|
Royal Pavilion
The Royal Pavilion, and surrounding gardens, also known as the Brighton Pavilion, is a Grade I listed former royal residence located in Brighton, England. Beginning in 1787, it was built in three stages as a seaside retreat for George IV of the United Kingdom, George, Prince of Wales, who became the Prince Regent in 1811, and King George IV in 1820. It is built in the Indo-Saracenic style prevalent in India for most of the 19th century. The current appearance of the Pavilion, with its domes and minarets, is the work of architect John Nash (architect), John Nash, who extended the building starting in 1815. George IV's successors William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, and Queen Victoria, Victoria, also used the Pavilion, but Queen Victoria decided that Osborne House should be the royal seaside retreat, and the Pavilion was sold to the city of Brighton in 1850. On 1 October 2020, management and operation of the Royal Pavilion & Museums' buildings and collections were tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Pavilion (18814891875)
The Royal Pavilion, and surrounding gardens, also known as the Brighton Pavilion, is a Grade I listed former royal residence located in Brighton, England. Beginning in 1787, it was built in three stages as a seaside retreat for George IV of the United Kingdom, George, Prince of Wales, who became the Prince Regent in 1811, and King George IV in 1820. It is built in the Indo-Saracenic style prevalent in India for most of the 19th century. The current appearance of the Pavilion, with its domes and minarets, is the work of architect John Nash (architect), John Nash, who extended the building starting in 1815. George IV's successors William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, and Queen Victoria, Victoria, also used the Pavilion, but Queen Victoria decided that Osborne House should be the royal seaside retreat, and the Pavilion was sold to the city of Brighton in 1850. On 1 October 2020, management and operation of the Royal Pavilion & Museums' buildings and collections were tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Pavilion, Aldershot
The Royal Pavilion, also known as the Queen's Pavilion, was a royal residence located at Aldershot in Hampshire. The most unpretentious of all royal residences,Philip Marsh, ''A Little-known Royal Pavilion'', '' Country Life'' 27 September 1962 it was built by George Myers as a wooden structure in 1855 for Queen Victoria and Prince Albert for use by members of the Royal Family when in Aldershot to attend military reviews and other occasions. Located off the Farnborough Road opposite the former West Cavalry Barracks, nearby are the Royal Garrison Church and the Wellington Statue. It was dismantled in the early 1960s. Today the site is the location of the Royal Pavilion Office Park. Origins of the Royal Pavilion Before the establishment of the 'Camp at Aldershot', the British Army did not have any single permanent camp for training troops on a large scale. Prince Albert realised that the training and resources of the British Army compared unfavourably with some European arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Steine
The Old Steine () is a thoroughfare in central Brighton, East Sussex, and is the southern terminus of the A23. The southern end leads to Marine Parade, the Brighton seafront and the Palace Pier. The Old Steine is also the site of a number of City Centre bus stops for Brighton buses. The Royal Pavilion is located immediately to the north of the Old Steine. History The Old Steine was originally an open green with a stream running adjacent to the easternmost dwellings of Brighthelmstone. The area was used by local fishermen to lay out and dry their nets. When Brighton started to become fashionable in the late 18th century, the area became the centre for visitors. Building around the area started in 1760, and railings started to appear around the green area in the 1770s, reducing its size. This continued throughout the 19th century. The eastern lawns of the Royal Pavilion were also originally part of the Old Steine. Dr. Richard Russell, whose 1750 paper on the health benefits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Crace
Frederick Crace (1779 – 18 September 1859) was an English interior decorator, who worked for George IV when Prince of Wales, for whom he created the chinoiserie interiors of the Brighton Pavilion. Crace was also a collector of maps and topographical prints and drawings, now at the British Library. Frederick was the son of the prominent London decorator John C. Crace (1754–1819), who had been hired in 1788 to provide Chinese works of art for the Royal Pavilion. Beside his familiar interiors at the Marine Pavilion, Brighton, Crace provided interiors at Windsor Castle and Buckingham Palace, in which he was assisted by his son, John Gregory Crace. Frederick married Augusta Harrop Gregory, the daughter of John Gregory, a London magistrate and treasurer of the Whig Club. In 1830 his son John Gregory became a full partner in the family business, thereafter known as Frederick Crace & Son, in 1830, on inheriting property and capital from his mother, who had died in 1827. Crace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
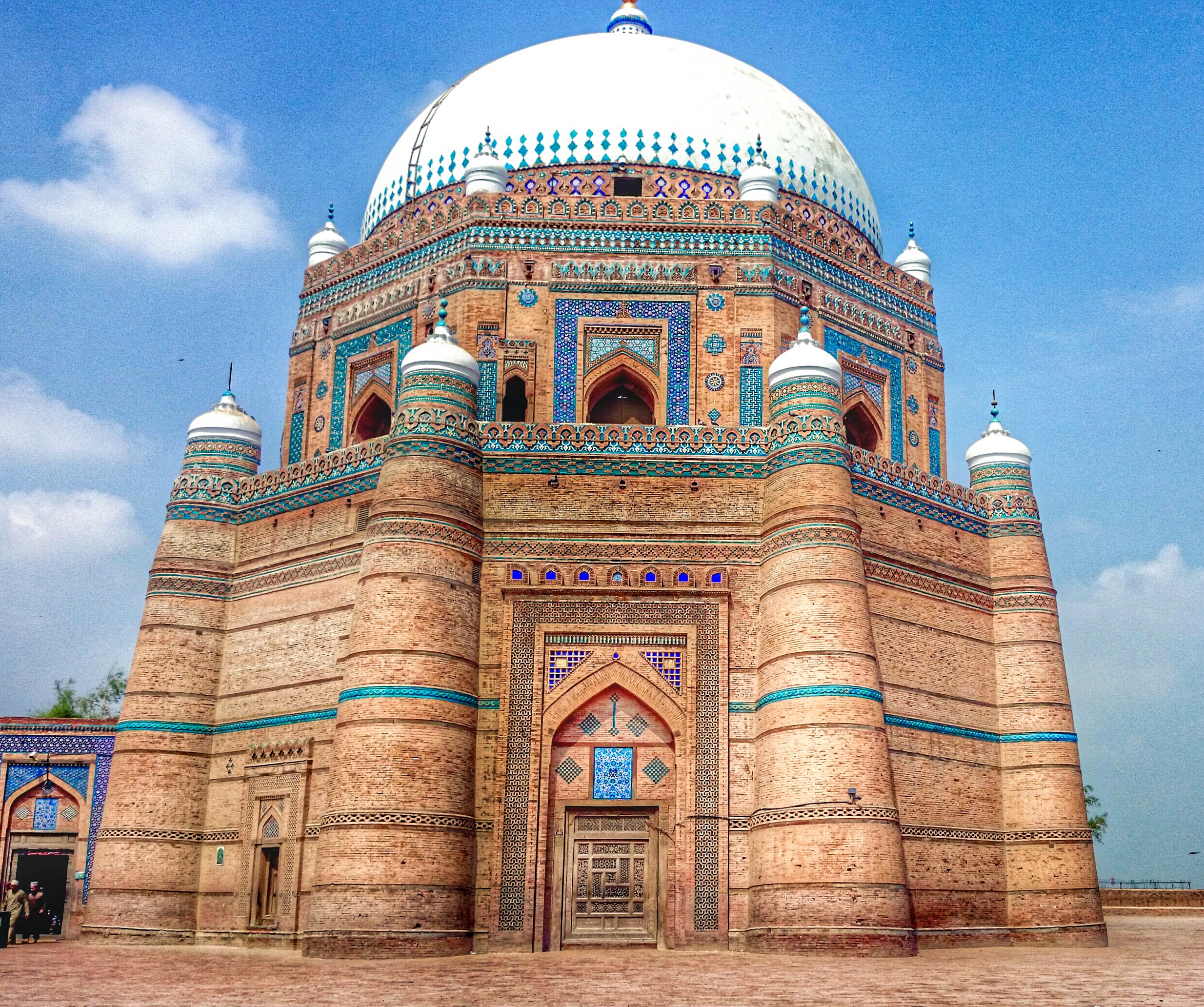
Indo-Islamic Architecture
Indo-Islamic architecture is the architecture of the Indian subcontinent produced by and for Islamic patrons and purposes. Despite an initial Arab presence in Sindh, the development of Indo-Islamic architecture began in earnest with the establishment of Delhi as the capital of the Ghurid dynasty in 1193. Succeeding the Ghurids was the Delhi Sultanate, a series of Central Asian dynasties that consolidated much of North India, and later the Mughal Empire by the 15th century. Both of these dynasties introduced Persianate architecture and art styles from Western Eurasia into the Indian subcontinent. The types and forms of large buildings required by Muslim elites, with mosques and tombs much the most common, were very different from those previously built in India. The exteriors of both were very often topped by large domes, and made extensive use of arches. Both of these features were hardly used in Hindu temple architecture and other indigenous Indian styles. Both types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Porden
William Porden (c. 1755 – 1822) was a versatile English architect who worked for the 1st Earl Grosvenor and the Prince Regent. Life Born in Kingston upon Hull, (Subscription required) he trained under James Wyatt and Samuel Pepys Cockerell. In 1784, the year of his marriage to Mary Plowman, Porden was appointed estate surveyor by the 1st Earl Grosvenor. This position involved assessing buildings on the Grosvenor Estate in Mayfair and determining the "fine" which an occupier had to pay when his lease fell in, and the revised ground rent. More than twenty years later Porden was appointed to reconstruct the Grosvenors' country seat, Eaton Hall in Cheshire. This project was carried out in a Gothic revival style. From 1804 to 1808, he designed the stables, riding house and tennis court at the Brighton Pavilion for the Prince of Wales. The riding school was in the "Indo-Saracenic" style, inspired by pictures of Indian buildings. The main building was a notable technical ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Frederick Robinson
Peter Frederick Robinson (1776–24 June 1858) was an English architect. Career Robinson began his career in Henry Holland's office and worked under William Porden at the Brighton Pavilion in 1801–02. In 1805 he designed Hans Town Assembly Rooms, Cadogan Place, and in 1811–12 the Egyptian Hall, Piccadilly, for William Bullock's museum. The details of the elevation were taken from Denon's work on the Egyptian monuments, and especially from the temple at Denderah; but the composition of the design was less authentic. In 1813 he designed the town-hall and market-place at Lampeter, Cardiganshire. He visited Rome 1816. In 1819 he made alterations at Bulstrode for the Duke of Somerset; in 1823 he restored the church at Mickleham, Surrey; in 1826–28 he made alterations to the prison at York Castle and in 1829–32 he built a Swiss Cottage at Decimus Burton's Colosseum in Regent's Park. He also designed various country houses. In 1820 he exhibited an architectural drawing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biagio Rebecca
Biagio Rebecca (1731–1808) was an Italian artist, active mainly as a decorative painter in England. Life Rebecca was born at Osimo, near Ancona, in the Marches, and served his apprenticeship in Rome. In England he became known for Neoclassicism, neoclassical scenes from mythology, often working on decorative schemes in collaboration with Robert Adam, for example at Harewood House and at Kedleston Hall. He also decorated Heaton Hall in Prestwich, near Bury, Lancashire and frescoed a ceiling at the Marine Pavilion (Brighton, England), Marine Pavilion at Brighton. With Angelica Kauffman, he painted the old lecture room at Somerset House, then home of the Royal Academy. He also designed a set of stained glass windows in the chapel at New College, Oxford. He was employed to do some painting at Audley End House by John Griffin, 4th Baron Howard de Walden, Sir John Griffin. In late 1772 Ann White, a servant at the house, gave birth to his illegitimate son, John Biagio Rebecca. Rebec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Holland (architect)
Henry Holland (20 July 1745 – 17 June 1806) was an architect to the English nobility. He was born in Fulham, London, where his father, also Henry, ran a building firm constructing several of Capability Brown's designs. His younger brother was Richard Holland, who later changed his surname to Bateman-Robson and became an MP. Although Henry would learn a lot from his father about the practicalities of construction, it was under Capability Brown that he would learn about architectural design. Brown and Holland formed a partnership in 1771 and Henry Holland married Brown's daughter Bridget on 11 February 1773 at St George's, Hanover Square. In 1772 Sir John Soane joined Holland's practice in order to further his education, leaving in 1778 to study in Rome. Holland paid a visit to Paris in 1787 which is thought to have been in connection with his design of the interiors at Carlton House. From this moment on his interior work owed less to the Adam style and more to contemporary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Grand Saloon From Nash's Views Edited
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon periods. The ancient settlement of "Brighthelmstone" was documented in the ''Domesday Book'' (1086). The town's importance grew in the Middle Ages as the Old Town developed, but it languished in the early modern period, affected by foreign attacks, storms, a suffering economy and a declining population. Brighton began to attract more visitors following improved road transport to London and becoming a boarding point for boats travelling to France. The town also developed in popularity as a health resort for sea bathing as a purported cure for illnesses. In the Georgian era, Brighton developed as a highly fashionable seaside resort, encouraged by the patronage of the Prince Regent, later King George IV, who spent mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Banqueting Room Nash Edited
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon periods. The ancient settlement of "Brighthelmstone" was documented in the ''Domesday Book'' (1086). The town's importance grew in the Middle Ages as the Old Town developed, but it languished in the early modern period, affected by foreign attacks, storms, a suffering economy and a declining population. Brighton began to attract more visitors following improved road transport to London and becoming a boarding point for boats travelling to France. The town also developed in popularity as a health resort for sea bathing as a purported cure for illnesses. In the Georgian era, Brighton developed as a highly fashionable seaside resort, encouraged by the patronage of the Prince Regent, later King George IV, who spent mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)

