|
Royal Inscription Of Simbar-≈Ýipak
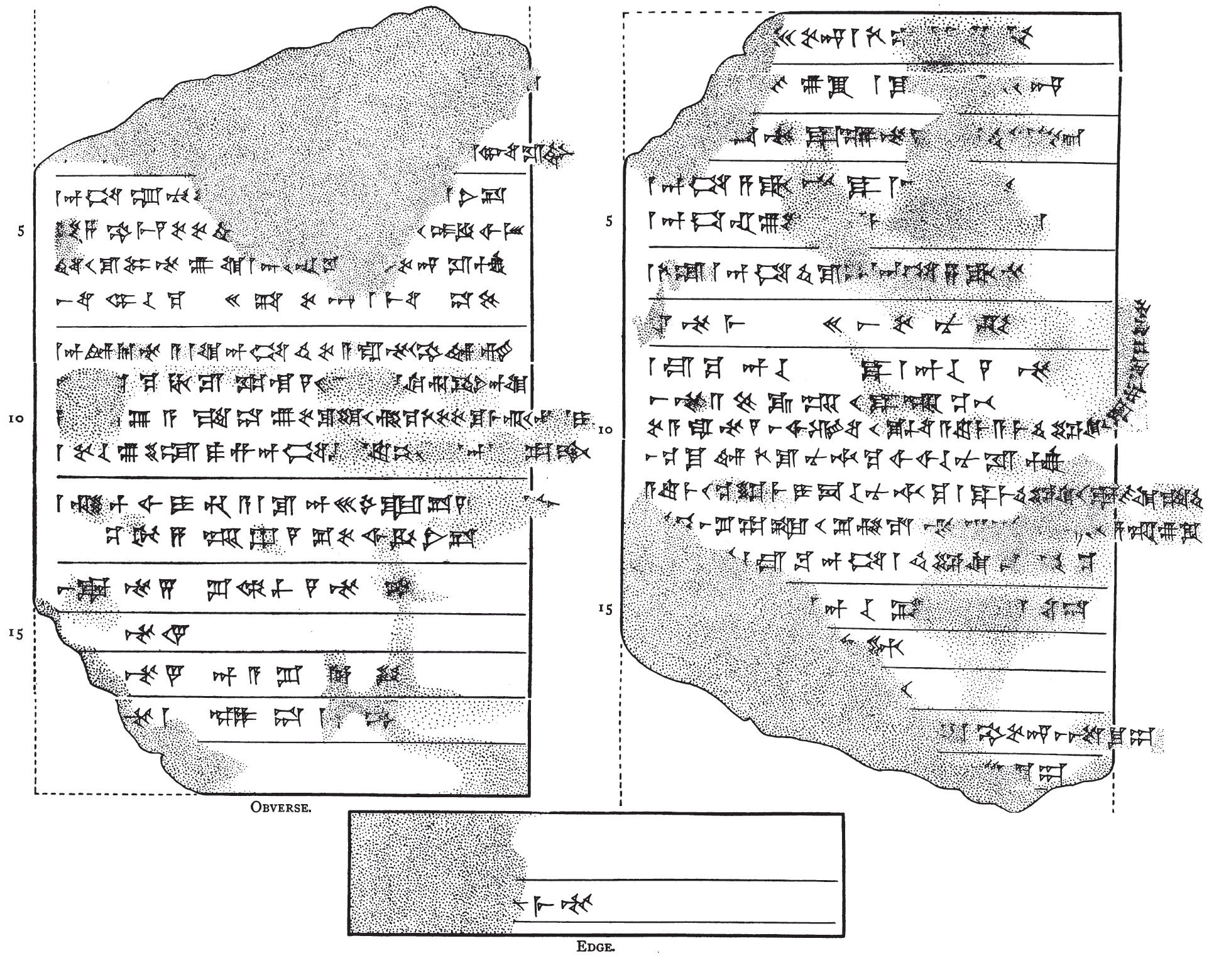
Simbar-≈Ýipak, or perhaps ''Simbar-≈Ýi·∏´u'',Earlier readings render his name as ''Simmash-Shipak''. typically inscribed m''sim-bar-''d''≈°i-i-''·∏™U or ''si-im-bar-≈°i-''·∏™U in cuneiform, where the reading of the last symbol is uncertain, ‚Äúoffspring of (the Kassite moon god) ≈Ýipak‚Äù, 1021‚Äì1004 BC, founded the 2nd Dynasty of the Sealand, Babylon‚Äôs 5th Dynasty and conducted a program of restoration of a number of temples that had been destroyed earlier by the marauding Arameans and the Sut√ª. His identification with the Sibir (m''Si-bir'') named by Ashurnasirpal II in his ''annals''''Annals of Ashurbanipal II'', ii 84: msi-bir ≈°ar4 kurkar-du-ni-√°≈°. as having earlier captured and laid waste Atlila (probably modern Bakr Awa), a city on Assyria‚Äôs eastern flank, remains unresolved. Biography Simbar-≈Ýipak lived during turbulent times, where crop failures and almost constant conflicts with semi-nomadic migrants caused the Babylonian government of the preceding 2nd Dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Babylon
The king of Babylon (Akkadian: ''šakkanakki Bābili'', later also ''šar Bābili'') was the ruler of the ancient Mesopotamian city of Babylon and its kingdom, Babylonia, which existed as an independent realm from the 19th century BC to its fall in the 6th century BC. For the majority of its existence as an independent kingdom, Babylon ruled most of southern Mesopotamia, composed of the ancient regions of Sumer and Akkad. The city experienced two major periods of ascendancy, when Babylonian kings rose to dominate large parts of the Ancient Near East: the First Babylonian Empire (or Old Babylonian Empire, 1894/1880–1595 BC) and the Second Babylonian Empire (or Neo-Babylonian Empire, 626–539 BC). Many of Babylon's kings were of foreign origin. Throughout the city's nearly two-thousand year history, it was ruled by kings of native Babylonian (Akkadian), Amorite, Kassite, Elamite, Aramean, Assyrian, Chaldean, Persian, Greek and Parthian origin. A king's cultural and ethnic bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriba-Adad II
Erƒ´ba-Adad II, inscribed mSU-dIM, ‚ÄúAdad has replaced,‚Äù was the king of Assyria 1056/55‚Äì1054 BC, the 94th to appear on the ''Assyrian Kinglist''.''SDAS Kinglist'', iii 31.''Nassouhi Kinglist'', iv 12. He was the son of A≈°≈°ur-bƒìl-kala whom he briefly succeeded and was deposed by his uncle ≈Ýam≈°i-Adad IV. Biography The ''Khorsabad kinglist''''Khorsabad Kinglist'', iii 45, mistakenly gives him as a son of Ilu-kabkabi, i.e. the father of the 18th century BC king ≈Ýam≈°i-Adad I. Despite his short two-year reign, there are fragmentary inscriptionsClay cone fragment from Nineveh BM 123467, 6 lines.Part of a clay tablet Rm-II.261 (RIMA 2 A.0.90.1), 7. where he claims his rule extended to the Aramaeans and lists conquests far and wide in intense military campaigns, imitating those of Tukultƒ´-apil-E≈°arra I, for which he styled himself ‚Äúking of the four quarters.‚Äù He would have appeared on a destroyed section of the eponym list designated as Cc.Eponym List VAT 11254, (KAV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century BC Babylonian Kings
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
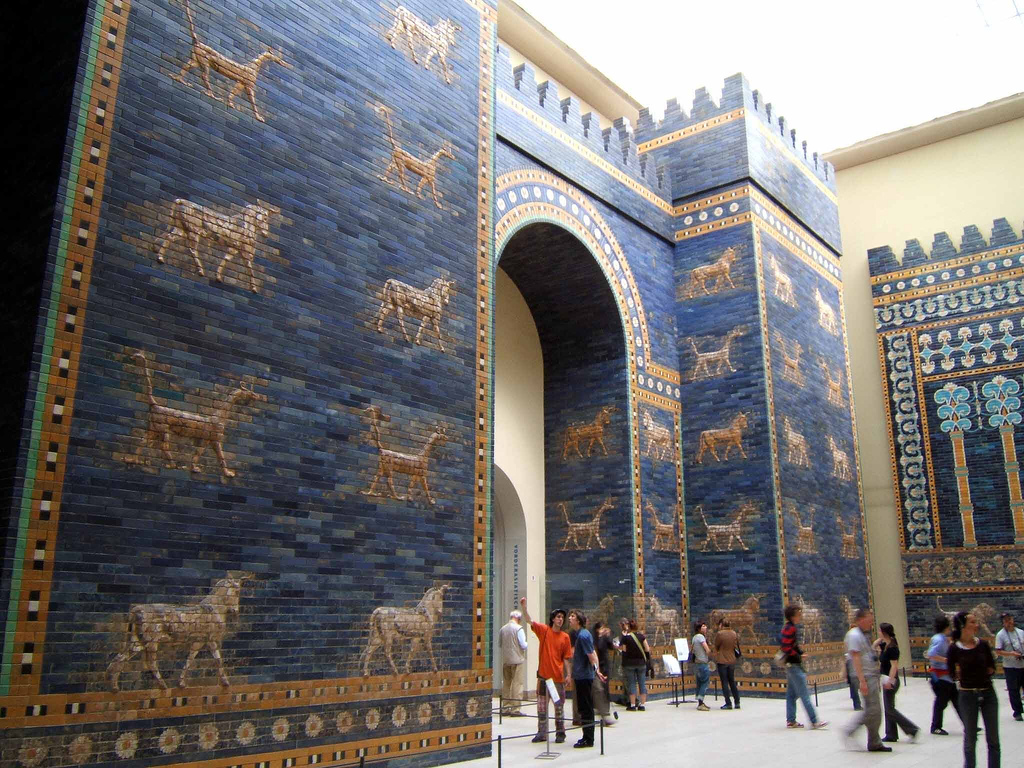
Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate was the eighth gate to the inner city of Babylon (in the area of present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq). It was constructed circa 575 BCE by order of King Nebuchadnezzar II on the north side of the city. It was part of a grand walled processional way leading into the city. The walls were finished in glazed bricks mostly in blue, with animals and deities in low relief at intervals, these also made up of bricks that are molded and colored differently. The German archaeologist Robert Koldewey led the excavation of the site from 1904 to 1914. After the end of the First World War in 1918, the smaller gate was reconstructed in the Pergamon Museum. The gate is 50 feet (15.2 meters) high, and the original foundations extended another 45 feet (13.7 meters) underground. The reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate in the Pergamon Museum is not a complete replica of the entire gate. The original structure was a double gate with a smaller frontal gate and a larger an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Chronicle
The Religious Chronicle is an ancient Mesopotamian register of portents such as the straying of wild animals into urban areas and extraordinary natural phenomena which presaged the disruptions which interfered with the Akƒ´tu or new year festival and the performance of its regular cultic activities which included the transport of the idols of the gods to the city of Babylon during the tumultuous years of chaos caused by the incursions of Aramean nomads. The text It seems to have drawn its sources from the protases of omen literature in contrast to the Chronicle of Early Kings which drew them from their apodoses. The tablet has two columns per side and is in poor condition, with the surface severely abraded and most of the left-hand side (columns I and IV) gone. It may have been part of a series as there is part of a catch-line evident on line 8 of column IV. It is designated BM 35968 (Sp III, 504) and is held in the British Museum. Written during the Seleucid era, it was acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sippar
Sippar ( Sumerian: , Zimbir) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its '' tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell Abu Habbah near Yusufiyah in Iraq's Baghdad Governorate, some north of Babylon and southwest of Baghdad. The city's ancient name, Sippar, could also refer to its sister city, Sippar-Amnanum (located at the modern site of Tell ed-Der); a more specific designation for the city here referred to as Sippar was Sippar-Yahrurum. History Despite the fact that thousands of cuneiform clay tablets have been recovered at the site, relatively little is known about the history of Sippar. As was often the case in Mesopotamia, it was part of a pair of cities, separated by a river. Sippar was on the east side of the Euphrates, while its sister city, Sippar-Amnanum (modern Tell ed-Der), was on the west. While pottery finds indicate that the site of Sippar was in use as early as the Uruk period, substantial occupat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamash
Utu (dUD "Sun"), also known under the Akkadian name Shamash, ''≈°m≈°'', syc, дадÐê ''≈°em≈°a'', he, ◊©÷∂◊Å◊û÷∂◊©◊Å ''≈°eme≈°'', ar, ÿ¥ŸÖÿ≥ ''≈°ams'', Ashurian Aramaic: ꣥꣨꣥ ''≈°'me≈°(ƒÅ)'' was the ancient Mesopotamian sun god. He was believed to see everything that happened in the world every day, and was therefore responsible for justice and protection of travelers. As a divine judge, he could be associated with the underworld. Additionally, he could serve as the god of divination, typically alongside the weather god Adad. While he was universally regarded as one of the primary gods, he was particularly venerated in Sippar and Larsa. The moon god Nanna (Sin) and his wife Ningal were regarded as his parents, while his twin sister was Inanna (Ishtar). Occasionally other goddesses, such as Manzat and Pinikir, could be regarded as his sisters too. The dawn goddess Aya (Sherida) was his wife, and multiple texts describe their daily reunions taking place on a mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabu-apla-iddina
Nabû-apla-iddina, inscribed md''Nábû-ápla-iddina''na''Synchronistic History'', tablet K4401a (ABC 21), iii 22–26. or md''Nábû-apla-íddina'';''Synchronistic Kinglist'' fragments VAT 11261 (KAV 10), ii 8, and Ass. 13956dh (KAV 182), iii 11. reigned about 886–853 BC, was the sixth king of the dynasty of ''E'' of Babylon and he reigned for at least thirty-two years.Kudurru AO 21422 in the Louvre. During much of Nabû-apla-iddina's reign Babylon faced a significant rival in Assyria under the rule of Ashurnasirpal II. Nabû-apla-iddina was able to avoid both outright war and significant loss of territory. There was some low level conflict, including a case where he sent a party of troops led by his brother to aid rebels in Suhu (Suhi, Sukhu, Suru). Later in his reign Nabu-apla-iddina agreed to a treaty with Ashurnasirpal II’s successor Shalmaneser III. Internally Nabu-apla-iddina worked on the reconstruction of temples and something of a literary revival took place during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebuchadnezzar I
Nebuchadnezzar I or Nebuchadrezzar I (), reigned 1121‚Äì1100 BC, was the fourth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and Fourth Dynasty of Babylon. He ruled for 22 years according to the ''Babylonian King List C'', and was the most prominent monarch of this dynasty. He is best known for his victory over Elam and the recovery of the cultic idol of Marduk. Biography He is unrelated to his later namesake, Nab√ª-kudurrƒ´-u·π£ur II, who has come to be known by the Hebrew form of his name ‚ÄúNebuchadnezzar.‚Äù Consequently, it is anachronistic but not inappropriate to apply this designation retroactively to the earlier king, as he does not make an appearance in the Bible. He is misidentified in the ''Chronicle Concerning the Reign of ≈Ýama≈°-≈°uma-ukin''''≈Ýama≈°-≈°uma-ukin Chronicle'' (ABC 15), tablet BM 96273. as the brother of ≈Ýirikti-≈°uqamuna probably in place of Ninurta-kudurr·øë-u·π£ur I. He succeeded his father, Ninurta-nƒÅdin-≈°umi, and was succeeded in turn by his son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adad-apla-iddina
Adad-apla-iddina, typically inscribed in cuneiform mdIM- DUMU.U≈Ý-SUM''-na'', mdIM-A-SUM''-na'' or dIM''-ap-lam-i-din-'' 'nam''meaning the storm god ‚ÄúAdad has given me an heir‚Äù, was the 8th king of the 2nd Dynasty of Isin and the 4th Dynasty of Babylon and ruled 1064‚Äì1043. He was a contemporary of the Assyrian King A≈°≈°ur-b√™l-kala and his reign was a golden age for scholarship. Biography Provenance The broken obelisk of A≈°≈°ur-b√™l-kala relates that the Assyrians raided Babylonia, early in his reign: Depending on the exact synchronization of the Assyrian and Babylonian chronologies, this would have been shortly before, or at the very beginning of Adad-apla-iddina‚Äôs reign. His ancestor ''Esagil-≈Ýaduni'' is named in the ''Synchronistic History''The ''Synchronistic History'' (ABC 21) column 2 lines 31 to 37. as his ‚Äúfather‚Äù, but he was actually ‚Äùa son of a nobody,‚Äù i.e. without a royal parent. This chronicle recounts that he was appointed by the Assyrian k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclectic Chronicle
The Eclectic Chronicle, referred to in earlier literature as the ''New Babylonian Chronicle'', is an ancient Mesopotamian account of the highlights of Babylonian history during the post-Kassite era prior to the 689 BC fall of the city of Babylon. It is an important source of historiography from the period of the early iron-age dark-age with few extant sources to support its telling of events. The text Although its provenance is unknown, it is thought to originate from Babylon itself as it is written in standard Babylonian in the late cuneiform script of the region. It was acquired by the British Museum in 1898 and given the accession number 98,0711.124, subsequently the Museum reference BM 27859. Approximately two-thirds of the text has survived with the top part of the tablet broken off, losing the beginning and end of the narrative. The work is written in a single column on a small tablet in the format of an administrative or economic text, suggesting it was for private use, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marduk
Marduk (Cuneiform: dAMAR.UTU; Sumerian: ''amar utu.k'' "calf of the sun; solar calf"; ) was a god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon. When Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of Hammurabi (18th century BC), Marduk slowly started to rise to the position of the head of the Babylonian pantheon, a position he fully acquired by the second half of the second millennium BCE. In the city of Babylon, Marduk was worshipped in the temple Esagila. Marduk is associated with the divine weapon Imhullu. His symbolic animal and servant, whom Marduk once vanquished, is the dragon Mušḫuššu. "Marduk" is the Babylonian form of his name. The name ''Marduk'' was probably pronounced ''Marutuk''. The etymology of the name ''Marduk'' is conjectured as derived from ''amar-Utu'' ("immortal son of Utu" or "bull calf of the sun god Utu"). The origin of Marduk's name may reflect an earlier genealogy, or have had cultural ties to the anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_in_Akkadian.png)