle, Saxony-Anhalt, Halle, and worked in the laboratory of Alfred Wilhelm Volkmann (1801-1877). While serving an assistant at Halle, he made improvements on Hermann Welcker’s procedure for measurement of blood volume. In 1859 he attained the chair of physiology at the University of Breslau, where he remained for the rest of his career. Three of his famous students at Breslau were Karl Weigert (1845-1904), Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (1849-1936), and Albert Wojciech Adamkiewicz (1850-1921). His laboratory was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidenhain
Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH is a privately owned enterprise located in Traunreut, Germany that manufactures numerical controls for machine tools, as well as mechatronic measuring devices for length and angle. Their linear and angle encoders are built for use in automated machines and systems, particularly in machine tools. History The company began as a metal etching factory founded in Berlin by Wilhelm Heidenhain in 1889 that manufactured templates, company plaques, product labels, and scales. In 1928 Heidenhain invented the Metallur process. This lead-sulfide copying process made it possible for the first time to make exact copies of an original grating on a metal surface for industrial use. By 1943, Heidenhain was producing linear scales with accuracy of ± 15 µm and circular scale disks with accuracy of ± 3 angular seconds. After World War II, in 1948, Dr. Johannes Heidenhain, a pupil of Otto Hahn, founded the present company in Traunreut. Its invention of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Weigert
Karl Weigert, Carl Weigert (19 March 1845 in Münsterberg in Silesia – 5 August 1904 in Frankfurt am Main) was a German Jewish pathologist. His nephew was Fritz Weigert and his cousin was Paul Ehrlich. He received his education at the universities of Berlin, Vienna, and Breslau, graduating in 1868. After having taken part in the Franco-Prussian war as assistant surgeon, he settled in Breslau, and for the following two years, was an assistant to Heinrich Waldeyer; from 1870 to 1874 to Hermann Lebert, and then to Julius Cohnheim, who he followed to the University of Leipzig in 1878. There he became an associate professor of pathology in 1879. In 1884, he was appointed professor of pathological anatomy at the Senkenbergsche Stiftung in Frankfurt am Main, and received the title of "Geheimer Medizinal-Rat" in 1899. He is buried in Old Jewish Cemetery, Frankfurt (Juedischer Friedhof Rat-Beil-Straße). Weigert assisted Cohnheim in many of his researches, and wrote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnotism
Hypnosis is a human condition involving focused attention (the selective attention/selective inattention hypothesis, SASI), reduced peripheral awareness, and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion.In 2015, the American Psychological Association Division 30 defined hypnosis as a "state of consciousness involving focused attention and reduced peripheral awareness characterized by an enhanced capacity for response to suggestion". For critical commentary on this definition, see: There are competing theories explaining hypnosis and related phenomena. ''Altered state'' theories see hypnosis as an altered state of mind or trance, marked by a level of awareness different from the ordinary state of consciousness. In contrast, ''non-state'' theories see hypnosis as, variously, a type of placebo effect,Kirsch, I., "Clinical Hypnosis as a Nondeceptive Placebo", pp. 211–25 in Kirsch, I., Capafons, A., Cardeña-Buelna, E., Amigó, S. (eds.), ''Clinical Hypnosis and Self-Regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed). In serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to muscarinic receptors in the glands, leading to increased salivation. The fourth pair of salivary glands, the tubarial glands discovered in 2020, are named for their location, being positioned in front and over the torus tubarius. However, this finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demilunes Of Heidenhain
Serous demilunes, also known as Crescents of Giannuzzi or Demilunes of Heidenhain, are cellular formations in the shape of a half-moon (hence the name "demilune") on some salivary glands. Serous demilunes are the serous cells at the distal end of mucous tubuloalveolar secretory unit of certain salivary glands. These demilune cells secrete the proteins that contain the enzyme lysozyme, which degrades the cell walls of bacteria. In this way, lysozyme confers antimicrobial activity to mucus. The serous demilune is an artifact from traditional methods of preparing samples. Samples are traditionally preserved and fixed in formaldehyde. When samples were preserved by quick-freezing in liquid nitrogen and then fixed with osmium tetraoxide in acetone, no demilunes were found. Examination showed that the serous cells and mucosal cells were aligned in the acinus. The traditional preparation caused mucous cells to swell during fixation which results in the serous cells being popped out of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
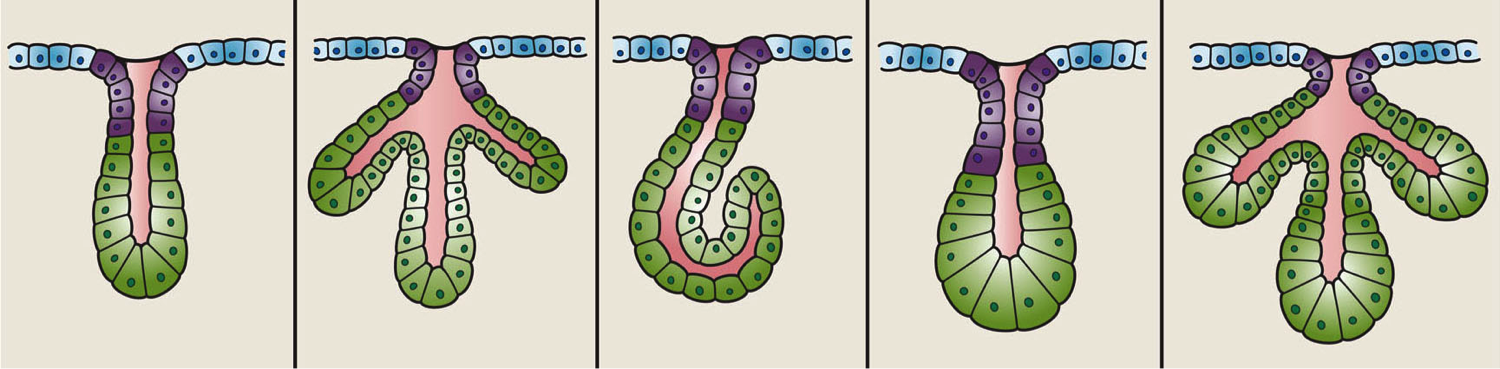
Glands
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectrics
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |