|
Rotomahana
Lake Rotomahana is an lake in northern New Zealand, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Rotorua. It is immediately south-west of the dormant volcano Mount Tarawera, and its geography was substantially altered by a major 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera. Along with the mountain, it lies within the Okataina caldera. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "warm lake" for , following Hochstetter. Before the 1886 eruption, only two small lakes were present in the current lake's basin. High quality pictures of the then Lake Rotomahana and associated tourist attractions were widely available in Europe by 1875. Following the eruption, a number of craters filled over the course of 15 years to form today's Lake Rotomahana. It is the most recently formed larger natural lake in New Zealand, and the deepest in the Rotorua district. The lake's northern shore lies close to the lower Lake Tarawera, separated by less than of terrain that is mostly mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pink And White Terraces
The Pink and White Terraces ( and ), were natural wonders of New Zealand. They were reportedly the largest silica sinter deposits on earth. Until recently, they were lost and thought destroyed in the 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera, while new hydrothermal features formed to the south-west i.e. Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley. The Pink and White Terraces were formed by upwelling geothermal springs containing a cocktail of silica-saturated, near-neutral pH chloride water. These two world-famous springs were part of a group of hot springs and geysers, chiefly along an easterly ridge named Pinnacle Ridge (or the Steaming Ranges by Mundy). The main tourist attractions included Ngahapu, Ruakiwi, Te Tekapo, Waikanapanapa, Whatapoho, Ngawana, Koingo and Whakaehu. The Pink and the White Terrace springs were around apart. The White Terraces were at the north-east end of Lake Rotomahana and faced west to north west at the entrance to the Kaiwaka Channel. Te Tarata descended to the lake edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1886 Eruption Of Mount Tarawera
In 1886, a violent eruption occurred at Mount Tarawera, near the city of Rotorua on New Zealand's North Island. At an estimated Volcanic Explosivity Index of 5, the eruption is the largest and deadliest in New Zealand during the past 500 years, which includes the entirety of European history in New Zealand. The eruption began in the early hours of 10 June 1886 and lasted for approximately 6 hours, causing a ash column, earthquakes, lightning, and explosions to be heard as far away as Blenheim, New Zealand, Blenheim in the South Island — more than 500 kilometers (300 miles) away. A rift formed across the mountain and surrounding area during the eruption, starting from the Wahanga peak at the mountain's northern end and extending in a southwesterly direction, through Lake Rotomahana and forming the Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley. Damage in the local area was extensive, with ash fall blanketing nearby villages including Te Wairoa, New Zealand, Te Wairoa. The eruption is responsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Tarawera
Mount Tarawera is a volcano on the North Island of New Zealand within the older but volcanically productive Ōkataina Caldera. Located 24 kilometres southeast of Rotorua, it consists of a series of rhyolitic lava domes that were fissured down the middle by an explosive basaltic eruption in 1886. This eruption was one of New Zealand's largest historical eruptions, and killed an estimated 120 people. The fissures run for about northeast-southwest. The volcano's component domes include Ruawahia Dome (the highest at 1,111 metres), Tarawera Dome and Wahanga Dome. It is surrounded by several lakes, most of which were created or drastically altered by the 1886 eruption. These lakes include Lakes Tarawera, Rotomahana, Rerewhakaaitu, Ōkataina, Ōkareka, Tikitapu / Blue and Rotokākahi / Green. The Tarawera River runs northeastwards across the northern flank of the mountain from Lake Tarawera. In 2000, the mountain was ceded to the Ngāti Rangitihi sub-tribe of Te Araw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley
The Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley is the hydrothermal system created on 10 June 1886 by the volcanic eruption of Mount Tarawera, on the North Island of New Zealand. It encompasses Lake Rotomahana, the site of the Pink and White Terraces, as well as the location of the Waimangu Geyser, which was active from 1900 to 1904. The area has been increasingly accessible as a tourist attraction and contains Frying Pan Lake, which is the largest hot spring in the world, and the steaming and usually pale blue Inferno Crater Lake, the largest geyser-like feature in the world although the geyser itself cannot be seen since it plays at the bottom of the lake. ''Waimangu'' is a Māori-language word meaning "black water". This name comes from the water that was thrown up by the Waimangu Geyser, which was black with mud and rocks. From the 1890s onwards, the valley has gradually been re-populated naturally by plants ranging from hot water-loving algae and bacteria to mosses and many species of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tarawera
Lake Tarawera is the largest of a series of lakes which surround the volcano Mount Tarawera in the North Island of New Zealand. Like the mountain, it lies within the Okataina caldera. It is located to the east of Rotorua, and beneath the peaks of the Tarawera massif i.e. Wahanga, Ruawahia, Tarawera and Koa. The lake's surface area is . Geography The lake was substantially affected by the eruption of Mount Tarawera on 10 June 1886.Royal Society of New Zealand (1984)''Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand'' Vol. 14–15 p. 121. ISSN 0303-6758 The lake outlet was blocked for two decades and the lake level increased. The eruption killed over 150 people, and buried the Māori village of Te Wairoa on the southwest shore of the lake. Also assumed destroyed were the famed Pink and White Terraces. However, in February 2011 a team mapping the lake floor discovered what appeared to be part of the Pink Terraces. The lowest two tiers of the terraces were reportedly found in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
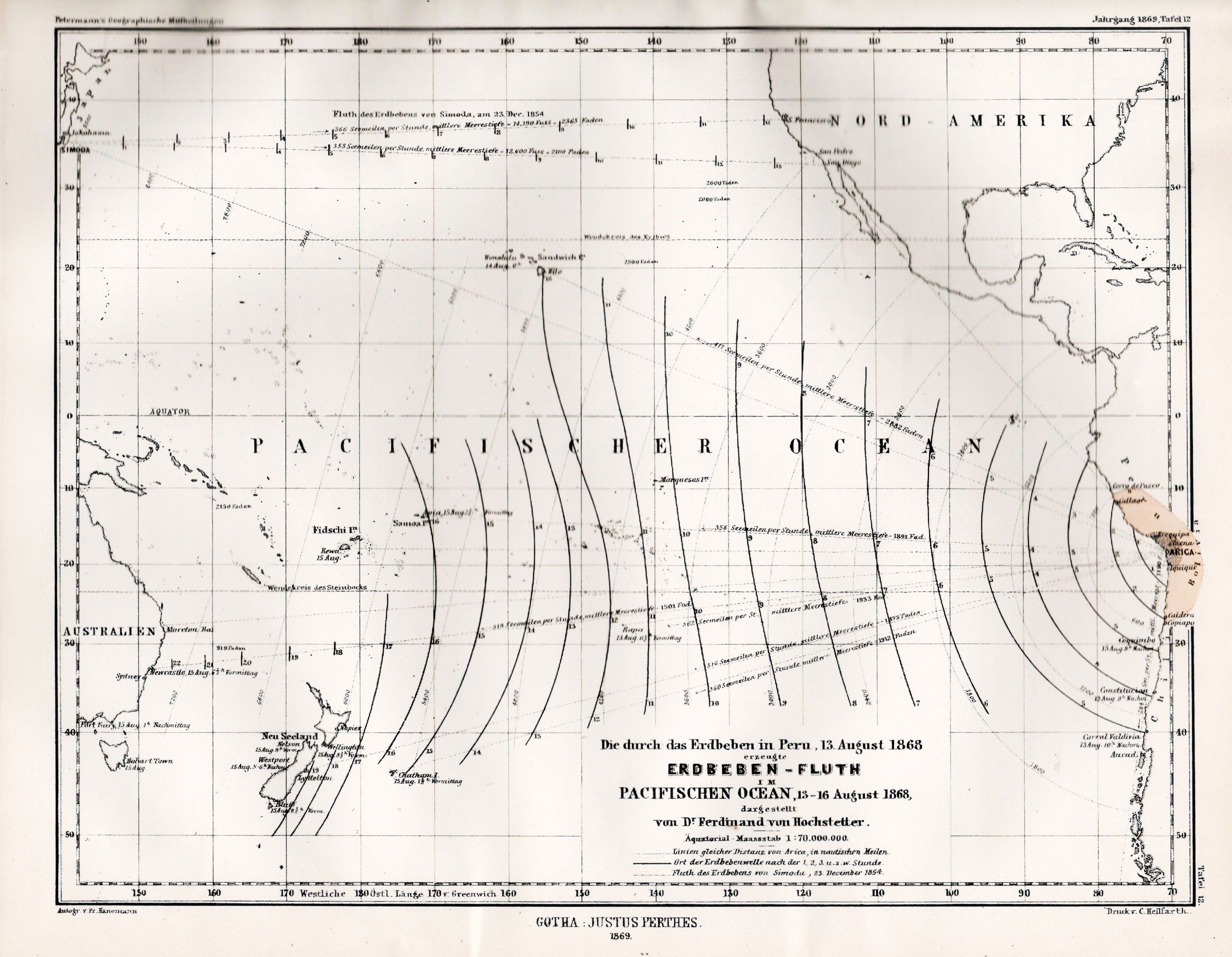
Ferdinand Von Hochstetter
Christian Gottlieb Ferdinand Ritter von Hochstetter (30 April 1829 – 18 July 1884) was a German-Austrian geologist. Career Having received his early education at the evangelical seminary at Maulbronn, Ferdinand proceeded to the University of Tübingen and the Tübinger Stift; there, under Friedrich August von Quenstedt, the interest he already felt in geology became permanently fixed, and he obtained his doctor's degree and a travelling scholarship. In 1852 he joined the staff of the Imperial Geological Survey of Austria and was engaged until 1856 in parts of Bohemia, especially in the Bohemian Forest, and in the Fichtel Hills and Karlsbad mountains. His excellent reports established his reputation. Thus he came to be chosen as geologist to the Novara expedition (1857–59), and made numerous valuable observations in the voyage round the world. The Novara arrived in New Zealand on 22 December 1858. Almost immediately he met the German scientist Julius von Haast who had al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lake
A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a crater that was formed by explosive activity or a collapse during a volcanic eruption. Formation Lakes in calderas fill large craters formed by the collapse of a volcano during an eruption. Lakes in maars fill medium-sized craters where an eruption deposited debris around a vent. Crater lakes form as the created depression, within the crater rim, is filled by water. The water may come from precipitation, groundwater circulation (often hydrothermal fluids in the case of volcanic craters) or melted ice. Its level rises until an equilibrium is reached between the rates of incoming and outgoing water. Sources of water loss singly or together may include evaporation, subsurface seepage, and, in places, surface leakage or overflow when the lake level reaches the lowest point on its rim. At such a saddle location, the upper portion of the lake is contained only by its adjacent natural volcanic dam; continued leakage through or surface outflow ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lake
A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a crater that was formed by explosive activity or a collapse during a volcanic eruption. Formation Lakes in calderas fill large craters formed by the collapse of a volcano during an eruption. Lakes in maars fill medium-sized craters where an eruption deposited debris around a vent. Crater lakes form as the created depression, within the crater rim, is filled by water. The water may come from precipitation, groundwater circulation (often hydrothermal fluids in the case of volcanic craters) or melted ice. Its level rises until an equilibrium is reached between the rates of incoming and outgoing water. Sources of water loss singly or together may include evaporation, subsurface seepage, and, in places, surface leakage or overflow when the lake level reaches the lowest point on its rim. At such a saddle location, the upper portion of the lake is contained only by its adjacent natural volcanic dam; continued leakage through or surface outflow ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry For Culture And Heritage
The Ministry for Culture and Heritage (MCH; ) is the department of the New Zealand Government responsible for supporting the arts, culture, built heritage, sport and recreation, and broadcasting sectors in New Zealand and advising government on such. History The Ministry of Cultural Affairs had been created in 1991; prior to this, the Department of Internal Affairs (DIA) had provided oversight and support for arts and culture functions. MCH was founded in 1999 with the merger of the former Ministry of Cultural Affairs and the history and heritage functions of the DIA, as well as some functions from the Department of Conservation and Ministry of Commerce. The purpose of the merger of functions and departments was to create a coherent, non-fragmented overview of the cultural and heritage sector, rather than spreading services and functions across several departments. Minister for Cultural Affairs Marie Hasler oversaw the transition of functions into the new agency. Opposition La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of The Bay Of Plenty Region
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotokakahi
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(1873)_(14782100062).jpg)







_2020.jpg)