|
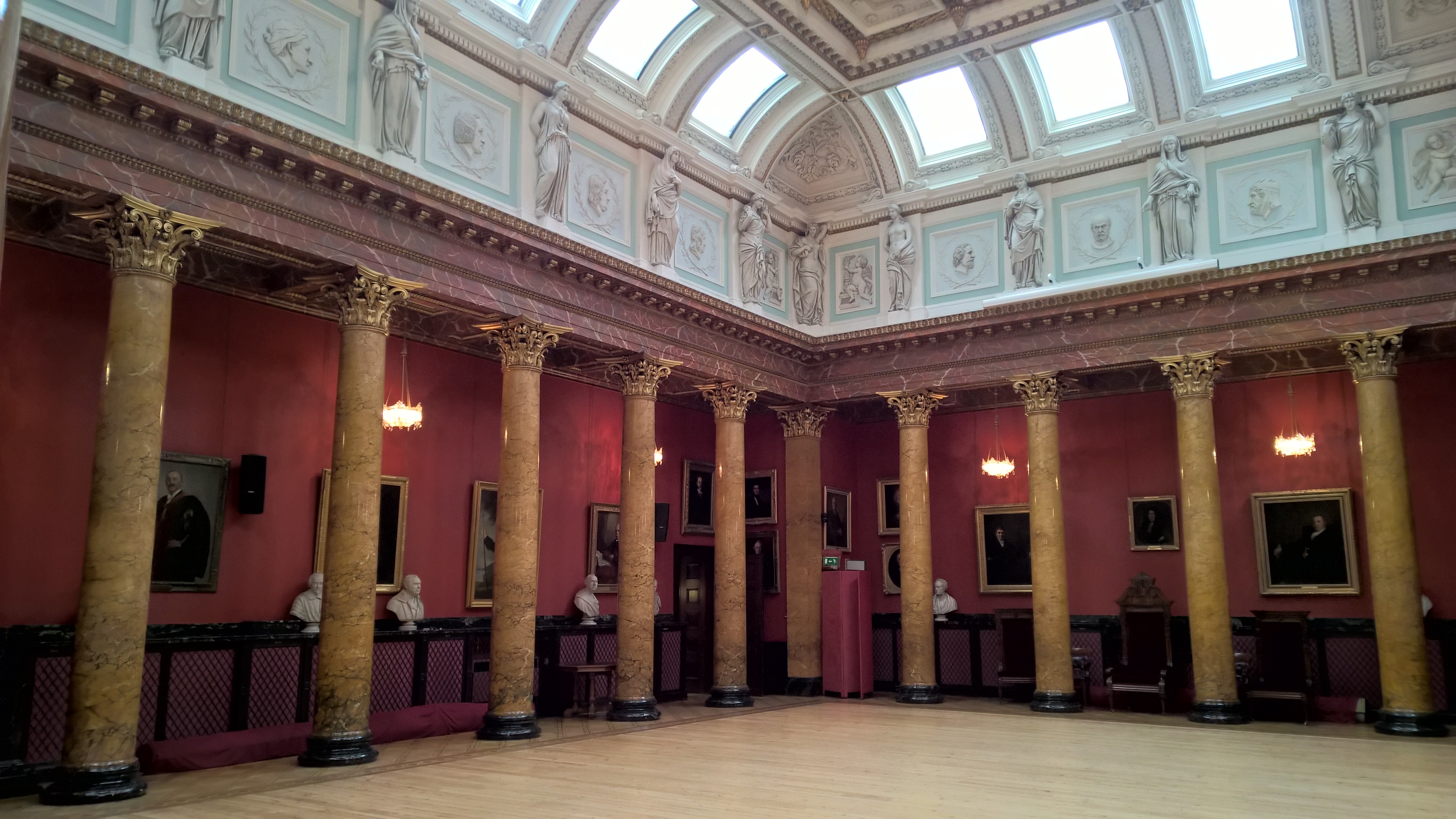
Royal College Of Physicians, Edinburgh
The Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh (RCPE) is a medical royal college in Scotland. It is one of three organisations that sets the specialty training standards for physicians in the United Kingdom. It was established by Royal charter in 1681. The college claims to have 12,000 fellows and members worldwide. History The RCPE was formed by a royal charter, granted in 1681, with Sir Robert Sibbald recognised as playing a key part in the negotiations. Three applications preceded this and had been unsuccessful. There were 21 original Fellows, eleven of whom were graduates or students of the University of Leiden. The Universities (Scotland) Act 1858 resulted in several items from the College's Charter becoming obsolete, and they obtained a further charter on 31 October 1861. In 1920 the College enacted changes that allowed women to be admitted on the same terms as men. The charter was amended on 7 May 2005. Edinburgh Pharmacopoeia In 1699 The College first published a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Royal College
In the United Kingdom, some Commonwealth realm, Commonwealth realms and Republic of Ireland, Ireland, a medical royal college is a professional body in the form of a royal college responsible for the development of and training in one or more medical speciality, medical specialities. United Kingdom and Ireland Standards and guidance They are generally charged with setting standards within their field and for supervising the training of doctors within that speciality, although the responsibility for the application of those standards in the UK, since 2010, rests with the General Medical Council. In the United Kingdom and Ireland most medical royal colleges are members of the Academy of Medical Royal Colleges (AoMRC) are listed below, with their postgraduate faculties (some of which are independently members of the academy) and institutes. The Academy of Medical Royal Colleges itself has one faculty of its own - the Faculty of Medical Leadership and Management. International role Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
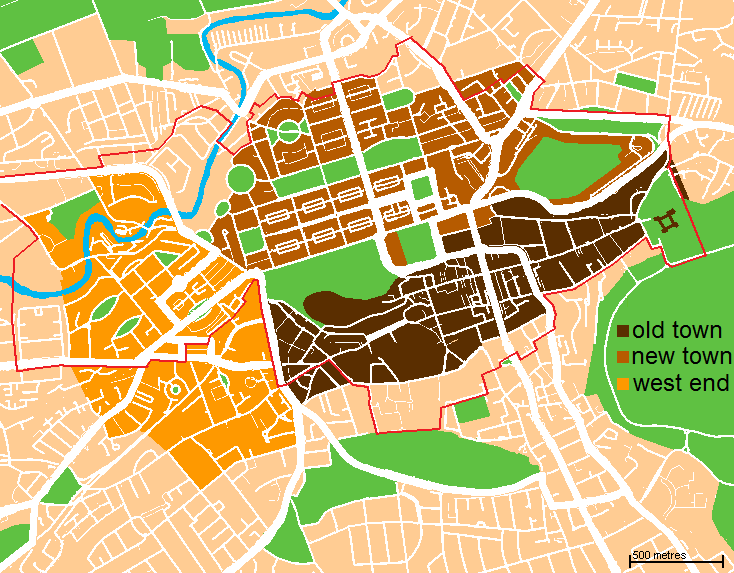
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's four ancient universities and the sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played an important role in Edinburgh becoming a chief intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the " Athens of the North." Edinburgh is ranked among the top universities in the United Kingdom and the world. Edinburgh is a member of several associations of research-intensive universities, including the Coimbra Group, League of European Research Universities, Russell Group, Una Europa, and Universitas 21. In the fiscal year ending 31 July 2021, it had a total income of £1.176 billion, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibbald Library
Sibbald is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within Special Area No. 3. It is located on Highway 9, approximately west of the provincial border with Saskatchewan and northeast of Medicine Hat. Climate Sibbald experiences a semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification ''BSk''). Winters are cold, while summers are warm to hot, and dry. Precipitation is generally low year round, with an annual average of , and is heavily concentrated in the warmer months. Demographics Sibbald recorded a population of 33 in the 1991 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada. See also *List of communities in Alberta *List of hamlets in Alberta Hamlets in the province of Alberta, Canada, are unincorporated communities administered by, and within the boundaries of, specialized municipalities or rural municipalities ( municipal districts, improvement districts and special areas). The ... References Hamlets in Alberta Special Area No. 3 {{SouthernAlb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Glasgow Herald
''The Herald'' is a Scottish broadsheet newspaper founded in 1783. ''The Herald'' is the longest running national newspaper in the world and is the eighth oldest daily paper in the world. The title was simplified from ''The Glasgow Herald'' in 1992. Following the closure of the ''Sunday Herald'', the ''Herald on Sunday'' was launched as a Sunday edition on 9 September 2018. History Founding The newspaper was founded by an Edinburgh-born printer called John Mennons in January 1783 as a weekly publication called the ''Glasgow Advertiser''. Mennons' first edition had a global scoop: news of the treaties of Versailles reached Mennons via the Lord Provost of Glasgow just as he was putting the paper together. War had ended with the American colonies, he revealed. ''The Herald'', therefore, is as old as the United States of America, give or take an hour or two. The story was, however, only carried on the back page. Mennons, using the larger of two fonts available to him, put it in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Morison
Sir Alexander Morison M.D. (1 May 1779 – 14 March 1866) was a Scottish physician and alienist (psychiatrist). Life Morison was born at Anchorfield, near Edinburgh, and was educated at Edinburgh High School and the University of Edinburgh, where he graduated M.D. on 12 September 1799. He became a licentiate of the Edinburgh College of Physicians in 1800 and a Fellow in 1801. He would serve as President of the college from 1827 to 1829. For a time, Morison practised in Edinburgh, but during 1808 he moved to London; on 11 April that year he was admitted a licentiate of the College of Physicians of London, and 10 July 1841 he was elected a Fellow. He was appointed inspecting physician of lunatic asylums in Surrey in 1810, and from 7 May 1835 physician to Bethlehem Hospital. He was physician to Charlotte, Princess Royal, and was knighted in 1838. Morison gave an annual course of lectures on mental diseases – commemorated in the ''Morisonian Lectures'' of the Royal College of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Dadd
Richard Dadd (1 August 1817 – 7 January 1886) was an English painter of the Victorian era, noted for his depictions of fairies and other supernatural subjects, Orientalist scenes, and enigmatic genre scenes, rendered with obsessively minuscule detail. Most of the works for which he is best known were created while he was a patient in Bethlem and Broadmoor hospitals. Early life Richard Dadd was born at Chatham, Kent, England, on 1 August 1817, the son of chemist Robert Dadd (1788/9–1843) and Mary Ann (1790–1824), daughter of shipwright Richard Martin. He was educated at King's School, Rochester where his aptitude for drawing was evident at an early age, leading to his admission to the Royal Academy of Arts at the age of 20. He was awarded the medal for life drawing in 1840.Souter 2012, p. 23 With William Powell Frith, Augustus Egg, Henry O'Neil and others, he founded The Clique, of which he was generally considered the leading talent. He was also trained at William Dad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Ord
The Right Hon. Lord Robert Ord FRS MP (1700 – 12 February 1778) was a British lawyer and politician. Life Ord was born the son of John Ord, Under-Sheriff of Newcastle-upon-Tyne, of Newbiggin, Fenham and Newminster, Northumberland, and his wife, Anne Hutchinson. He studied law at Lincoln's Inn in London from 1718, and was called to the bar in 1724. In 1723 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of London. He inherited the estates of Hunstanworth Manor and Newbiggin Hall upon the death of his elder brother Ralph Ord. He was a Member of Parliament (MP) for Mitchell, Cornwall, from 1734 to 1741 and for Morpeth, Northumberland, from 1741 to 1755. He was Secretary to the Chancellor of the Exchequer (1742–43), Deputy Cofferer of the Household (1743–44), Chief Baron of the Scottish Exchequer (1755–75) and Chancellor of the Diocese of Durham (1753–64). He was Rector of Glasgow University 1767/8. Ord died aged 77. He is buried in Restalrig Churchyard in Edinburgh. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his older brother John, Robert took on the family business, which included lucrative work for the Board of Ordnance, after William's death. In 1754, he left for Rome, spending nearly five years on the continent studying architecture under Charles-Louis Clérisseau and Giovanni Battista Piranesi. On his return to Britain he established a practice in London, where he was joined by his younger brother James. Here he developed the "Adam Style", and his theory of "movement" in architecture, based on his studies of antiquity and became one of the most successful and fashionable architects in the country. Adam held the post of Architect of the King's Works from 1761 to 1769. Robert Adam was a leader of the first phase of the classical revival in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hamilton (architect)
Thomas Hamilton (11 January 1784 – 24 February 1858) was a Scottish architect, based in Edinburgh where he designed many of that city's prominent buildings. Born in Glasgow, his works include: the Burns Monument in Alloway; the Royal High School on the south side of Calton Hill (long considered as a possible home for the Scottish Parliament); the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh; the George IV Bridge, which spans the Cowgate; the Dean Orphan Hospital, now the Dean Gallery; the New North Road Free Church, now the Bedlam Theatre; Cumstoun, a private house in Dumfries and Galloway; and the Scottish Political Martyrs' Monument in Old Calton Cemetery, Edinburgh. He was one of the leading Greek Revivalists in Scotland, "more imaginative than his peers and more refined in his detailing". He was a favourite of the church for his Gothic designs, being commissioned to design many Free Churches after the Disruption of 1843. He also designed shops and banks, many of whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
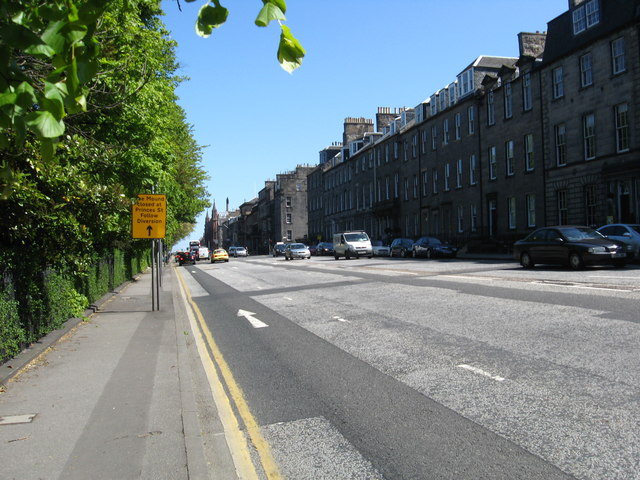
Queen Street, Edinburgh
Queen Street is the northernmost east-west street in Edinburgh's First New Town. It begins in the east, at the Scottish National Portrait Gallery. It links York Place with the Moray Estate. It was named "Queen Street" after Queen Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, the wife of George III of the United Kingdom and was so named on James Craig's plan of the New Town issued by the Town Council in 1768. Most early maps repeat this name but others misname it Queen's Street or Queens Street. History The street forms part of James Craig's plan of 1768 for a New Town to the north of Edinburgh's Old Town and the North Loch. This had three main east-west streets: Princes Street; George Street; and Queen Street. Queen Street was planned as a one-sided street, facing north over then fields towards the Firth of Forth. The first 30 metres beyond the road itself was originally laid out as private individual gardens to some of the Queen Street residents. Not until the opposite side was dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
