|
Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and Victoria Land, to the east Roosevelt Island and Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about from the South Pole. Its boundaries and area have been defined by the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research as having an area of . The circulation of the Ross Sea is dominated by a wind-driven ocean gyre and the flow is strongly influenced by three submarine ridges that run from southwest to northeast. The circumpolar deep water current is a relatively warm, salty and nutrient-rich water mass that flows onto the continental shelf at certain locations. The Ross Sea is covered with ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Expedition
The Ross expedition was a voyage of scientific exploration of the Antarctic in 1839 to 1843, led by James Clark Ross, with two unusually strong warships, HMS ''Erebus'' and HMS ''Terror''. It explored what is now called the Ross Sea and discovered the Ross Ice Shelf. On the expedition, Ross discovered the Transantarctic Mountains and the volcanoes Erebus and Terror, named after his ships. The young botanist Joseph Dalton Hooker made his name on the expedition. The expedition inferred the position of the South Magnetic Pole, and made substantial observations of the zoology and botany of the region, resulting in a monograph on the zoology, and a series of four detailed monographs by Hooker on the botany, collectively called ''Flora Antarctica'' and published in parts between 1843 and 1859. The expedition was the last major voyage of exploration made wholly under sail. Among the expedition's biological discoveries was the Ross seal, a species confined to the pack ice of Antarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
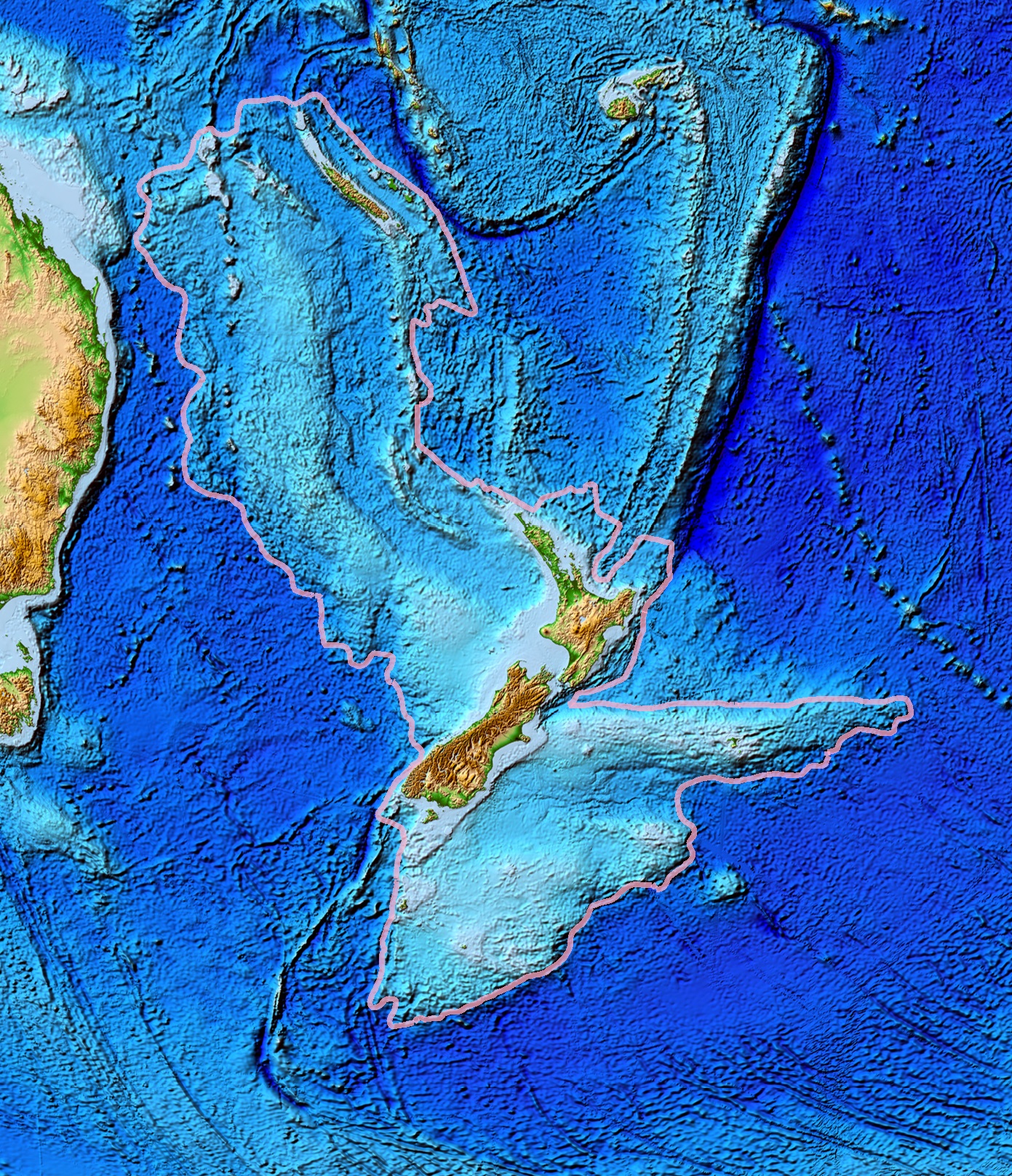
Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., 2004, Evolving force balance during incipient subduction: Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, v. 5, Q07001, https://doi.org/10.01029/02003GC000681 It has been described variously as a submerged continent, a continental fragment (or microcontinent), and a continent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995, and satellite imagery shows it to be almost the size of Australia. A 2021 study suggests Zealandia is 1 billion years old, about twice as old as geologists previously thought. By approximately 23 million years ago the landmass may have been completely submerged. Today, most of the landmass (94%) remains submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean. New Zealand is the largest part of Zealandia that is above sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |