|
Ruby Creek, British Columbia
Ruby Creek is a locality on the Fraser River in the District of Kent, British Columbia British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ..., Canada, in the Upper Fraser Valley region, located on BC Highway 7 and the mainline of the Canadian Pacific Railway, near the confluence of Ruby Creek with the Fraser, northeast of Sea Bird Island. Ruby Creek Indian Reserve No. 2 of the Skawahlook First Nation is nearby, as is also Skawahlook Indian Reserve No. 1, one mile northeast of the mouth of Ruby Creek. Also in the locality is Lukseetsissum Indian Reserve No. 9 of the Yale First Nation. References Populated places on the Fraser River Populated places in the Fraser Valley Regional District Lower Mainland Kent, British Columbia {{BritishColumbiaCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser River
The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. The river's annual discharge at its mouth is or , and it discharges 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean. Naming The river is named after Simon Fraser, who led an expedition in 1808 on behalf of the North West Company from the site of present-day Prince George almost to the mouth of the river. The river's name in the Halqemeylem (Upriver Halkomelem) language is , often seen archaically as Staulo, and has been adopted by the Halkomelem-speaking peoples of the Lower Mainland as their collective name, . The river's name in the Dakelh language is . The ''Tsilhqot'in'' name for the river, not dissimilar to the ''Dakelh'' name, is , meaning Sturgeon ''()'' River ''()''. Course The Fraser drains a area. Its source is a dripping spring at Fraser Pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent, British Columbia
The District of Kent is a district municipality located east of Vancouver, British Columbia. Part of the Fraser Valley Regional District, Kent consists of several communities, the largest and most well-known being Agassiz—the only town in the municipality— Harrison Mills, Kilby, Mount Woodside, Kent Prairie, Sea Bird Island and Ruby Creek. Included within the municipality's boundaries are several separately-governed Indian reserves, including the Seabird Island First Nation's reserves on and around the island of the same name. Kent's only incorporated municipal neighbours are Chilliwack, to the south across the Fraser, and Harrison Hot Springs which is an enclave on the north side of the municipality at the south end of Harrison Lake. Chehalis, to the west across the Harrison River from Harrison Mills, is unincorporated and largely an Indian reserve community of the Chehalis First Nation of the Sts'Ailes people. Neighbourhoods Located north of Chilliwack and south of Har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser Valley
The Fraser Valley is a geographical region in southwestern British Columbia, Canada and northwestern Washington State. It starts just west of Hope in a narrow valley encompassing the Fraser River and ends at the Pacific Ocean stretching from the North Shore Mountains, opposite the city of Vancouver BC, to just south of Bellingham, Washington. In casual usage it typically describes the Fraser River basin downstream of the Fraser Canyon. The term is sometimes used outside British Columbia to refer to the entire Fraser River sections including the Fraser Canyon and up from there to its headwaters, but in general British Columbian usage the term refers to the stretch of Lower Mainland west of the Coquihalla River mouth at the inland town of Hope, and includes all of the Canadian portion of the Fraser Lowland as well as the valleys and upland areas flanking it. It is divided into the Upper Fraser Valley and Lower Fraser Valley by the Vedder River mouth at the eastern foothills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Highway 7
Highway 7, known for most of its length as the Lougheed Highway and Broadway, is an alternative route to Highway 1 through the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. Whereas the controlled-access Highway 1 follows the southern bank of the Fraser River, Highway 7 follows the northern bank. Highway 7 was first commissioned in 1941, and originally went from Vancouver to Harrison Hot Springs, following Dewdney Trunk Road between Port Moody and Port Coquitlam. In 1953, Highway 7 was moved to its current alignment between Vancouver and Coquitlam. Its eastern end was moved south from Harrison Hot Springs to Agassiz in 1956, and then east to Ruby Creek in 1968. Since September 1972, Highway 7 has travelled to a junction with Highway 1 just north of Hope. The name of the highway, unlike that of Alberta Premier Peter Lougheed, is pronounced . The highway is named after Nelson Seymour Lougheed, MLA for the Dewdney District and the BC Minister of Public Works (1928–1929), who ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby Creek (Canada)
Ruby Creek is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Lower Mainland of British Columbia, Canada, rising in the southern Lillooet Ranges and joining the Fraser east of Sea Bird Island at the locality of Ruby Creek and the associated Ruby Creek Indian Reserve No. 2. It is the largest tributary along the north side of the Fraser between Hope and Agassiz Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz ( ; ) FRS (For) FRSE (May 28, 1807 – December 14, 1873) was a Swiss-born American biologist and geologist who is recognized as a scholar of Earth's natural history. Spending his early life in Switzerland, he rec .... References * Lillooet Ranges Rivers of the Lower Mainland Tributaries of the Fraser River Rivers of the Pacific Ranges {{BritishColumbiaCoast-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Bird Island (British Columbia)
Sea Bird Island is an island in the Fraser River just east of Agassiz, British Columbia, Canada, in the Upper Fraser Valley region of that province, about 75 miles east of Vancouver. Though within the District of Kent, most of the island is the Seabird Island Indian reserve and is the community of the Seabird Island First Nation, a member government of the Sto:lo Tribal Council. Name The name is derived from the ''Sea Bird'', one of the first steamboats to operate on the Fraser during the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush, (also Fraser Gold Rush and Fraser River Gold Rush) began in 1858 after gold was discovered on the Thompson River in British Columbia at its confluence with the Nicoamen River a few miles upstream from the Thompson's c ... of 1858–1860. First gazetted in 1930 as Seabird Island, the name was changed in 1967 to Sea Bird Island. References * Populated places on the Fraser River Islands of British Columbia Kent, British Columbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby Creek Indian Reserve No
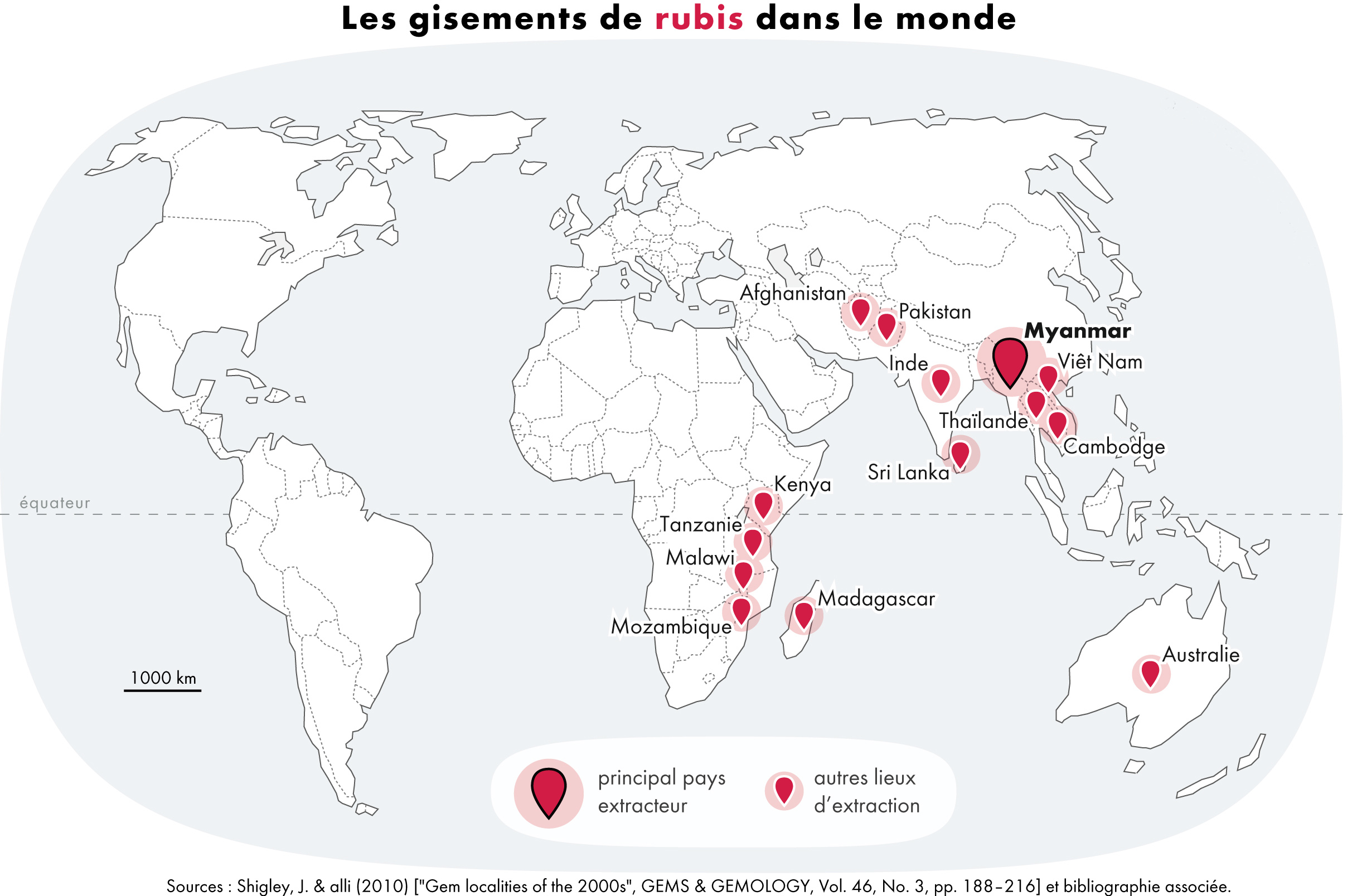
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skawahlook First Nation
The Skawahlook First Nation ( hur, Sq'ewá:lxw), formerly the Tait Indian Band is a band government of the Sto:lo people whose reserves and communities are located in the Fraser Valley, Upper Fraser Valley region of British Columbia, Canada, near Ruby Creek, British Columbia, the community of Ruby Creek, which is at the eastern end of the Kent, British Columbia, District of Kent. It is a member government of the Sto:lo Nation tribal council, one of two tribal councils of the Sto:lo. Total registered population of the band is 75 people, 59 of them living off-reserve. Indian Reserves Indian Reserves under the jurisdiction of the Skawahlook First Nation are: *Pekw'Xe:yles, Pekw'Xe: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale First Nation
Yale First Nation ( hur, X̲wóx̲welá:lhp) is a First Nations government located at Yale, British Columbia. Yale has 16 distinct reserves stretching from near Sawmill Creek to American Creek, with the most southern reserve situated at Ruby Creek in the District of Kent. Indian reserves Indian reserves under the administration of the Yale First Nation are: * 4 1/2 Mile Indian Reserve No. 2, on the right bank of the Fraser River 3 miles northeast of Yale, 4.30 ha. * Albert Flat Indian Reserve No. 5, on the right bank of the Fraser River, 3 miles south of Yale, 52.30 ha. * Kaykaip Indian Reserve No. 7, on the left bank of the Fraser River at the mouth of Keikum Creek, 10.0 ha. * Lukseetsissum Indian Reserve No. 9, on the right bank of the Fraser River at Ruby Creek CPR station, 53.90 ha. * Qualark Indian Reserve No. 4, on the left bank of the Fraser River at the mouth of Qualark Creek, 10.0 ha. * Squeah Indian Reserve No. 6, on the left bank of the Fraser River, at the mouth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places On The Fraser River
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |